Memory leak in workloads with foreign keys or serializable reads
Description
A memory leak was identified on TServers under two specific conditions:
-
For tables with foreign keys if there isn't sufficient write workload on the referenced or parent table, but there is a lot of workload on the referencing or child table.
-
For tables with serializable read-only transactions that did not receive any writes.
A typical customer-facing symptom is for the system to reach its soft-memory limit, causing the system to reject requests. If there is a more rapid memory spike, it can also result in an OOM killer and the YB-TServer process will restart.
Background
Consider the following schema, with the parent table and child table.
CREATE TABLE parent_table (key int primary key);
CREATE TABLE child_table (fkey int references parent_table(key));
-- Insert a bunch of rows to parent_table
BEGIN;
INSERT INTO child_table(fkey) VALUES(..);
COMMIT;
The transaction inserts the row to the child table, and the insert generates intents on the child table's tablet. As this insert references the parent tablet's row, a lock record is generated corresponding to the row on the parent tablet (to maintain the foreign key referential integrity). After the transaction commits, these intents can be applied to regular RocksDB and no longer be maintained in the system.
In every tablet (parent and child), the DocDB apply process adds the transaction that generates intents to a map. This map is used to determine the set of transactions that the transaction loader loads during the tablet bootstrap process and is needed to ensure that all the transactions necessary for bootstrap are loaded. This map (consisting of transaction IDs) is persisted, along with retryable requests structure at the time of transaction log (WAL) rollover, and is used during the tablet bootstrap process.
Bug
The map that tracks the transactions grows unbounded on the parent tablet due to the following reasons:
-
The current logic to trim the map occurs during transaction log (WAL) rollover for that tablet, so unless there is enough WAL activity on the tablet, this map ends up consuming memory (even though those transactions have committed from a user perspective, applied from the DocDB perspective, and are no longer necessary for bootstrap).
-
If the workload only generates a lot of write traffic to the child table, then the intents generated for the parent table's tablets do not have any write_batches. The result is that the existing trimming logic, which relies on checking that
max_replicated_op_iddoesn't qualify asmax_replicated_op_id, does not take effect, rendering the existing cleanup logic useless, which in turn causes the memory of the map to grow unbounded.
Currently, the memory corresponding to this map is untracked. If the memory growth is proportional to the number of tablets on the node (can be unbounded in some cases), it can lead to TServer soft memory limit being hit and workload would get throttled.
Other impacted scenarios
Workloads that use serializable isolation and have read-only traffic suffer from similar problems. This is less common compared to the described foreign key workloads.
Identifying the issue
You can use the metric wal_replayable_applied_transactions to determine the current size of the map in question.
For example, the following PromQL query shows the approximate memory overhead of the map in MB. (Each entry is about 64 bytes. So you multiply by 64 and divide by 1024*1024 to get the number of MBs.)
wal_replayable_applied_transactions{export_type="tserver_export", node_prefix="yb-dev-rthallam-csgyj"}*64/(1024*1024)
Heap snapshot URL on the TServer (<t-server-endpoint>/pprof/heap_snapshot) would show a lot of allocations from TransactionParticipant::Impl::RemoveTransaction() as per the following illustration:
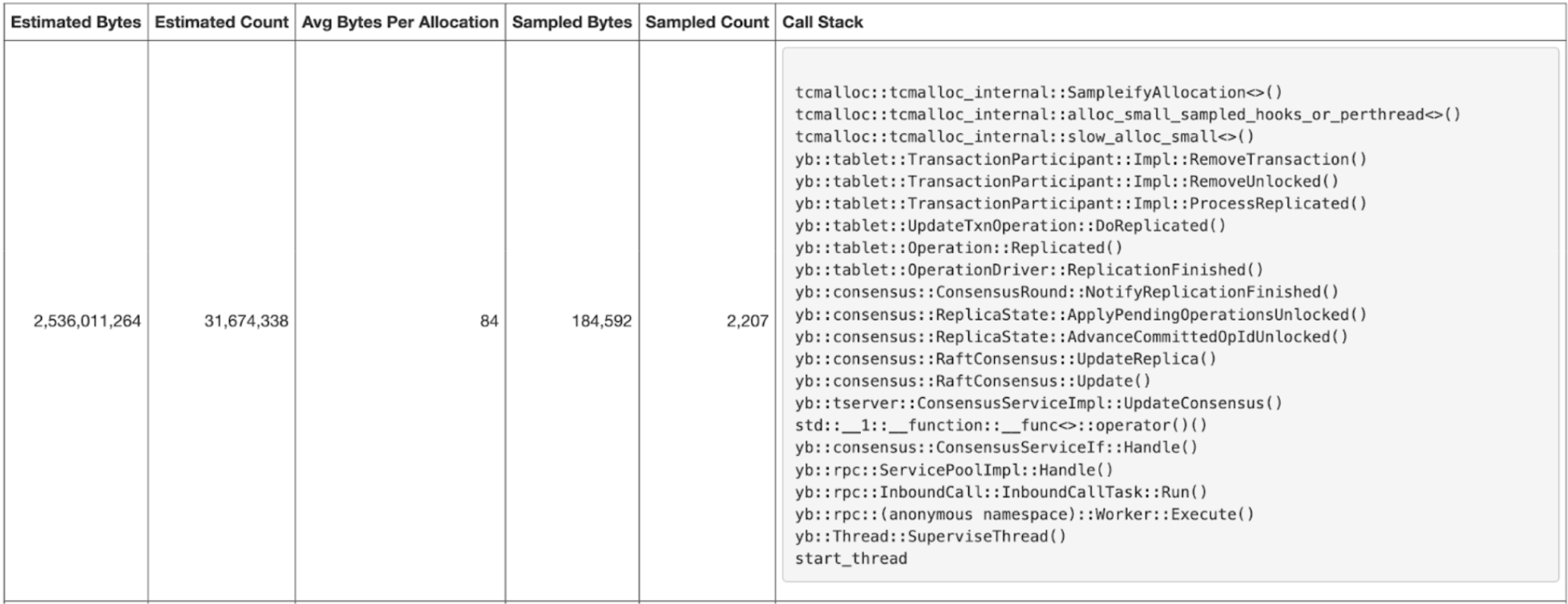
Mitigation
You can take the following actions to mitigate the issue:
- Restart the TServer process to clean up the map and reclaim the memory.
- Where feasible, applications can temporarily disable the foreign key constraints.
Details
This issue is a regression introduced by fix for issue 23890 (commit d6bbf59).
Fix
The fix addresses the root cause of the memory leak by ensuring that transactions that generate only "lock only" intents (without performing any writes) are not added to the internal tracking map. This prevents the map from growing indefinitely on the parent tablets and stops the memory leak on affected ones. The fix also adds code to properly account for the memory consumed by this map.
The fix was implemented in two parts, tracked by 26860 and 26666, and is available in v2024.2.3 and later.