Migration assessment TECH PREVIEW
The Voyager Migration Assessment feature streamlines database migration from PostgreSQL and Oracle to YugabyteDB. It analyzes the source database, captures essential metadata, and generates a report with recommended migration strategies and cluster configurations for optimal performance with YugabyteDB.
Overview
When you run an assessment, Voyager gathers key metadata and metrics from the source database, such as table column details, sizes of tables and indexes, and read/write IOPS.
Voyager then generates a report that includes:
- Recommended schema changes: Analyzes compatibility with YugabyteDB, highlighting unsupported features and data types. Also, analyzes the schema for any caveats to ensure smooth migration.
- Recommended cluster sizing: Estimates the resources needed for the target environment based on table sizes, number of tables, and throughput requirements.
- Recommended data distribution: Suggests effective sharding strategies for tables and indexes.
- Performance metrics: Analyzes workload characteristics to recommend optimizations in YugabyteDB.
- Performance optimizations: Identifies schema DDLs that may impact application performance after migrating to YugabyteDB. It highlights potentially inefficient DDLs and provides recommendations to optimize them for better performance.
- Migration time estimate: Provides an estimated time for data import into YugabyteDB based on experimental data.
- Unsupported query constructs: Identifies SQL features and constructs not supported by YugabyteDB, such as advisory locks, system columns, and XML functions, and provides a list of queries containing these constructs.
- Unsupported PL/pgSQL objects: Identifies SQL features and constructs that are not supported by YugabyteDB, such as advisory locks, system columns, and XML functions, within PL/pgSQL objects in the source schema. It reports the individual queries within these objects that are not supported, such as queries in the PL/pgSQL block for functions and procedures, or the select statements in views and materialized views that contain unsupported constructs.
When running migration assessment, keep in mind the following:
-
The recommendations are based on testing using a RF3 YugabyteDB cluster on instance types with 4GiB memory per core and running v2024.1.
-
To detect unsupported query constructs, ensure the pg_stat_statements extension is properly installed and enabled on source.
-
To disable unsupported query construct detection, set the environment variable
REPORT_UNSUPPORTED_QUERY_CONSTRUCTS=false. -
To disable unsupported PL/pgSQL object detection, set the environment variable
REPORT_UNSUPPORTED_PLPGSQL_OBJECTS=false. -
To detect certain performance optimizations, ensure that ANALYZE (PostgreSQL) is run on the source database.
The following table describes the type of data that is collected during a migration assessment.
| Data | Collected | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Application or user data | No | No application or user data is collected. |
| Passwords | No | The assessment does not store any passwords. |
| Database metadata schema, object, object names |
Yes | Voyager collects the schema metadata including table IOPS, table size, and so on, and the actual schema. |
| Database name | Yes | Voyager collects database and schema names to be used in the generated report. |
| Performance metrics | Optional | Voyager captures performance metrics from the database (IOPS) for rightsizing the target environment. |
| Server or database credentials | No | No server or database credentials are collected. |
Get started with migration assessment
To get started with migration assessment, do the following:
-
Install YugabyteDB to view migration assessment report in the yugabyted UI. Using the yugabyted UI, you can visualize and review the database migration workflow performed by YugabyteDB Voyager.
-
Start a local YugabyteDB cluster. Refer to the steps described in Use a local cluster.
-
To see the Voyager migration workflow details in the UI, set the following environment variables before starting the migration:
export CONTROL_PLANE_TYPE=yugabyted export YUGABYTED_DB_CONN_STRING=<ysql-connection-parameters>Provide the standard PostgreSQL connection parameters, including user name, host name, and port. For example,
postgresql://yugabyte:yugabyte@127.0.0.1:5433Note
Don't include thedbnameparameter in the connection string; the defaultyugabytedatabase is used to store the meta information for showing the migration in the yugabyted UI.
-
-
Assess your migration.
Voyager supports two primary modes for conducting migration assessments, depending on your access to the source database as follows:
This mode requires direct connectivity to the source database from the client machine where voyager is installed. You initiate the assessment by executing the
assess-migrationcommand ofyb-voyager. This command facilitates a live analysis by interacting directly with the source database, to gather metadata required for assessment. A sample command is as follows:yb-voyager assess-migration --source-db-type postgresql \ --source-db-host hostname --source-db-user ybvoyager \ --source-db-password password --source-db-name dbname \ --source-db-schema schema1,schema2 --export-dir /path/to/export/dirIf you are using a configuration file, use the following:
yb-voyager assess-migration --config-file <path-to-config-file>PostgreSQL only. In situations where direct access to the source database is restricted, there is an alternative approach. Voyager includes packages with scripts for PostgreSQL at
/etc/yb-voyager/gather-assessment-metadata.You can perform the following steps with these scripts:
-
On a machine which has access to the source database, copy the scripts and install dependencies psql and pg_dump version 14 or later. Alternatively, you can install yb-voyager on the machine to automatically get the dependencies.
-
Run the
yb-voyager-pg-gather-assessment-metadata.shscript by providing the source connection string, the schema names, path to a directory where metadata will be saved, and an optional argument of an interval to capture the IOPS metadata of the source (in seconds with a default value of 120). For example:/path/to/yb-voyager-pg-gather-assessment-metadata.sh 'postgresql://ybvoyager@host:port/dbname' 'schema1|schema2' '/path/to/assessment_metadata_dir' '60' -
Copy the metadata directory to the client machine on which voyager is installed, and run the
assess-migrationcommand by specifying the path to the metadata directory as follows:yb-voyager assess-migration --source-db-type postgresql \ --assessment-metadata-dir /path/to/assessment_metadata_dir --export-dir /path/to/export/dirIf you are using a configuration file, use the following:
yb-voyager assess-migration --config-file <path-to-config-file>
The output is a migration assessment report, and its path is printed on the console.
Important
For the most accurate migration assessment, the source database must be actively handling its typical workloads at the time the metadata is gathered. This ensures that the recommendations for sharding strategies and cluster sizing are well-aligned with the database's real-world performance and operational needs. -
-
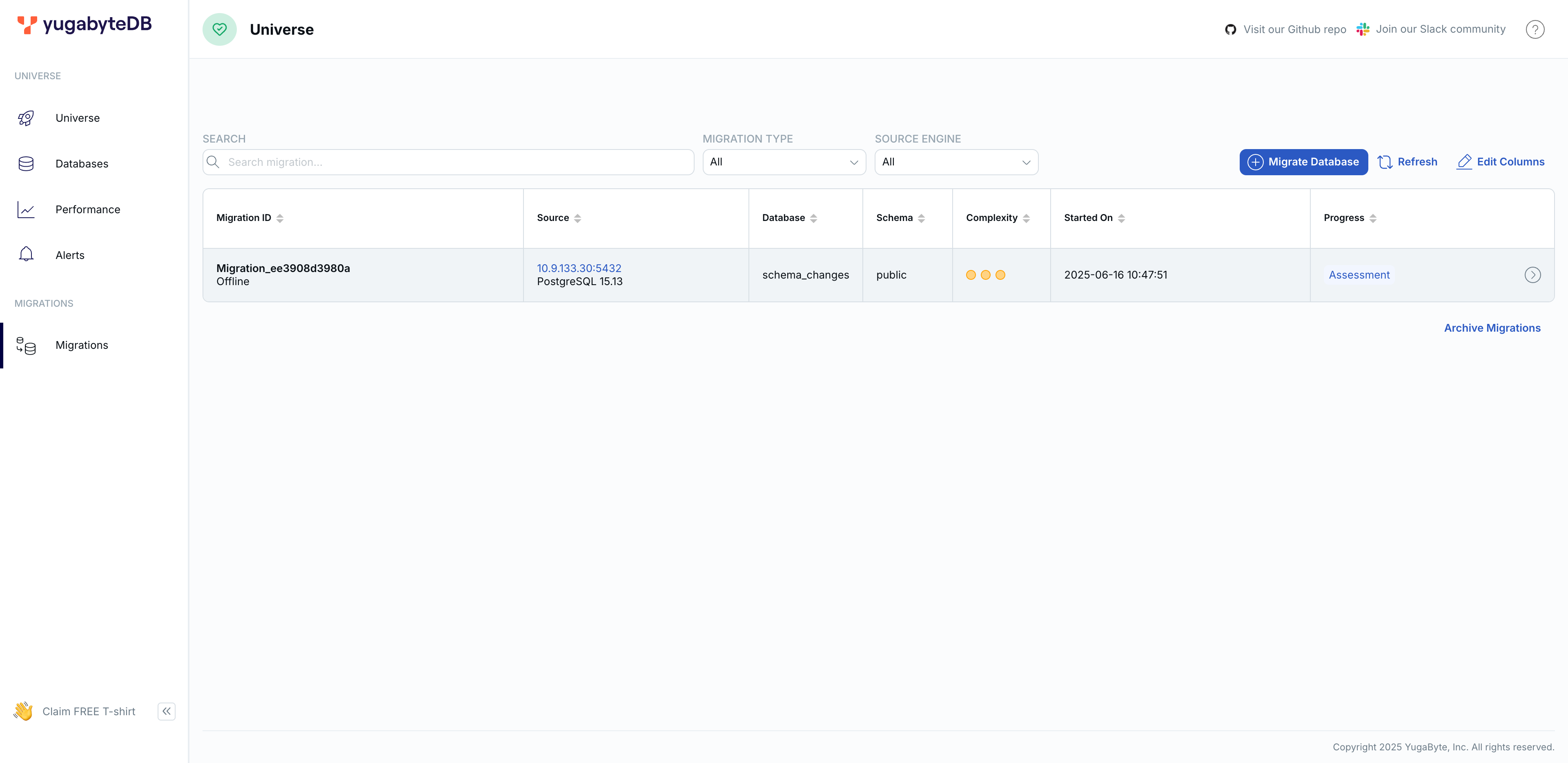
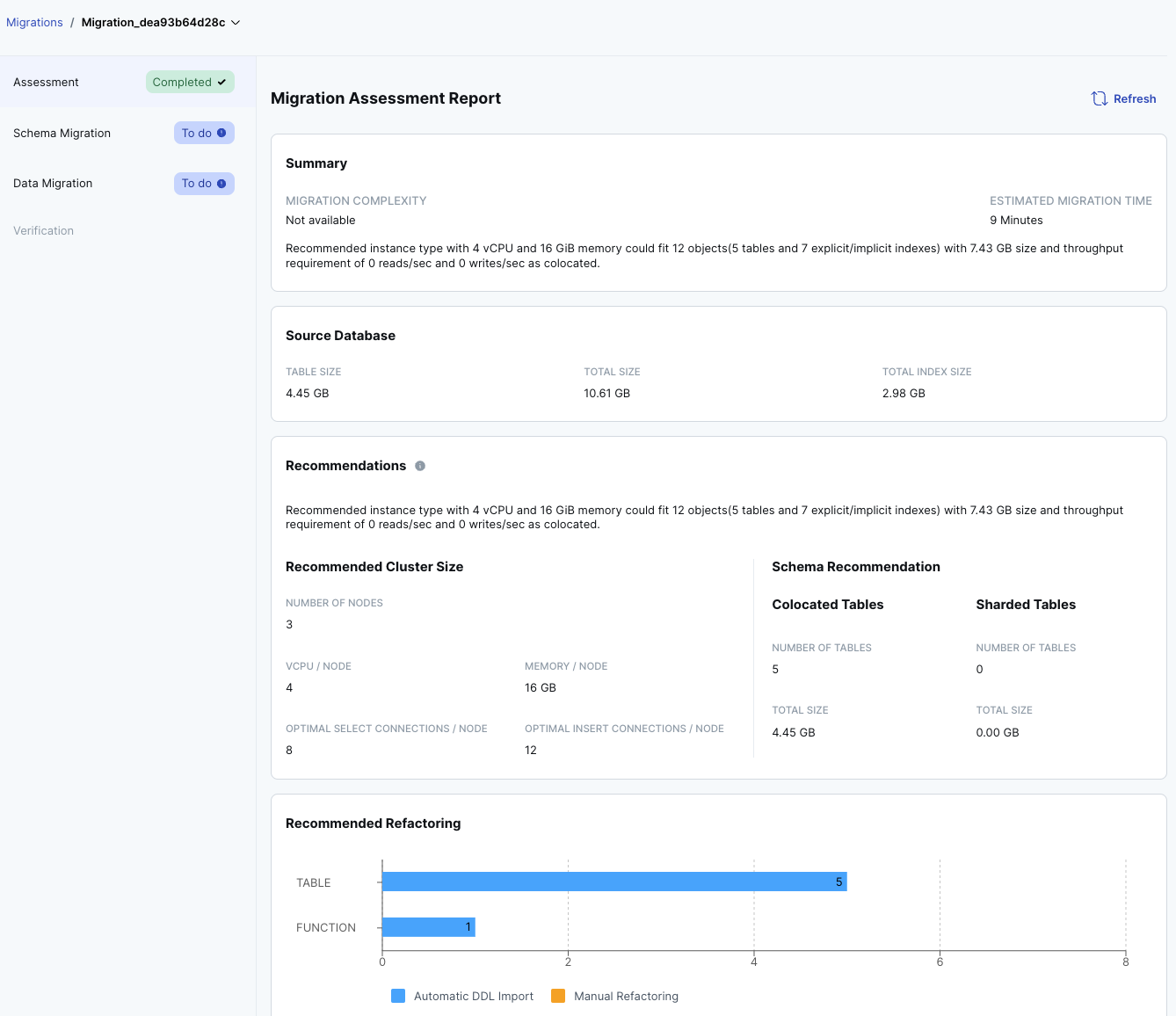
View the assessment report.
Use the yugabyted UI to review the assessment report, which includes migration strategies, complexity, and effort estimates.
After generating the report, navigate to the Migrations tab in the yugabyted UI at http://127.0.0.1:15433 to see the available migrations.
-
Create a target YugabyteDB cluster as follows:
-
Create a cluster in Enhanced PostgreSQL Compatibility Mode, based on the sizing recommendations in the assessment report.
For a universe in YugabyteDB Anywhere, enable compatibility mode by setting flags on the universe.
-
Create a database with colocation set to TRUE.
CREATE DATABASE <TARGET_DB_NAME> with COLOCATION=TRUE;
-
-
Proceed with migration with one of the migration workflows:
Assess a fleet of databases (Oracle only)
Use the Bulk Assessment command (assess-migration-bulk) to assess multiple schemas across one or more database instances simultaneously. It offers:
- Multi-Schema Assessment: Assess multiple schemas in different database instances with a single command, simplifying migration planning.
- Centralized Reporting: All assessment reports are generated and stored in one organized directory, making
Command
To perform a bulk assessment, use the following command syntax:
yb-voyager assess-migration-bulk \
--fleet-config-file /path/to/fleet_config_file.csv \
--bulk-assessment-dir /path/to/bulk-assessment-dir \
[--continue-on-error true|false] \
[--start-clean true|false]
Fleet configuration file
Bulk assessment is managed using a fleet configuration file, which specifies the schemas to be assessed. The file is in CSV format.
- Header Row: The first row contains headers that define the fields for each schema.
- Schema Rows: Each subsequent row corresponds to a different schema to be assessed.
The following table outlines the fields that can be included in the fleet configuration file.
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
| source-db-type | Required. The type of source database. Currently, only Oracle is supported. |
| source-db-user | Required. The username used to connect to the source database. |
| source-db-password | Optional. The password for the source database user. If not provided, you will be prompted for the password during assessment of that schema. |
| source-db-schema | Required. The specific schema in the source database to be assessed. |
| source-db-host | Optional. The hostname or IP address of the source database server. |
| source-db-port | Optional. The port number on which the source database is running. This is required if oracle-tns-alias is not used. |
| source-db-name | Optional. The database name for connecting to the Oracle database. This is required if oracle-db-sid or oracle-tns-alias is not used. |
| oracle-db-sid | Optional. The Oracle System Identifier (SID). This is required if source-db-name or oracle-tns-alias is not used. |
| oracle-tns-alias | Optional. The TNS alias used for Oracle databases, which can include connection details such as host, port, and service name. This is required if source-db-name or oracle-db-sid is not used. |
The following is an example fleet configuration file.
source-db-type,source-db-host,source-db-port,source-db-name,oracle-db-sid,oracle-tns-alias,source-db-user,source-db-password,source-db-schema
oracle,example-host1,1521,ORCL,,,admin,password,schema1
oracle,example-host2,1521,,ORCL_SID,,admin,password,schema2
oracle,,,,,tns_alias,oracle_user,password,schema3
Directory structure
After the bulk assessment is completed, the top-level directory specified using the --bulk-assessment-dir flag includes subdirectories for each assessed schema. Additionally, a top-level report is generated that provides links to the individual assessment reports for each schema.
/bulk-assessment-dir/
├── bulk_assessment_report.html
├── bulk_assessment_report.json
├── DBNAME-SCHEMA1-export-dir/
│ └── assessment/
│ └── reports/
│ ├── migration_assessment_report.html
│ └── migration_assessment_report.json
├── SID-SCHEMA2-export-dir/
│ └── assessment/
│ └── reports/
│ ├── migration_assessment_report.html
│ └── migration_assessment_report.json
└── logs/
└── yb-voyager-assess-migration-bulk.log