Camunda
Camunda is a Java-based framework supporting BPMN (Business Process Modeling Notation) for workflow and process automation, CMMN (Case Management Model and Notation) for Case Management and DMN (Decision Model and Notation) for business decision management.
Camunda supports PostgreSQL as a datasource. Because YugabyteDB is wire compatible with PostgreSQL, it works out of the box with Camunda as a datasource. This document covers how to:
- Configure Camunda to use YugabyteDB (YSQL) as a data source.
- Run a hello world example in Camunda.
Prerequisites
This tutorial assumes that:
- YugabyteDB is up and running. Download and install YugabyteDB by following the steps in Quick start. Alternatively, you can use YugabyteDB Aeon to get a fully managed database-as-a-service (DBaaS) for YugabyteDB.
- Java JDK 1.8 or later is installed.
- NodeJS v10 or later is installed.
- Camunda Platform 7 and Modeler are installed following the instructions on Camunda's quick-start page.
Configure Camunda Platform 7
-
Locate the
spring.datasourcesection in the following files:camunda-bpm-run-7.17.0/configuration/default.ymlcamunda-bpm-run-7.17.0/configuration/production.yml
-
Modify the
spring.datasourcesection that uses standard PostgreSQL JDBC driver. Change theurlvalue to point to the YugabyteDB cluster you started:# datasource configuration is required spring.datasource: url: jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5433/yugabyte driver-class-name: org.postgresql.Driver username: yugabyte password: yugabyte -
Download the PostgreSQL JDBC driver JAR fileand place it in the
camunda-bpm-run-7.17.0/configuration/userlibdirectory. Alternatively, you can also use the YugabyteDB JDBC driver to connect Camunda to a YugabyteDB cluster. To do so, modify thespring.datasourcesection in each file to point to the YugabyteDB cluster you started, and replace the value ofdriver-class-namewithcom.yugabyte.Driver.# datasource configuration is required spring.datasource: url: jdbc:yugabytedb://localhost:5433/yugabyte driver-class-name: com.yugabyte.Driver username: yugabyte password: yugabyteThen, download the YugabyteDB JDBC driver JAR file and place it in the
camunda-bpm-run-7.17.0/configuration/userlibdirectory. Read more about the YugabyteDB JDBC driver. -
Start the Camunda Platform server using
./start.shon Linux or macOS, or./start.baton Windows.
Verify the integration
After the server is started, you'll be able to see a few tables getting created in the database. To verify, do the following:
- Log in to the database using
./bin/ysqsh. - Use
\dto see the list of tables. - Verify that a list of tables with the prefix
ACT_are created.
See the Camunda docs for more details regarding the tables created.
Run a hello world application
In this example, taken from the Camunda quick-start, you'll use Camunda Modeler to design and deploy a small BPMN for charging the cards.
You'll need three events:
- Start event
- Service event
- End event
Note that for the service event, you need an external task worker. For that purpose, you'll use Node.js.
Model the process as BPMN
- Start Camunda Modeler.
- Click File > New File > BPMN Diagram to create a new BPMN diagram.
- Double-click the start event, and name the event "Payment Retrieval Requested".
- Create a service event:
- Click the start event. From its context menu, select the activity shape (rounded rectangle).
- The activity shape appears on the canvas. Drag it to your preferred position, and name the shape "Charge Credit Card".
- Click the activity shape, and use the wrench button to change the activity type to Service Task.
- Repeat the previous step to add an end event named "Payment Received".
- Configure the service task:
- Enter
payment-retrievalin the ID property field to configure an ID for the process. The process engine uses the property ID as an identifier for the executable process; it's good practice to set it to a human-readable name. - Enter "Payment Retrieval" in the Name property field.
- Ensure that the box next to the Executable property is checked. If you don't check this box, the process engine ignores the process definition.
- Enter
- Save the BPMN diagram.
Implement an external task worker
After modeling the process, you can create some business logic. Camunda Platform is built so that you can implement your business logic in different languages. You have the choice which language suits your project best. For this example, you'll use JavaScript (Node.js).
-
Create a new Node.js project:
mkdir charge-card-worker cd ./charge-card-worker npm init -y -
Add the Camunda External Task Client library to your project:
npm install camunda-external-task-client-js npm install -D open
Implement the NodeJS script
Next, you'll create a new ExternalTaskClient that subscribes to the charge-card topic.
When the process engine encounters a service task configured to be externally handled, it creates an external task instance on which your handler reacts. The handler in this example uses long polling in the ExternalTaskClient to make the communication more efficient.
-
Create a new file called
worker.jswith the following contents:const { Client, logger } = require('camunda-external-task-client-js'); const open = require('open'); // configuration for the Client: // - 'baseUrl': URL to the Process Engine // - 'logger': utility to automatically log important events // - 'asyncResponseTimeout': long polling timeout (then a new request will be issued) const config = { baseUrl: 'http://localhost:8080/engine-rest', use: logger, asyncResponseTimeout: 10000 }; // create a Client instance with custom configuration const client = new Client(config); // susbscribe to the topic: 'charge-card' client.subscribe('charge-card', async function({ task, taskService }) { // Put your business logic here // Get a process variable const amount = task.variables.get('amount'); const item = task.variables.get('item'); console.log(`Charging credit card with an amount of ${amount}€ for the item '${item}'...`); // Complete the task await taskService.complete(task); }); -
Run the Node.js script you just created:
node ./worker.js
Deploy the process using Camunda Modeler
To deploy the process, do the following:
-
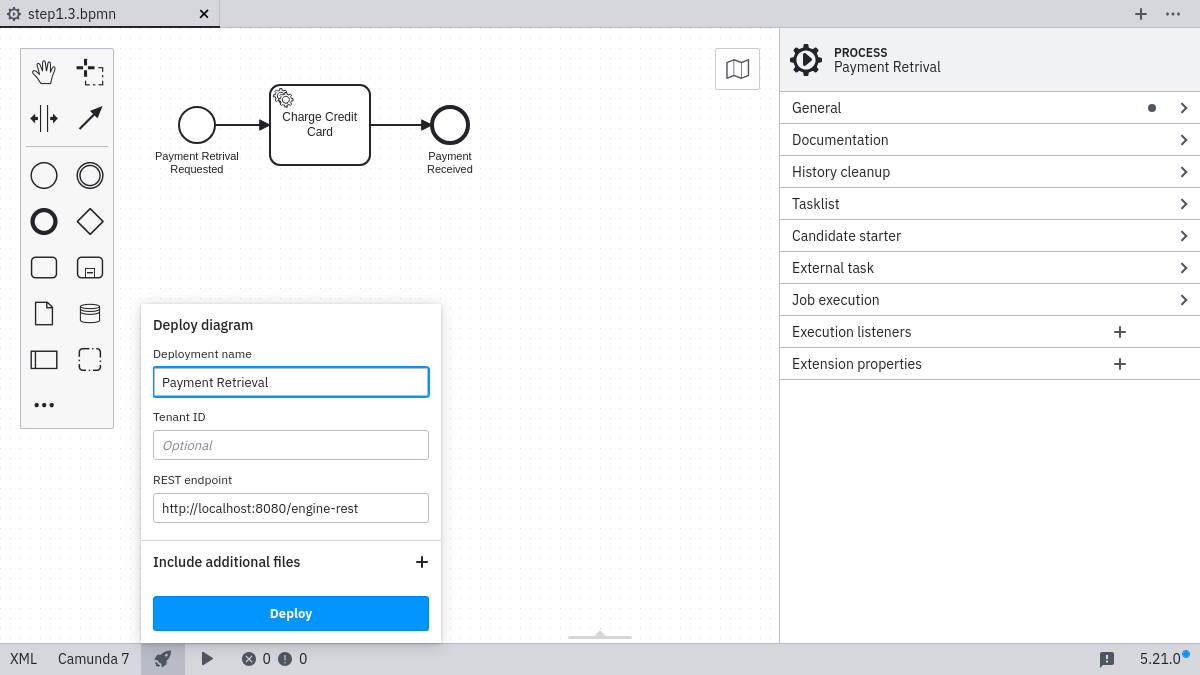
Click the deploy button in Camunda Modeler, enter the deployment name "Payment Retrieval", and click the Deploy button.
If you're running Camunda Modeler version 3.0.0 or later, you need to provide the URL of an Endpoint Configuration along with the deployment details. This can be either the root endpoint to the REST API (such as http://localhost:8080/engine-rest) or an exact endpoint to the deployment creation method (such as http://localhost:8080/engine-rest/deployment/create).
-
Use Cockpit to verify the deployment.
Navigate to http://localhost:8080/camunda/app/cockpit/ and log in with a username and password of
demo. Your process called Payment Retrieval should be visible on the dashboard. -
Use the Camunda REST API to start a new process instance by sending a POST request:
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -X POST \ -d '{"variables": {"amount": {"value":555,"type":"integer"}, "item": {"value":"item-xyz"} } }' \ http://localhost:8080/engine-rest/process-definition/key/payment-retrieval/start -
You can also make a POST request from another tool, such as Postman, with the following JSON body:
{ "variables": { "amount": { "value":555, "type":"integer" }, "item": { "value": "item-xyz" } } }
In your worker, you should now see the output in your console. You have successfully started and executed your first small process.