Secure applications using Azure Key Vault, Azure SDKs, and YugabyteDB
In this tutorial, we'll explore how you can leverage Azure SDKs to interact with Azure services and use SDKs with database-backed applications, like those running YugabyteDB.
The Azure SDKs are developed in a modular fashion. They provide developers with hooks into the services that their applications rely on, without bloating bundle sizes. The SDKs are developed for parity across many programming languages, but in this example we will use the JavaScript SDK for Node.js.
In the following sections, you will:
- Create a node.js application that uses the Azure Key Vault SDK.
- Connect to the Azure Key Store from the application.
- Connect to the YugabyteDB database using the credentials stored in the key vault.
Prerequisites
- A Microsoft Azure subscription, with authentication
- An Azure Key Vault
- Node.js version v18+
- A YugabyteDB Aeon account with a cluster deployed
Introduction to the Azure SDKs and Tools
As the Azure Cloud continues to expand and evolve, so do the mechanisms used to deploy and interact with its services. Azure provides well over 150 SDKs, and the list is growing.
For instance, Azure's new OpenAI SDK can be used to build generative AI applications.
SDKs provide an interface to interact with Azure services via application code, but there are also tools available for download, including a rich command-line interface and a comprehensive set of Visual Studio Code extensions.
Now, let's build a sample application which connects to the Azure Key Vault from Node.js. We'll then use the secrets stored in this service to connect to a YugabyteDB Aeon cluster.
Example SDK usage
A reference to the application we'll be developing can be found on GitHub.
-
Initialize a new directory for your project.
mkdir YBAzureKeyStore && cd YBAzureKeyStore npm init -y -
Install the YugabyteDB node-postgres smart driver.
npm install @yugabytedb/pg -
Install the Azure Key Vault secrets client library.
npm install @azure/keyvault-secrets -
Install the Azure Identity client library.
npm install @azure/identity -
Install Dotenv and use it to set environment variables.
npm install dotenv --save-dev// .env KEY_VAULT_NAME="[NAME_OF_KEY_VAULT_IN_AZURE]" DB_USERNAME="admin" DB_PASSWORD="[YB_MANAGED_DB_PASSWORD]" //TIP: convert certificate to single line string for ease of use with DB client DB_CERTIFICATE="[YB_MANAGED_CERTIFICATE]" DB_HOST="[YB_DB_HOST]" -
Connect to the Azure Key Store from Node.js.
// createSecrets.js const { SecretClient } = require("@azure/keyvault-secrets"); const { DefaultAzureCredential } = require("@azure/identity"); async function main() { // As stated by Microsoft, if you're using MSI, DefaultAzureCredential should "just work". // Otherwise, DefaultAzureCredential expects the following three environment variables: // - AZURE_TENANT_ID: The tenant ID in Azure Active Directory // - AZURE_CLIENT_ID: The application (client) ID registered in the Azure AD tenant // - AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET: The client secret for the registered application const credential = new DefaultAzureCredential(); const keyVaultName = process.env["KEY_VAULT_NAME"]; if (!keyVaultName) throw new Error("KEY_VAULT_NAME is empty"); const url = "https://" + keyVaultName + ".vault.azure.net"; const client = new SecretClient(url, credential); -
Use the secret client to set the secrets needed to establish a YugabyteDB Aeon connection.
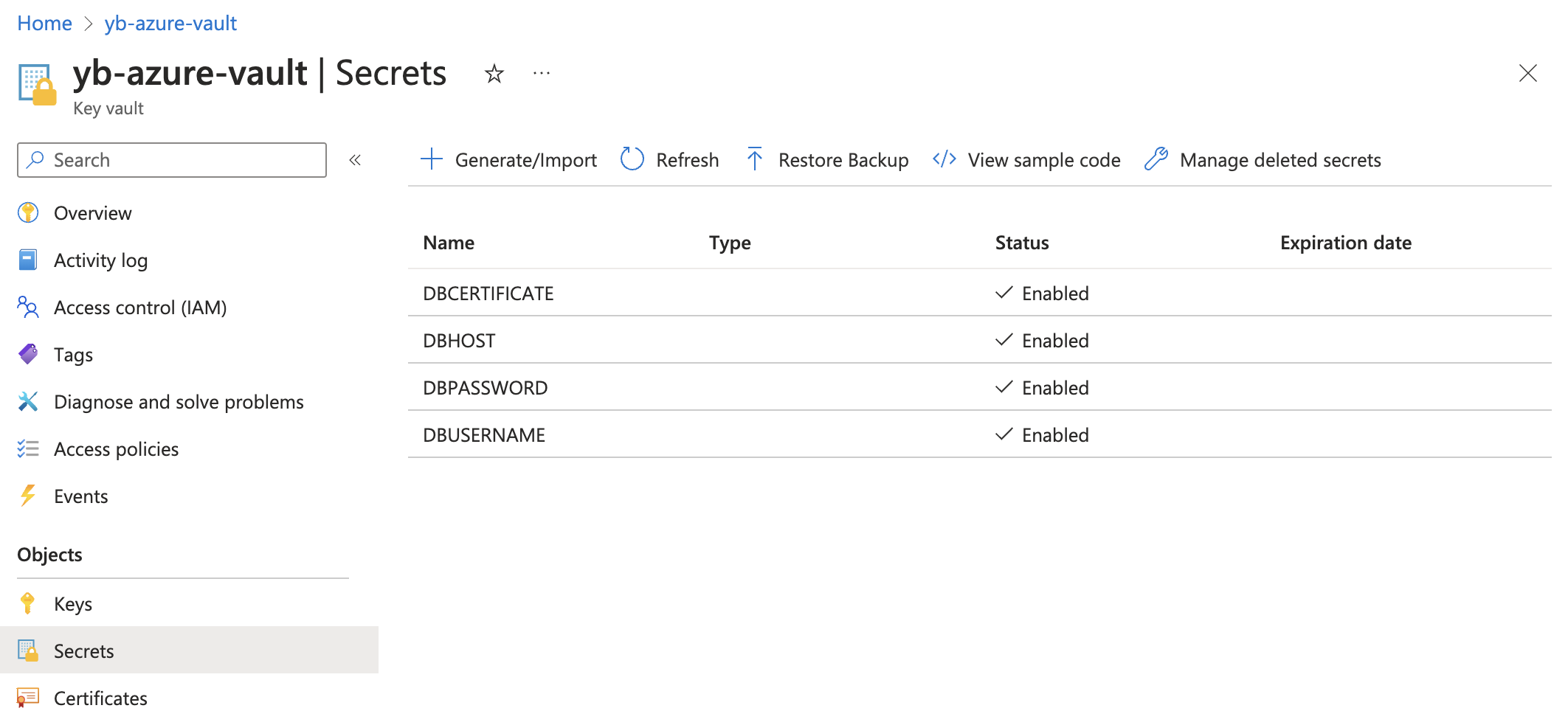
// createSecrets.js async function main(){ ... // Create secrets for YugabyteDB Aeon connection await client.setSecret("DBUSERNAME", process.env.DB_USERNAME); await client.setSecret("DBPASSWORD", process.env.DB_PASSWORD); await client.setSecret("DBCERTIFICATE", process.env.DB_CERTIFICATE); await client.setSecret("DBHOST", process.env.DB_HOST); // Get secrets to confirm they've been set in Azure Key Vault for await (let secretProperties of client.listPropertiesOfSecrets()) { console.log("Secret Name: ", secretProperties.name); const secret = await client.getSecret(secretProperties.name); console.log("Secret Val:", secret.value); } } main().catch((error) => { console.error("An error occurred:", error); process.exit(1); });node createSecrets.js -
Read these secrets from Azure and connect to YugabyteDB Aeon.
// index.js const { Client } = require("@yugabytedb/pg"); const { SecretClient } = require("@azure/keyvault-secrets"); const { DefaultAzureCredential } = require("@azure/identity"); async function main() { const credential = new DefaultAzureCredential(); const keyVaultName = process.env["KEY_VAULT_NAME"]; if (!keyVaultName) throw new Error("KEY_VAULT_NAME is empty"); const url = "https://" + keyVaultName + ".vault.azure.net"; const secretClient = new SecretClient(url, credential); const dbhost = await secretClient.getSecret("DBHOST"); const dbusername = await secretClient.getSecret("DBUSERNAME"); const dbpassword = await secretClient.getSecret("DBPASSWORD"); const dbcertificate = await secretClient.getSecret("DBCERTIFICATE"); const ybclient = new Client({ database: "yugabyte", host: dbhost.value, user: dbusername.value, port: 5433, password: dbpassword.value, max: 10, idleTimeoutMillis: 0, ssl: { rejectUnauthorized: true, ca: dbcertificate.value, servername: dbhost.value, }, }); console.log("Establishing connection with YugabyteDB Aeon"); await ybclient.connect(); console.log("Connected successfully."); } main().catch((error) => { console.error("An error occurred:", error); process.exit(1); });node index.jsEstablishing connection with YugabyteDB Aeon... Connected successfully.
Thanks to the Azure Key Vault SDK, we've successfully connected to YugabyteDB, using credentials stored securely in the cloud. This protects our data and ensures a simplified development environment, where credentials can be centrally updated by multiple end users.
The Azure Key Vault SDK comes with additional features for interacting with secrets. These include the ability to update, delete, and purge values if required. You can also use the Azure web console to make any necessary changes.
Wrap-up
We've just scratched the surface with what is possible using Azure SDKs and the surrounding ecosystem. We'll be developing more applications on Azure in the coming months as the list of tools continues to expand.
If you're also interested in building applications using Azure App Service, refer to building applications using Azure App Service and YugabyteDB.
You can also use Azure Key Vault to store customer managed keys for encrypting clusters in YugabyteDB Aeon - see Encryption at rest.