Back up and restore clusters
Back Up and Restore → across different products
YugabyteDB Aeon can perform full and incremental cluster (all namespaces) level backups, and the backups are stored in the same region as your cluster.
By default, clusters are backed up automatically every 24 hours, and these automatic full backups are retained for 8 days. The first automatic backup is triggered after 24 hours of creating a table, and is scheduled every 24 hours thereafter.
Full backups are a complete copy of the cluster. You can additionally schedule incremental backups between full backups. Incremental backups only include the data that has changed since the last backup, be it a full or incremental backup. Incremental backups provide the following advantages:
- Faster - Incremental backups are much quicker as they deal with a smaller amount of data.
- Reduced storage - Because only the delta from previous backup is captured, incremental backups consume less storage space compared to full backups.
- Higher frequency - Incremental backups can be scheduled at smaller intervals (down to hourly), providing a lower recovery point objective (RPO).
Back up and restore clusters, configure the scheduled backup policy, and review previous backups and restores using the cluster Backups tab.
To change the backup schedule, create your own schedule.
You can also perform backups on demand and manually restore backups.
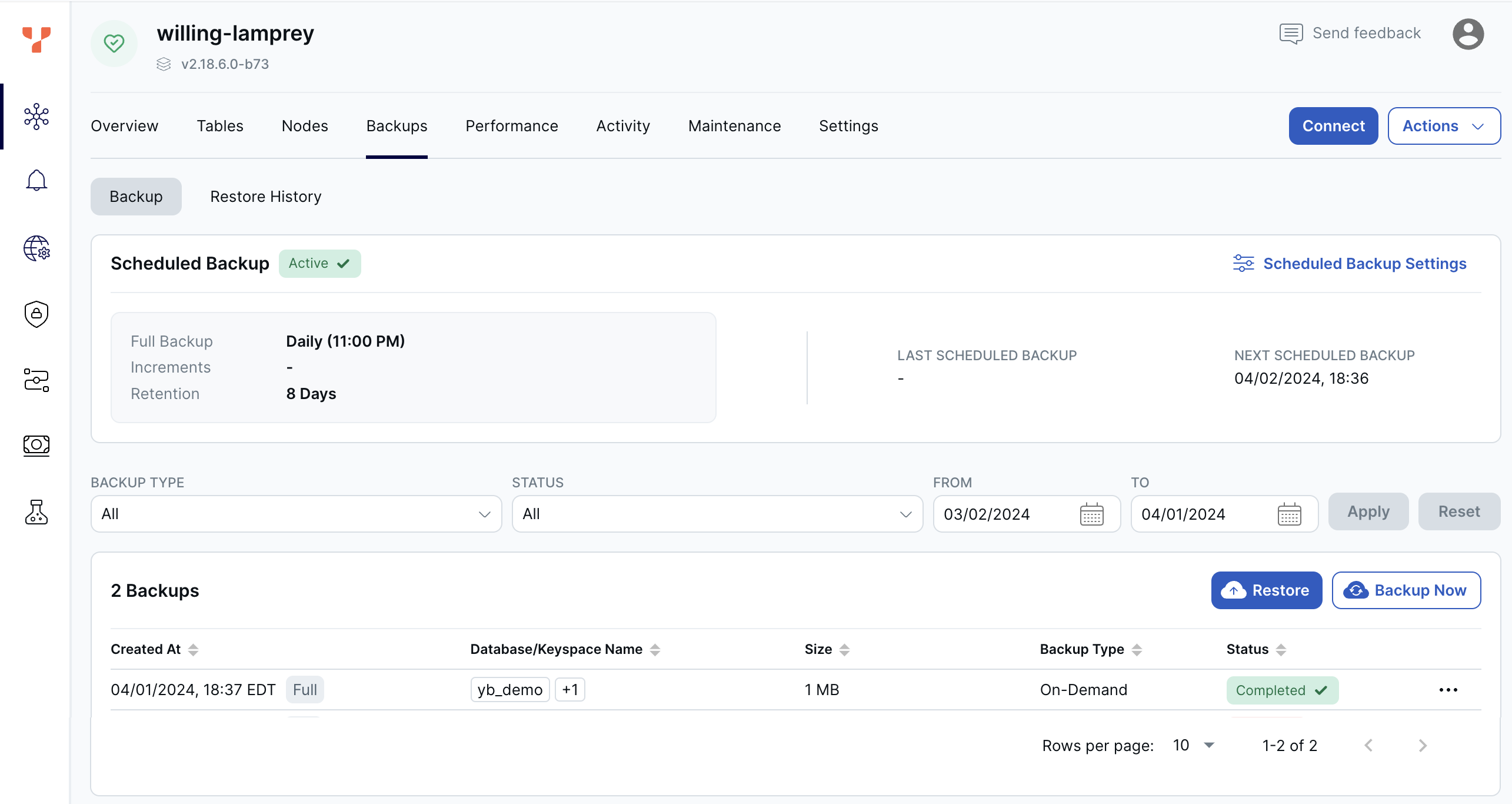
To delete a backup, click the Delete icon.
To review previous backups, click Backup. To review previous restores, click Restore.
Location of backups
Backups are located in cloud storage of the provider where the cluster is deployed. The storage is located is the same region as the cluster. For example, for a cluster deployed in AWS and located in us-east-2, backups are stored in an S3 bucket in us-east-2.
For Replicate across region clusters, all backups are stored in one of the cluster regions, as determined automatically by Aeon when the cluster is created or infrastructure is updated.
For Partition by region clusters, the database schema and tablet details are stored in the primary region, and the regional tablespace data is stored in its respective region to preserve data residency.
Limitations
If some cluster operations are already running during a scheduled backup window, the backup may be prevented from running.
Backups that don't run are postponed until the next scheduled backup. You can also perform a manual backup after the blocking operation completes.
You can't restore a backup to a cluster with an version of YugabyteDB that is earlier than that of the backup. If you need to restore to an earlier version, contact Yugabyte Support.
Backups are not supported for Sandbox clusters.
Backups and high DDL activity
In some circumstances, a backup can fail during high DDL activity. Avoid performing major DDL operations during scheduled backups or while a backup is in progress.Recommendations
- Don't perform cluster operations at the same time as your scheduled backup.
- Configure your maintenance window and backup schedule so that they do not conflict.
- Perform full backups before performing a large operation, such as a DDL change.
- Performing a backup or restore incurs a load on the cluster. Perform backup operations when the cluster isn't experiencing heavy traffic. Backing up during times of heavy traffic can temporarily degrade application performance and increase the length of time of the backup.
- Avoid running a backup during or before a scheduled maintenance.
On demand backups
Typically, you perform on-demand backups before making critical planned changes to the database.
To back up a cluster:
- On the Backups tab, click Backup Now to display the Create Backup dialog.
- Set the retention period for the backup.
- To back up database roles (YSQL only), choose the Include roles and grants option.
- Optionally, enter a description of the backup.
- Click Backup Now.
The backup, along with its status, is added to the Backups list.
Manage scheduled backups
Use a backup policy to schedule backups and override the default 24 hour/8-day retention policy.
Any changes to the retention policy are applied to new backups only.
To manage the cluster backup policy, do the following:
- On the Backups tab, click Scheduled Backup Settings and choose Edit Backup Policy to display the Backup Policy dialog.
- Specify how often to take full backups of the database.
- To take incremental backups, select the Enable incremental backup option and specify how often to take incremental backups.
- To back up database roles (YSQL only), choose the Include roles and grants option.
- Set the retention period for the backup. The maximum retention is 31 days.
- Click Save.
To disable the scheduled backup, click Scheduled Backup Settings and choose Disable Scheduled Backup. Click Enable Scheduled Backup to re-enable the policy.
Restore a backup
Before performing a restore, ensure the following:
- the target cluster is sized appropriately; refer to Scale and configure clusters
- if the target cluster has the same namespaces as the source cluster, those namespaces don't have any tables
- the target cluster has the same users as the source cluster. If you restore to a cluster where some users are missing, ownership of objects owned by missing users defaults to
yugabyte, and you must contact Yugabyte Support to reset the owners.
To review previous restores, on the Backups tab, select Restore History.
To restore a backup of a cluster:
-
On the Backups tab, select a backup in the list to display the Backup Details sheet.
-
Click Restore to display the Restore Backup dialog.
-
Choose the databases or keyspaces to restore.
-
If the backup includes roles, choose the Restore roles and grants option to restore roles.
Note that if the target cluster already has matching roles, those roles are not overwritten.
-
Click Next.
-
Select the target cluster.
-
To rename databases, select the Rename database/s before restoring option and click Next.
Note that if the target cluster already has databases with the same name, you must rename databases.
-
If you are renaming databases, enter a new name for the databases you want to rename in the Assign new name column.
-
Click Restore Now.
Grants and permissions
When restoring a backup that includes roles and grants, YugabyteDB Aeon reconciles roles and permissions on the target cluster as follows:
- New roles are added with grants
- Existing roles are updated with permissions/attributes if any, and not overwritten
- Credentials are not changed for existing roles
Remote backup replication
EA Use remote backup replication to copy all your cluster backups (scheduled, incremental, and on demand) to a storage bucket in the same cloud provider.
Only new backups (that is, backups created after backup replication has been enabled on the cluster) are transferred. Backups are transferred to the bucket once a day.
Remote backup replication counts against your data transfer allowance. This may incur additional costs for network transfer, especially for cross-region transfers, if usage exceeds your cluster allowance. To avoid cross-region data transfer costs, use a bucket in the same region as the cluster.
To restore from a remote backup, contact Yugabyte Support.
Currently, only clusters deployed to GCP are supported.
Prerequisites
The remote storage bucket must be on the same cloud provider as the cluster; for clusters deployed in GCP, the bucket must be in Google Cloud Storage. Transfer is performed using Google Storage Transfer Service.
Set up target buckets
-
Identify and configure the Google Cloud Storage buckets that will serve as replication targets for your backup data.
It is highly recommended to use a new, empty bucket rather than one that already contains data. Although safeguards are in place, remote replication requires delete permissions. To minimize the risk of accidental data loss, using a fresh bucket is the safest approach.
-
Set up service account permissions.
Grant the required permissions to the Storage Transfer Service agent on each target bucket.
Service Account Principal:
project-426074570168@storage-transfer-service.iam.gserviceaccount.comThe service account must have the following permissions on each target bucket:
storage.objects.list storage.objects.delete storage.objects.create storage.objects.get storage.buckets.getYou can provide these permissions using one of the following methods:
- Custom role (Recommended): Create a custom IAM role with only the required permissions.
- Predefined role: Use existing Google Cloud IAM roles that include the necessary permissions.
For more information, see IAM roles for Cloud Storage and Configure access to a sink in the GCS documentation.
Manage remote backup replication
To enable or modify remote backup replication, do the following:
-
On the Backups tab, click Enable Remote Backup Replication. If backup replication is enabled, click Edit Settings.
-
Enter the address of the bucket.
For Replicate across regions clusters, provide the bucket address. To reduce transfer costs, use a bucket in the same region as the current backup region (the region selected by Aeon to store cluster backups). See Location of backups for more information.
For Partition by region clusters, provide a bucket address for each region. To reduce transfer costs and for compliance, use buckets located in the same regions.
-
Click Enable or, if you are modifying settings, Apply Changes.
To disable remote backup replication, on the Backups tab, click Disable Remote Backup Replication.
Disabling backup replication does not immediately stop transfers. To ensure no data is lost, the transfer job remains active for a few additional days so that any backups created before disabling replication are fully replicated. Because Google Cloud does not provide a SLA on transfer completion time or on how many transfer operations may be needed, you should keep destination buckets available for at least 7 days after disabling backup replication or after changing remote backup regions. This ensures that all in-progress and pending transfers complete successfully.
If backup replication fails, YugabyteDB Aeon displays an alert and also sends a notification email. After you have addressed the issue (by, for example, fixing permissions on the bucket, or setting up a new bucket), click the alert in YugabyteDB Aeon and try the connection again, either with the current bucket or new bucket, as appropriate.