Peer VPCs
YugabyteDB Aeon supports peering virtual private cloud (VPC) networks on AWS and GCP.
Using YugabyteDB Aeon, you can create a VPC on AWS, deploy clusters in the VPC, and peer the VPC with application VPCs hosted on AWS.
To peer VPCs that reside in AWS, you need to complete the following tasks:
| Task | Notes |
|---|---|
| Create the VPC | Reserves a range of private IP addresses for the network. You need to create a VPC for each region in multi-region clusters. The status of the VPC is Active when done. |
| Create a peering connection | Connects your VPC and the application VPC on the cloud provider network. The status of the peering connection is Pending when done. |
| Accept the peering request in AWS |
Confirms the connection between your VPC and the application VPC. The status of the peering connection is Active when done. |
| Add the route table entry in AWS |
Adds a route to the route table of the application VPC so that you can send and receive traffic across the peering connection. |
| Deploy a cluster in the VPC | This can be done at any time - you don't need to wait until the VPC is peered. |
| Add the application VPC to the IP allow list | Allows the peered application VPC to connect to the cluster. Add at least one of the CIDR blocks associated with the peered application VPC to the IP allow list for your cluster. |
With the exception of accepting the peering request and adding the route table entry in AWS, these tasks are performed in YugabyteDB Aeon.
For information on VPC peering in AWS, refer to VPC Peering in the AWS documentation.
Create a VPC
To avoid cross-region data transfer costs, deploy your VPC in the same region as the application VPC you are peering with.
If you intend to deploy a multi-region cluster, you need to create a separate VPC for each region.
The CIDR range for the application VPC with which you want to peer, as the addresses can't overlap.
Where to find it
Navigate to the AWS Your VPCs page for the region hosting the VPC you want to peer.
To create a VPC, do the following:
- On the Networking page, select VPC Network, then VPCs.
- Click Create VPC to display the Create VPC sheet.
- Enter a name for the VPC.
- Choose the provider (AWS).
- Select the region. Typically, the same region that hosts the VPC with which you want to peer.
- Specify the CIDR address. Ensure the following:
- the address does not overlap with that of the application VPC.
- the address does not overlap with the VPCs that will be used for the other regions of a multi-region cluster.
- for production clusters, use network sizes of /24 or /25.
- Click Save.
YugabyteDB Aeon adds the VPC to the VPCs list with a status of Creating. If successful, after a minute or two, the status will change to Active.
Create a peering connection
After creating a VPC in YugabyteDB Aeon that uses AWS, you can peer it with an AWS application VPC.
The following details for the AWS application VPC you are peering with:
- Account ID
- VPC ID
- VPC region
- VPC CIDR address
Where to find it
Navigate to your AWS Your VPCs page for the region hosting the VPC you want to peer.
To create a peering connection, in YugabyteDB Aeon do the following:
- On the Networking page, select VPC Network, then Peering Connections.
- Click Add Peering Connection to display the Create Peering sheet.
- Enter a name for the peering connection.
- Choose AWS.
- Choose the YugabyteDB Aeon VPC you are peering. Only VPCs that use AWS are listed.
- Enter the AWS account ID, and the application VPC ID, region, and CIDR address.
- Click Initiate Peering.
The peering connection is created with a status of Pending.
Accept the peering request in AWS
To complete a Pending AWS peering connection, you need to sign in to AWS, where you accept the peering request. After accepting the request, you will add a route table entry for the application VPC.
The CIDR address of the YugabyteDB Aeon VPC you are peering with.
Where to find it
The VPC Details sheet on the VPCs page or the Peering Details sheet on the Peering Connections page.
Sign in to your AWS account and navigate to the region hosting the application VPC you want to peer.
DNS settings
Before accepting the request, ensure that the DNS hostnames and DNS resolution options are enabled for the application VPC. This ensures that the cluster's hostnames in standard connection strings automatically resolve to private instead of public IP addresses when the YugabyteDB Aeon cluster is accessed from the application VPC.
To set DNS settings:
- On the AWS Your VPCs page, select the application VPC in the list.
- Click Actions and choose Edit DNS hostnames or Edit DNS resolution.
- Enable the DNS hostnames or DNS resolution option and click Save changes.
Accept the peering request
To accept the peering request, do the following:
-
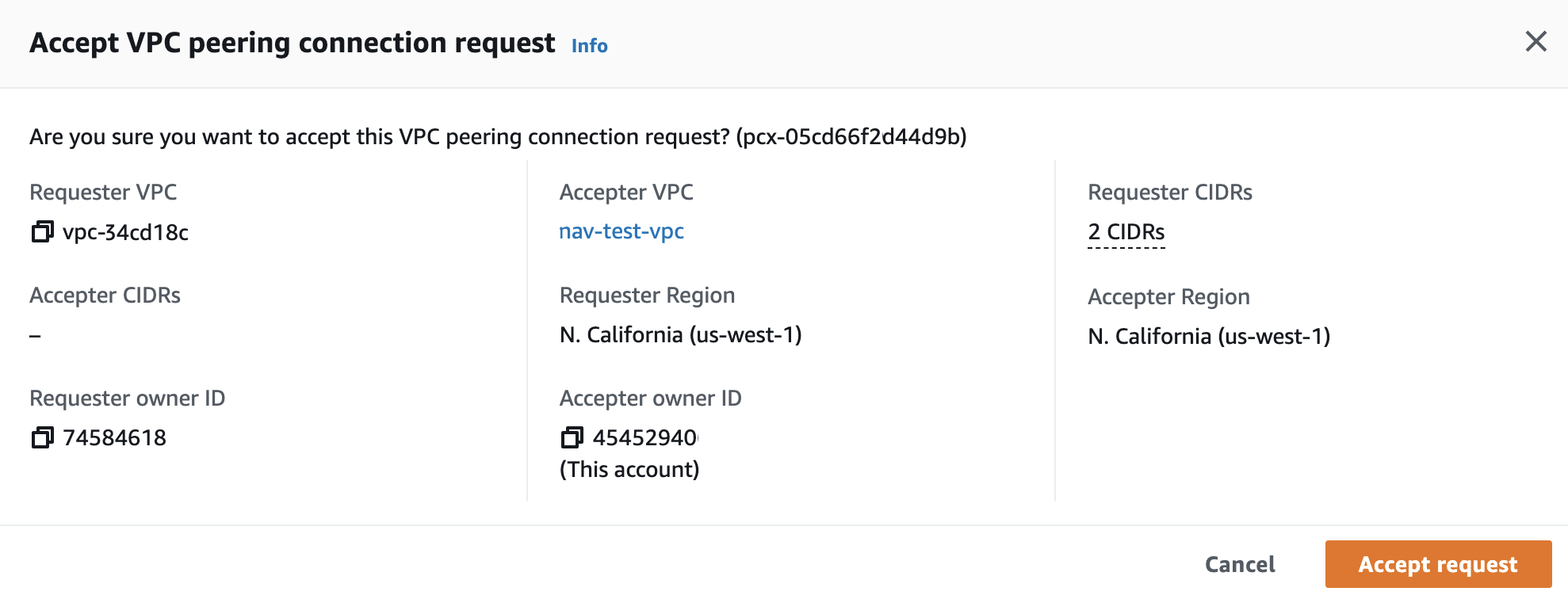
On the AWS Peering Connections page, select the pending peering connection in the list; its status is Pending acceptance.
-
Click Actions and choose Accept request to display the Accept VPC peering connection request window.
-
Click Accept request.
Tip: After accepting the request, click Modify my route tables now to navigate directly to adding a route table entry.
On the Peering connections page, note the Peering connection ID; you will use it when adding the route table entry.
When finished, the status of the peering connection in YugabyteDB Aeon changes to Active if the connection is successful.
Add the route table entry in AWS
Add a route to the route table of the application VPC so that you can send and receive traffic across the peering connection.
Ensure you are signed in to your AWS account and navigate to the region hosting the application VPC being peered.
To add a route table entry:
-
On the AWS Route Tables page, select the route table associated with the subnet of the application VPC.
-
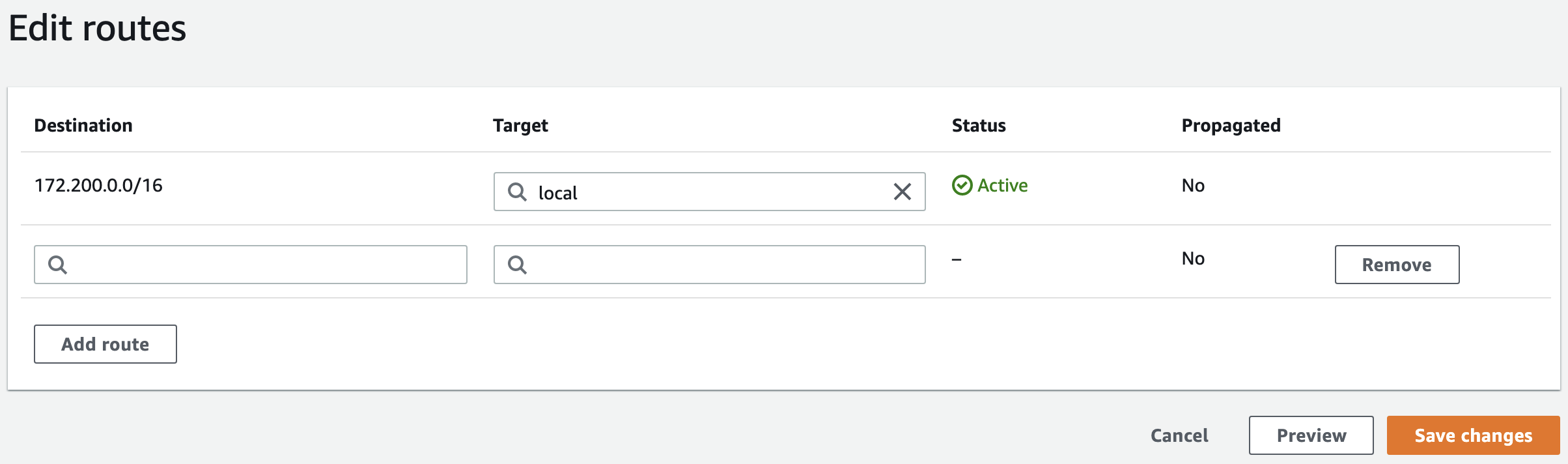
Click Actions and choose Edit routes to display the Edit routes window.
-
Click Add route.
-
Add the YugabyteDB Aeon VPC CIDR address to the Destination column, and the Peering connection ID to the Target column.
-
Click Save changes.
If your application runs in multiple subnets that use separate route tables, repeat these steps for all route tables associated with your application subnets.
Deploy a cluster in the VPC
You can deploy your cluster in a VPC any time after the VPC is created. You must deploy the cluster in the VPC; the VPC can't be changed after cluster creation.
To deploy a cluster in a VPC:
-
On the Clusters page, click Add Cluster.
-
Choose Dedicated.
-
Enter a name for the cluster, choose AWS, and click Next.
-
For a Single-Region Deployment, choose the region where the VPC is deployed, and under Configure VPC, choose Use VPC peering, and select your VPC.
For a Multi-Region Deployment, select each region and its corresponding VPC.
For more information on creating clusters, refer to Create a cluster.
Add the application VPC to the cluster IP allow list
To enable the peered application VPC to connect to the cluster, you need to add the peered VPC to the cluster IP allow list.
To add the application VPC to the cluster IP allow list:
-
On the Clusters page, select the cluster you are peering, click Actions, and choose Edit IP Allow List to display the Add IP Allow List sheet.
-
Click Add Peered VPC Networks.
-
Click Save when done.
For more information on IP allow lists, refer to IP allow lists.