Configure backup storage
Before you can back up universes, you need to configure a storage location for your backups.
Depending on your environment, you can save your YugabyteDB universe data to a variety of storage solutions.
Amazon S3
You can configure AWS S3 and S3-compatible storage as your backup target.
S3-compatible storage requires S3 path style access
By default, the option to use S3 path style access is not available.
To enable the feature in YugabyteDB Anywhere, set the Enable Path Access Style for Amazon S3 Global Runtime Configuration option (config key yb.ui.feature_flags.enable_path_style_access) to true. Refer to Manage runtime configuration settings. Note that only a Super Admin user can modify Global configuration settings.
Create an AWS backup configuration
To configure S3 storage, do the following:
-
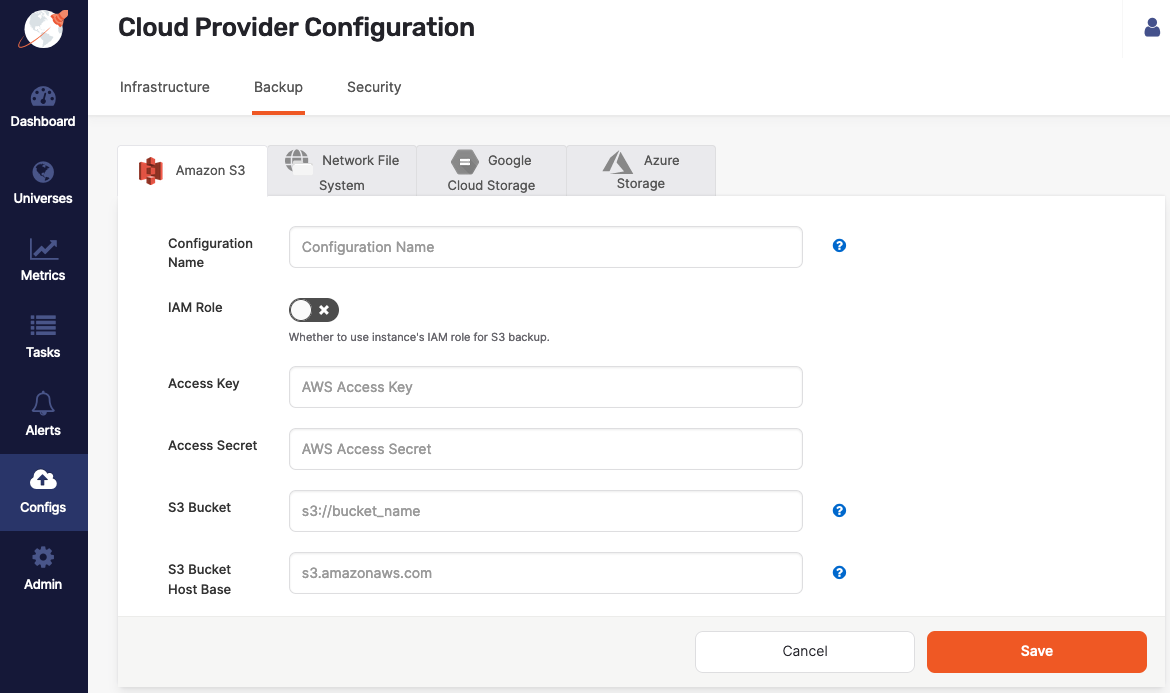
Navigate to Integrations > Backup > Amazon S3.
-
Click Create S3 Backup.
-
Use the Configuration Name field to provide a meaningful name for your storage configuration.
-
Enable IAM Role to use the YugabyteDB Anywhere instance's Identity Access Management (IAM) role or universe node IAM role for the S3 backup. See Required S3 IAM permissions.
To enable universe node IAM roles to access storage in S3, set the Use S3 IAM roles attached to DB node for Backup/Restore Universe Configuration option (config key
yb.backup.s3.use_db_nodes_iam_role_for_backup) to true. Refer to Manage runtime configuration settings. -
If IAM Role is disabled, enter values for the Access Key and Access Secret fields.
For information on AWS access keys, see Manage access keys for IAM users.
-
In the S3 Bucket field, enter the bucket name in the format
s3://bucket_name, orhttps://storage_vendor/s3-bucket-namefor S3-compatible storage. -
In the S3 Bucket Host Base field, enter the HTTP host header (endpoint URL) of the AWS S3 or S3-compatible storage, in the form
s3.amazonaws.comormy.storage.com. -
If you are using S3-compatible storage, set the S3 Path Style Access option to true. (The option is only available if the enablePathStyleAccess feature is enabled.)
-
Click Save.
You can configure access control for the S3 bucket as follows:
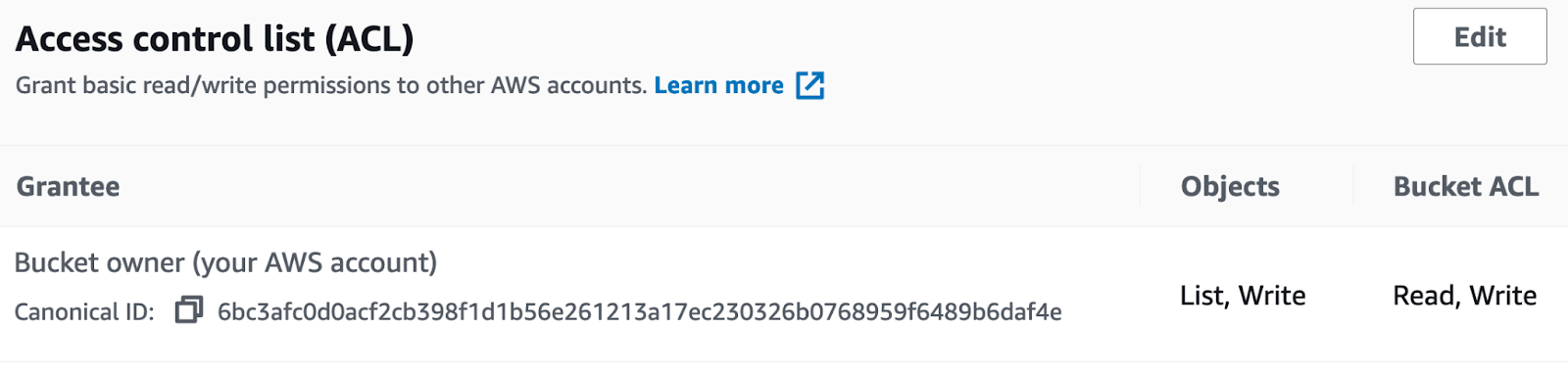
-
Provide the required access control list (ACL), and then define List, Write permissions to access Objects, as well as Read, Write permissions for the bucket, as shown in the following illustration:
-
Create Bucket policy to enable access to the objects stored in the bucket.
Required S3 IAM permissions
The following S3 IAM permissions are required:
"s3:DeleteObject",
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:ListAllMyBuckets",
"s3:GetBucketLocation"
Specify signing region
In some circumstances, you may need to additionally specify the signing region for the AWS backup configuration. For example:
- The S3 bucket uses a non-standard S3 endpoint, such as a private VPC endpoint, or S3-compatible storage; and
- YugabyteDB Anywhere is running in a region that is different than the region where the S3 bucket is located.
In these cases you can encounter errors such as 'Cannot list objects in backup location'.
Typically, the signing region is the AWS region where the S3 bucket is located (for example, us-east-1). Enter the AWS region in the Signing region field.
By default, the Signing region field is not available in the UI. To make it available, set the Enable Signing Region Global Runtime Configuration option (config key yb.ui.feature_flags.enable_signing_region) to true. Refer to Manage runtime configuration settings. You must be a Super Admin to set global runtime configuration flags.
Google Cloud Storage
You can configure Google Cloud Storage (GCS) as your backup target.
Required GCP service account permissions
To grant access to your bucket, create a GCP service account with IAM roles for cloud storage with the following permissions:
roles/storage.admin
The credentials for this account (in JSON format) are used when creating the backup storage configuration. For information on how to obtain GCS credentials, see Cloud Storage authentication.
You can configure access control for the GCS bucket as follows:
- Provide the required access control list (ACL) and set it as either uniform or fine-grained (for object-level access).
- Add permissions, such as roles and members.
Create a GCS backup configuration
To create a GCP backup configuration, do the following:
-
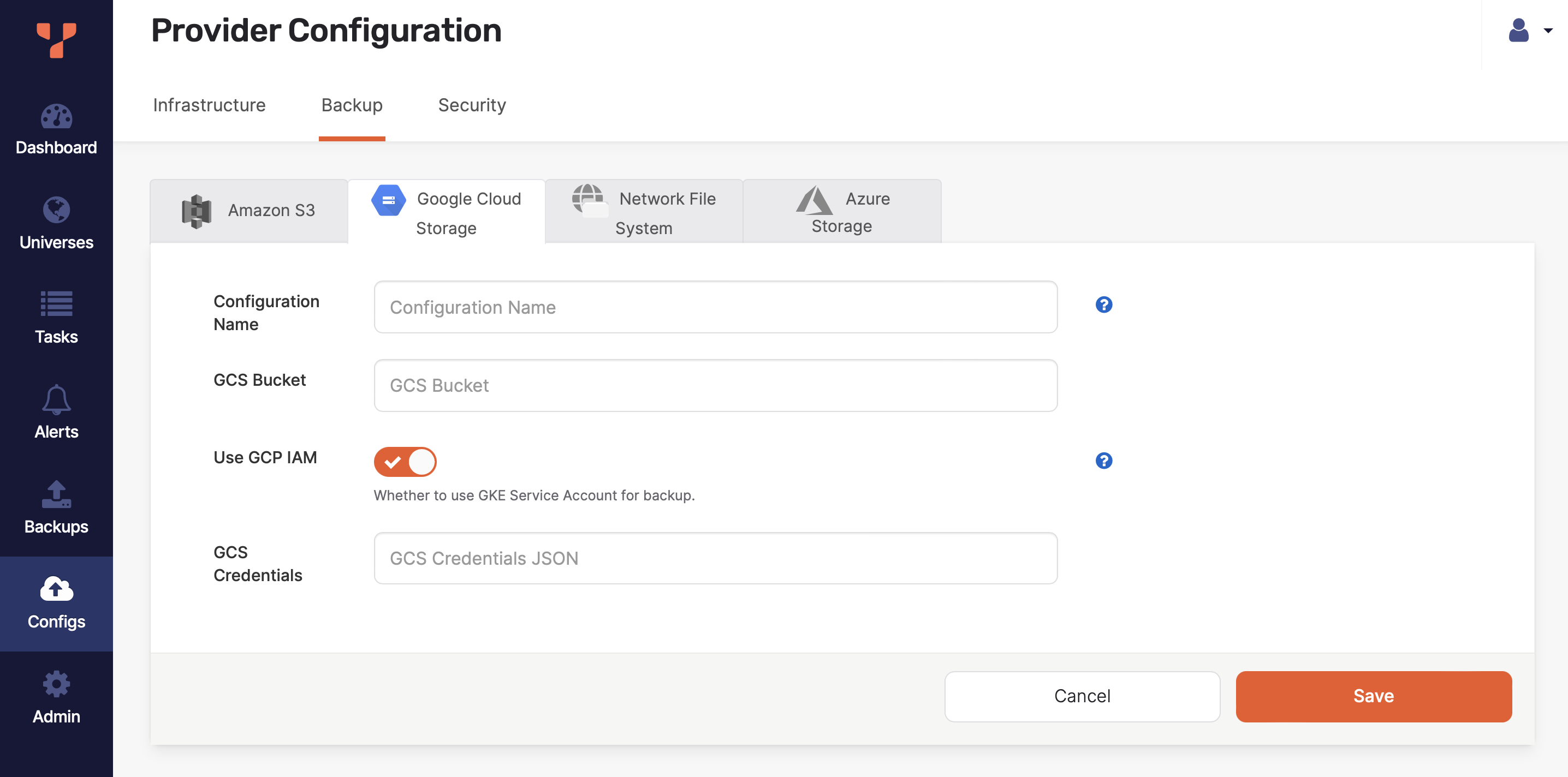
Navigate to Integrations > Backup > Google Cloud Storage.
-
Click Create GCS Backup.
-
Use the Configuration Name field to provide a meaningful name for your storage configuration.
-
Enter the URI of your GCS bucket in the GCS Bucket field. For example,
gs://gcp-bucket/test_backups. -
Select Use GCP IAM to use the YugabyteDB Anywhere instance's Identity Access Management (IAM) role for the GCS backup.
-
If Use GCP IAM is disabled, enter the credentials for your account in JSON format in the GCS Credentials field.
-
Click Save.
Network File System
You can configure Network File System (NFS) as your backup target, as follows:
-
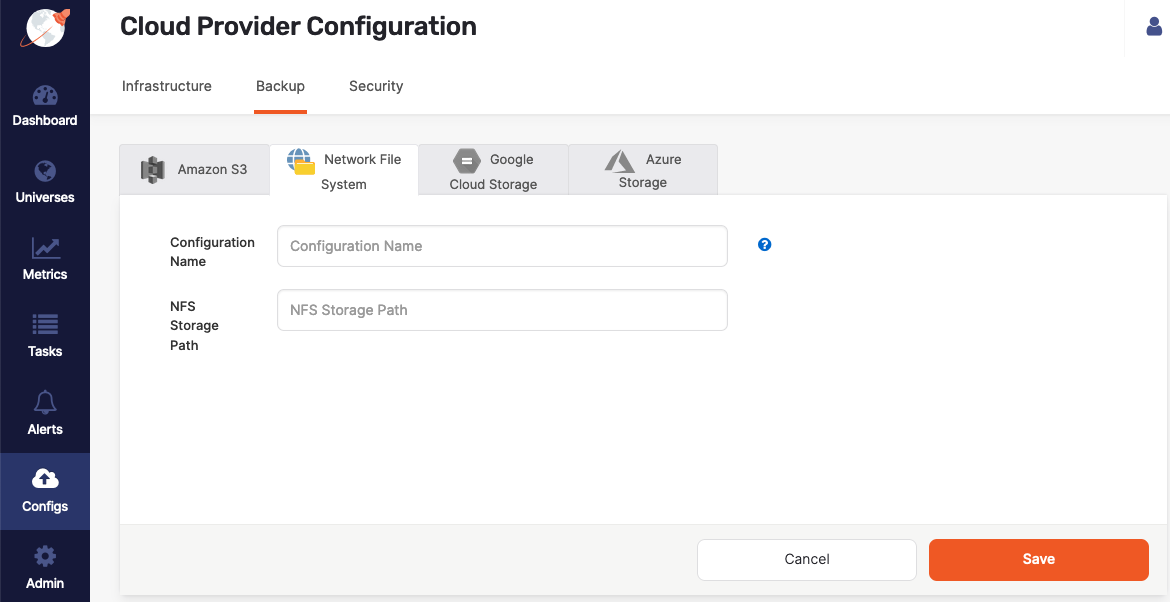
Navigate to Integrations > Backup > Network File System.
-
Click Create NFS Backup to access the configuration form shown in the following illustration:
-
Use the Configuration Name field to provide a meaningful name for your storage configuration.
-
Complete the NFS Storage Path field by entering
/backupor another directory that provides read, write, and access permissions to the SSH user of the YugabyteDB Anywhere instance. -
Click Save.
Prevent back up failure due to NFS unmount on cloud VM restart
To avoid potential backup and restore errors, add the NFS mount to/etc/fstab on the nodes of universes using the backup configuration. When a cloud VM is restarted, the NFS mount may get unmounted if its entry is not in /etc/fstab. This can lead to backup failures, and errors during backup or restore.
Azure Storage
You can configure Azure as your backup target.
Configure storage on Azure
-
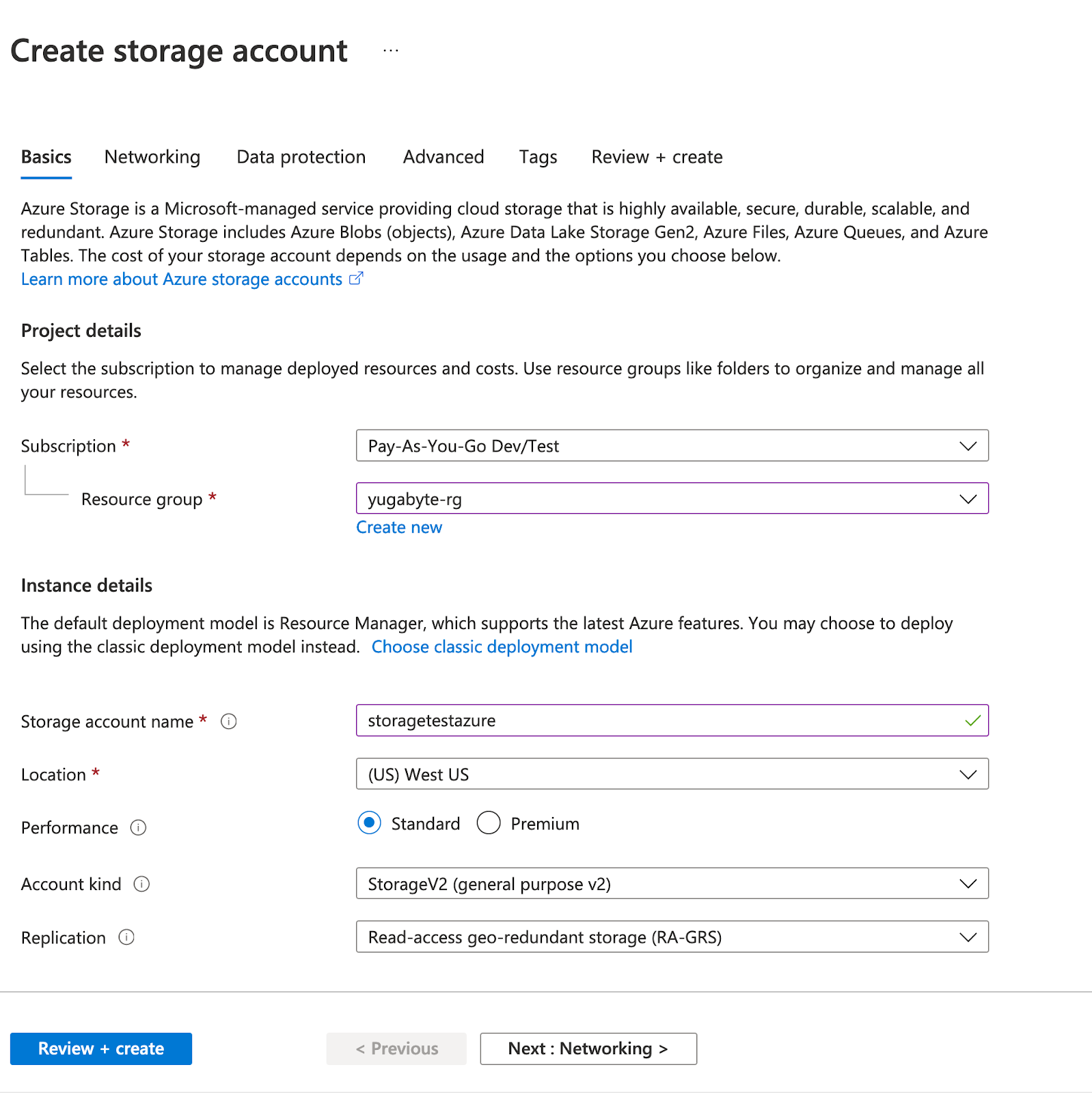
Create a storage account in Azure, as follows:
-
Navigate to Portal > Storage Account and click Add (+).
-
Complete the mandatory fields, such as Resource group, Storage account name, and Location, as per the following illustration:
-
-
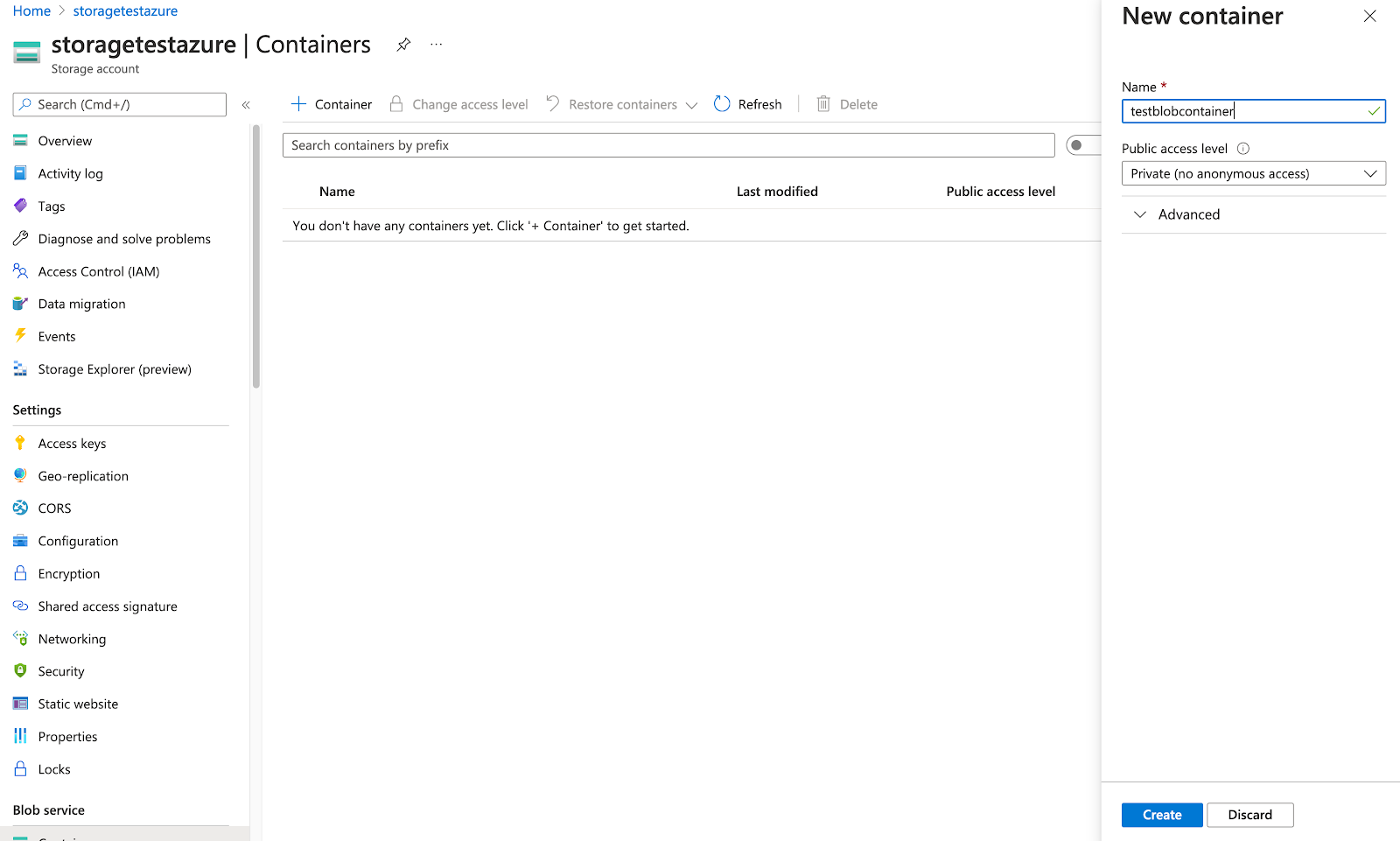
Create a blob container, as follows:
-
Open the storage account (for example, storagetestazure, as shown in the following illustration).
-
Navigate to Blob service > Containers > + Container and then click Create.
-
-
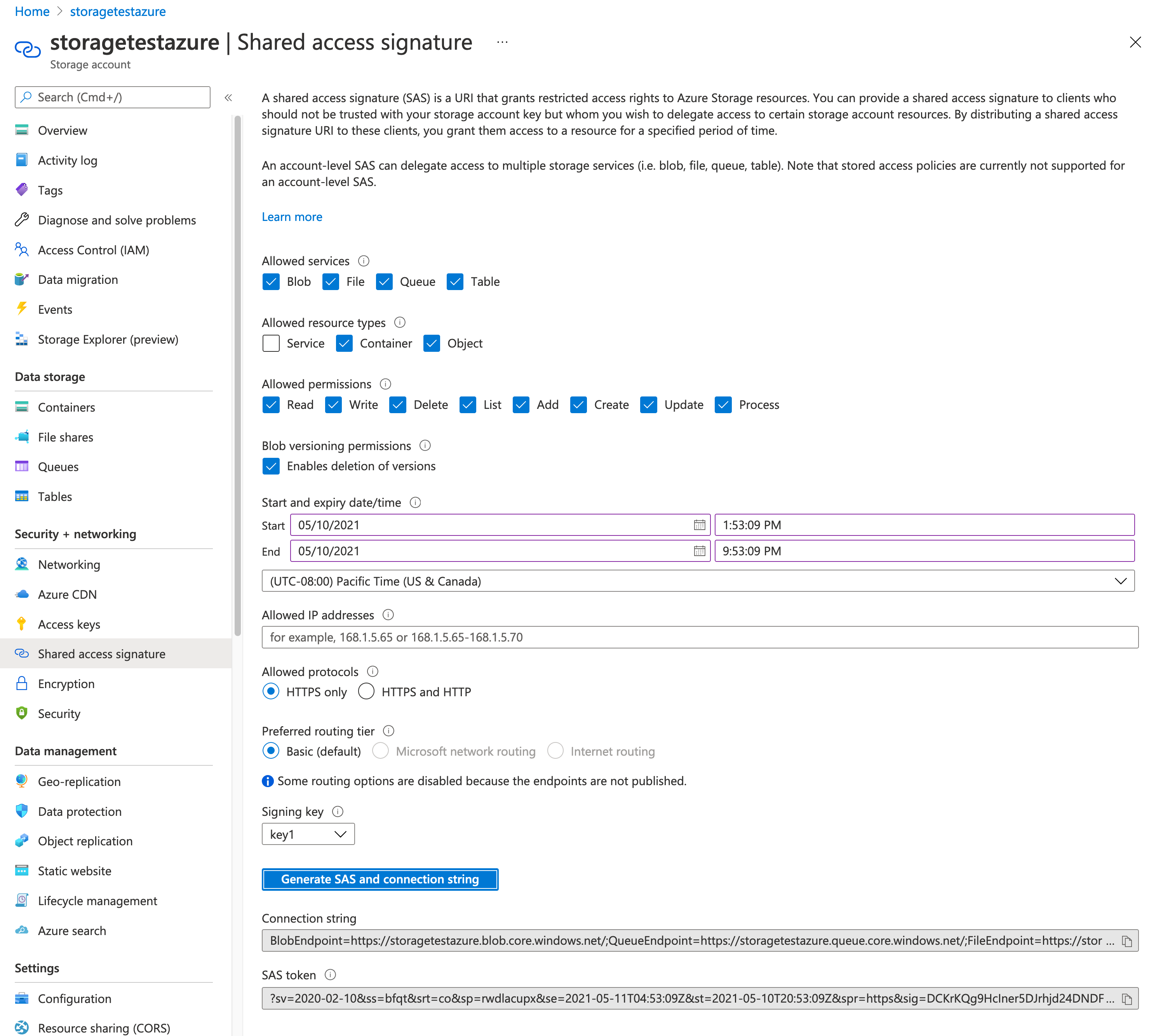
Generate an SAS Token, as follows:
-
Navigate to Storage account > Shared access signature, as shown in the following illustration. (Note that you must generate the SAS Token on the Storage Account, not the Container. Generating the SAS Token on the container will prevent the configuration from being applied.)
-
Under Allowed resource types, select Container and Object.
-
Under Allowed permissions, select all options as shown.
-
Click Generate SAS and connection string and copy the SAS token.
-
Create an Azure storage configuration
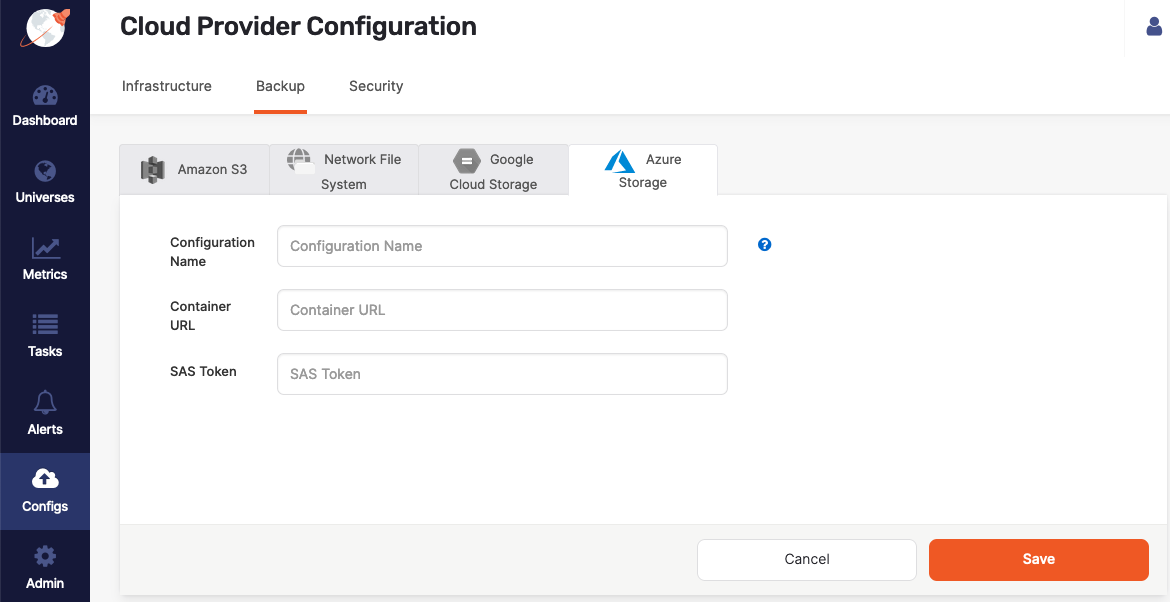
In YugabyteDB Anywhere:
-
Navigate to Integrations > Backup > Azure Storage.
-
Click Create AZ Backup.
-
Use the Configuration Name field to provide a meaningful name for your storage configuration.
-
Enter the Container URL of the container you created. You can obtain the container URL in Azure by navigating to Container > Properties, as shown in the following illustration:
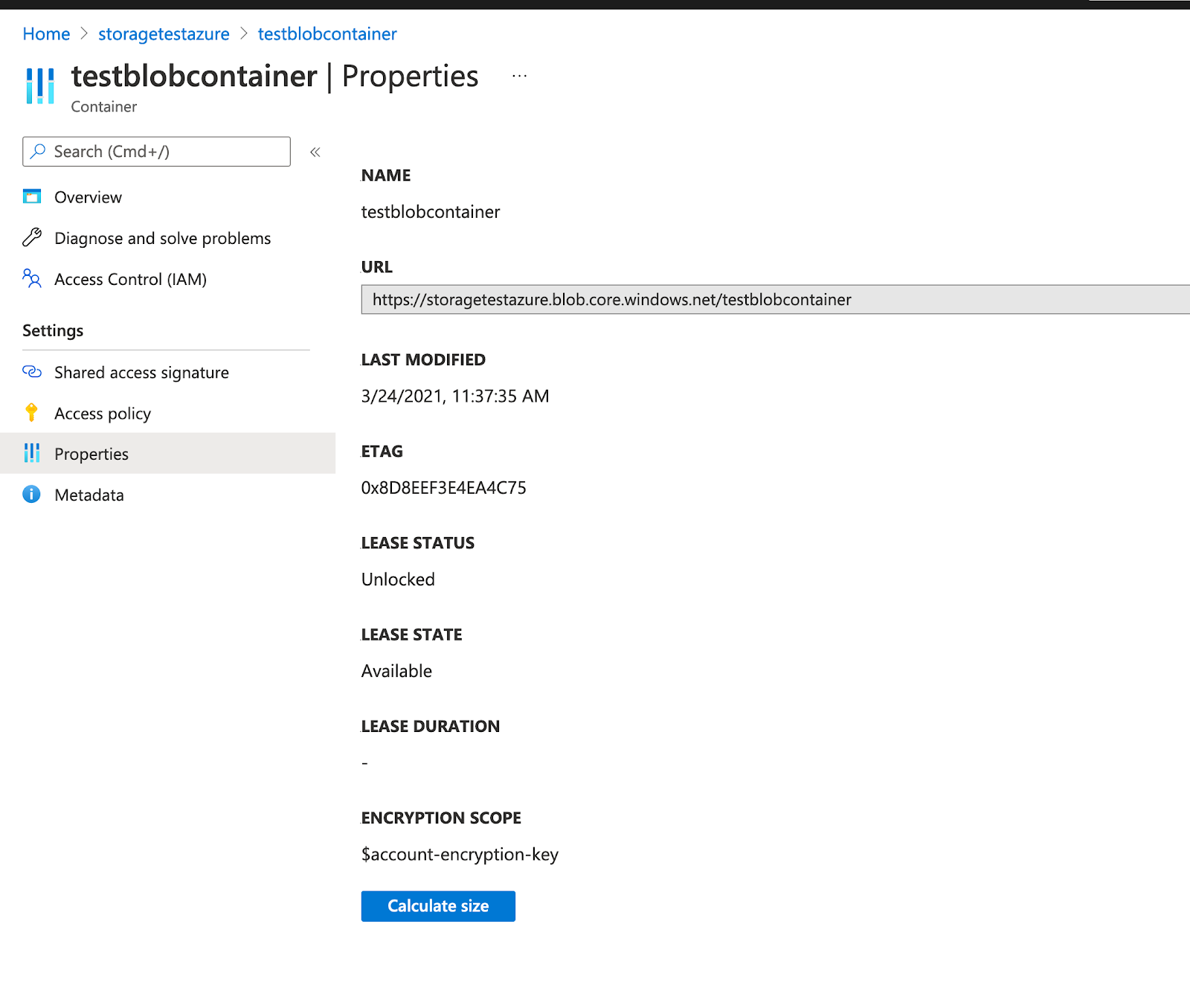
-
Provide the SAS Token you generated. You can copy the SAS Token directly from Shared access signature page in Azure.
-
Click Save.
Azure Managed Identity authentication
EA YugabyteDB Anywhere supports Azure Managed Identity (IAM) authentication for backup storage configurations, providing an alternative to SAS tokens.
Note that this feature is currently supported only for VM-based universes and via API.
When Azure IAM is enabled (via the parameter USE_AZURE_IAM set using the API):
- YugabyteDB Anywhere stores the IAM-based Azure storage configuration and validates it using the identity of the YugabyteDB Anywhere host VM or Service Principal.
- During backup and restore, YB Controller on each database node authenticates to Azure using the node's Managed Identity or Service Principal, and then performs blob operations against the configured container.
- SAS tokens are not required for authentication.
Prerequisites
Before configuring Azure IAM authentication, ensure the following:
-
YugabyteDB Anywhere VM. Ensure the YugabyteDB Anywhere VM has one of the following:
-
Managed Identity enabled:
- In the Azure Portal, navigate to your YugabyteDB Anywhere VM.
- Go to Identity in the left menu.
- Under System assigned, set Status to On and save.
For detailed steps, see Configure managed identities on Azure virtual machines in the Azure documentation.
-
App registration (Service Principal) configured:
-
In Azure Portal, navigate to Azure Active Directory > App registrations.
-
Create a new app registration or use an existing one.
-
Note the Application (client) ID, Directory (tenant) ID, and create a Client secret.
-
Set the following environment variables on the YugabyteDB Anywhere VM:
AZURE_TENANT_ID=<tenant-id> AZURE_CLIENT_ID=<client-id> AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET=<client-secret>
For detailed steps, see Register a Microsoft Entra app and create a service principal in the Azure documentation.
-
-
-
Database nodes. Ensure your database nodes are hosted on Azure VMs with one of the following:
-
Managed Identity enabled.
For each database node VM, follow the same steps as for the YugabyteDB Anywhere VM to enable system-assigned managed identity.
This is the recommended approach as it requires no additional credentials.
-
App registration with Azure credentials configured in the environment.
-
Use the same Service Principal as created for the YugabyteDB Anywhere VM.
-
Set the following environment variables on each database node VM:
AZURE_TENANT_ID=<tenant-id> AZURE_CLIENT_ID=<client-id> AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET=<client-secret>
-
-
-
Azure IAM role and permissions. Assign the Storage Blob Data Contributor role (or a stricter role) on the target storage account/container to the Managed Identity or Service Principal:
- In Azure Portal, navigate to your Storage account.
- Go to Access control (IAM).
- Click Add > Add role assignment.
- Select Storage Blob Data Contributor role.
- Assign access to either:
- Managed Identity: Select the VM(s) or the system-assigned managed identity.
- Service Principal: Select the app registration (Service Principal) you created.
- Click Save.
For detailed steps, see Assign Azure roles using the Azure portal in the Azure documentation.
Configure Azure storage with IAM using the API
Currently, you can only configure Azure storage with IAM using the YugabyteDB Anywhere API.
To create a storage configuration for a single Azure container with IAM:
curl -X POST \
'https://<yba-ip>/api/v1/customers/<customer-uuid>/configs' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-AUTH-YW-API-TOKEN: <api-token>' \
-d '{
"configName": "azure-iam-backup",
"type": "STORAGE",
"name": "AZ",
"data": {
"BACKUP_LOCATION": "https://storageaccount.blob.core.windows.net/container",
"USE_AZURE_IAM": true
}
}'
To create a storage configuration for multiple Azure regions with IAM:
curl -X POST \
'https://<yba-ip>/api/v1/customers/<customer-uuid>/configs' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-AUTH-YW-API-TOKEN: <api-token>' \
-d '{
"configName": "azure-multi-region-iam",
"type": "STORAGE",
"name": "AZ",
"data": {
"BACKUP_LOCATION": "https://account1.blob.core.windows.net/container1",
"USE_AZURE_IAM": true,
"REGION_LOCATIONS": [
{
"REGION": "us-west1",
"LOCATION": "https://account1.blob.core.windows.net/container1"
},
{
"REGION": "us-east1",
"LOCATION": "https://account2.blob.core.windows.net/container2"
}
]
}
}'
Use the following configuration parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
configName |
A meaningful name for your storage configuration. |
type |
Must be "STORAGE". |
name |
Must be "AZ" for Azure. |
data.BACKUP_LOCATION |
The container URL in the format https://storageaccount.blob.core.windows.net/container. |
data.USE_AZURE_IAM |
Set to true to enable IAM authentication. When this is true, do not include SAS token credentials. |
data.REGION_LOCATIONS |
Optional. Array of region-specific locations for multi-region configurations. Each entry contains:
|
Mutually exclusive authentication
You cannot use both SAS token and Azure IAM authentication in the same configuration. WhenUSE_AZURE_IAM is true, do not include SAS token credentials in the request.
Local storage
If your YugabyteDB universe has one node, you can create a local directory on a YB-TServer to which to back up, as follows:
-
Navigate to Universes, select your universe, and then select Nodes.
-
Click Connect.
-
Take note of the services and endpoints information displayed in the Connect dialog, as shown in the following illustration:
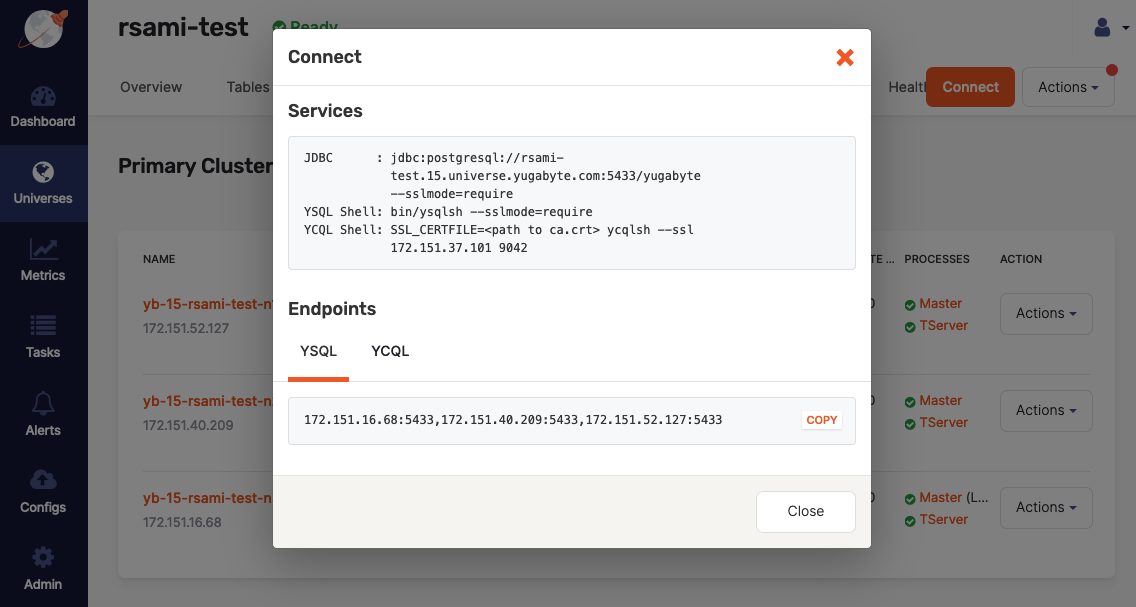
-
While connected using
ssh, create a directory/backupand then change the owner toyugabyte, as follows:sudo mkdir /backup; sudo chown yugabyte /backup
If there is more than one node, you should consider using a network file system mounted on each server.