Create on-premises provider configuration
Before you can deploy universes to private clouds using YugabyteDB Anywhere (YBA), you must create a provider configuration.
With on-premises providers, VMs are not auto-created by YBA; you must manually create your VMs, provision them with YugabyteDB software, and then add them to the provider's free pool of nodes.
Overview
To create, provision, and add nodes to your on-premises provider, you will perform tasks in roughly three stages.
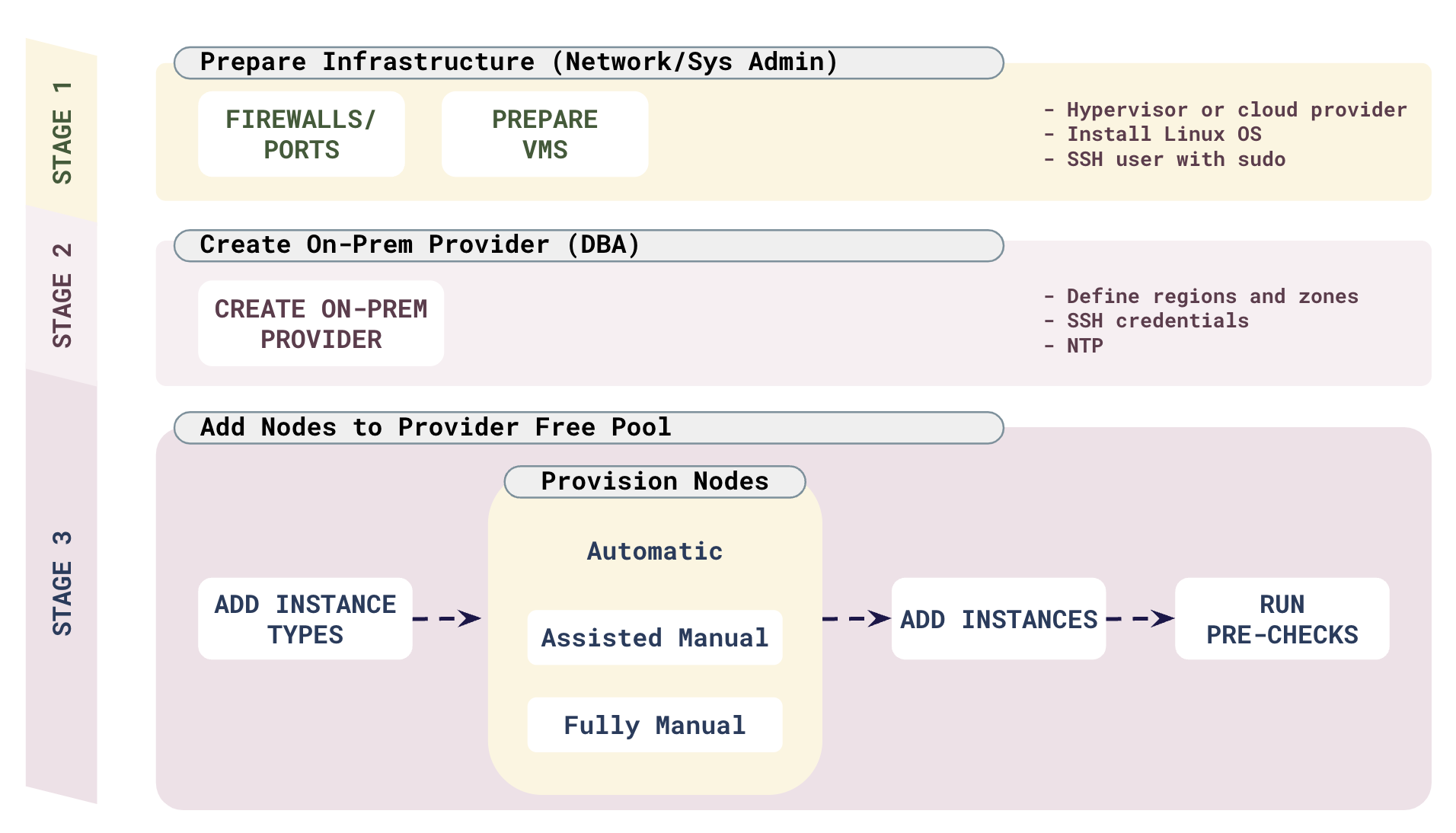
Stage 1: Prepare your infrastructure
-
Have your network administrator set up firewalls to open the ports required for YBA and the nodes to communicate. Refer to Prepare ports.
-
Have your system administrator create VMs that will be used as nodes in universes. This is typically done using your hypervisor or cloud provider. Do the following:
- Locate the VMs in the regions and availability zones where you will be deploying universes.
- Install a YugabyteDB-supported Linux OS on the VMs.
- Set up a
yugabyteuser with root privileges (SSH access and sudo-capable).
For guidelines on creating VMs that are suitable for deploying YugabyteDB, refer to Prepare nodes for on-premises deployment.
Stage 2: Create an on-premises provider configuration
In YBA, create an on-premises provider. This involves the following:
- Defining the regions and availability zones where the provider will be deploying universes.
- Providing SSH credentials for the
yugabyteuser. - Providing NTP setup.
- If the SSH user does not have passwordless sudo access, enabling Manual provisioning for the provider.
Refer to Create the provider configuration.
Stage 3: Add nodes to the provider free pool
In YBA, navigate to the provider you created in Stage 2 and do the following:
-
Define instance types. An instance type defines some basic properties of the VMs you will be adding.
-
Provision the VMs. YBA supports 3 ways of provisioning nodes for running YugabyteDB depending upon the level of SSH access provided to YBA:
Provisioning Description What happens Automatic YBA is provided an SSH user with sudo access for the nodes it needs to provision. For example, the ec2-userfor AWS EC2 instances.No action. YBA will automatically provision the VMs that you add. Assisted manual The SSH user requires a password for sudo access. Run a script, provided by YBA, to provision each VM, providing credentials for the SSH user with sudo access. Fully manual Neither YBA nor the user has access to an SSH user with sudo access; only a local (non-SSH) user is available with sudo access. Follow a sequence of steps to provision each VM manually before adding the VM to the pool. -
Add the VMs (instances). How you do this depends on whether you are using automatic or manual provisioning.
-
Run pre-checks to validate the nodes you added.
Refer to Add nodes to the on-premises provider.