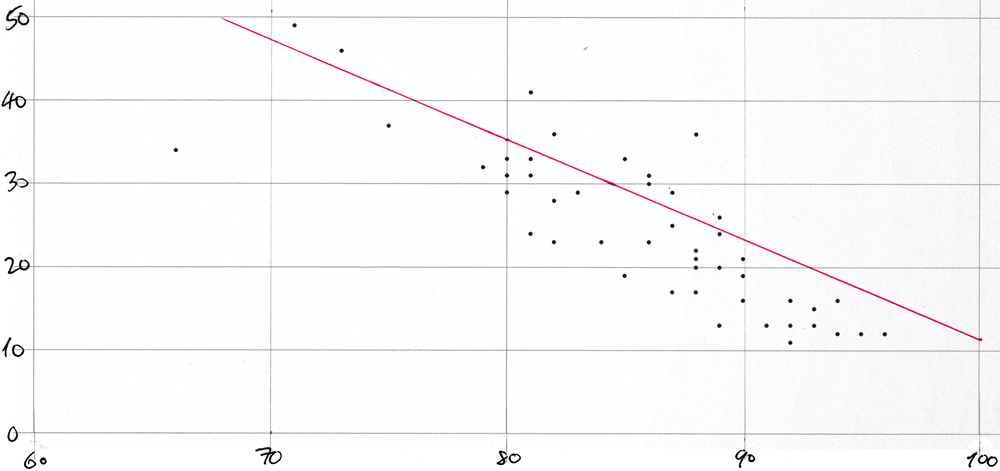
Average COVID-like symptoms vs average mask-wearing by state scatter plot for 21-Oct-2020
Scatter-plot for 21-Oct-2020
The dots on this plot represent "mask_wearing_pct" on the x-axis with "symptoms_pct" on the y-axis from this query:
select
round(mask_wearing_pct) as "% wearing mask",
round(symptoms_pct) as "% with symptoms",
state
from covidcast_fb_survey_results_v
where survey_date = to_date('2020-10-21', 'yyyy-mm-dd')
order by 1;
The plot would be too cluttered if each of the 51 points were labeled with its two-letter state abbreviation.
The plot was created simply by pasting a comma-separated list of "mask_wearing_pct"-"symptoms_pct" pairs into a spreadsheet and by using the app's built-in functionality to create a scatter plot from such pairs values. The values were produced with this query:
select
round(mask_wearing_pct)::text||','||round(symptoms_pct)::text
from covidcast_fb_survey_results_v
where survey_date = to_date('2020-10-21', 'yyyy-mm-dd')
order by 1;
Then the plot was printed and the line was drawn in by hand using the slope and y-axis intercept from this query:
with a as (
select
max(survey_date) as survey_date,
regr_slope (symptoms_pct, mask_wearing_pct) as s,
regr_intercept(symptoms_pct, mask_wearing_pct) as i
from covidcast_fb_survey_results_v
where survey_date = to_date('2020-10-21', 'yyyy-mm-dd'))
select
to_char(survey_date, 'mm/dd') as survey_date,
to_char(s, '90.9') as s,
to_char(i, '990.9') as i
from a;
This is the result:
survey_date | s | i
-------------+-------+--------
10/21 | -1.2 | 131.4
And here is the plot:
Scatter-plot for synthetic data
For comparison, the same technique was used to create a scatter-plot and to draw in the best-fit straight line using synthetic data by running the procedure "populate_t()" described in the section Create the test table within the section that introduces the built-in aggregate functions for linear regression analysis.
create table t(
k int primary key,
x double precision,
y double precision,
delta double precision);
create procedure populate_t(
no_of_rows in int,
slope in double precision,
intercept in double precision,
mean in double precision,
stddev in double precision)
language plpgsql
as $body$
...
This code, and the remaining code below, needed to make the scatter-plot for synthetic data is included in synthetic-data.sql.
It uses the function normal_rand(), brought by the tablefunc extension to add pseudorandomly generated normally distributed noise the y-axis values produced by the "y = m*x + c" formula for the straight line.
It was then invoked like this:
call populate_t(
no_of_rows => 100,
mean => 0.0,
stddev => 5.0,
slope => -1.2,
intercept => 131.4);
using the values for slope and intercept from the regression analysis of the COVIDcast data for 21-Oct-2020 and by choosing a value for the "stddev" actual argument arbitrarily.
The comma-separated pairs for the spreadsheet were produced by this query:
select
round(x)::text||','||round(y + delta)::text
from t
where
x > 60 and
x < 95 and
x is not null and
y is not null
order by x;
And the values for the slope and y-axis intercept were produced by this query:
with a as (
select
regr_r2 ((y + delta), x) as r2,
regr_slope ((y + delta), x) as s,
regr_intercept((y + delta), x) as i
from t)
select
to_char(r2, '0.99') as r2,
to_char(s, '90.9') as s,
to_char(i, '990.9') as i
from a;
This is the result:
r2 | s | i
-------+-------+--------
0.98 | -1.2 | 130.8
The emergent values for the slope and intercept are very close to the values (-1.2 and 131.4) that were used for the invocation of "populate_t()".
Here is the resulting plot
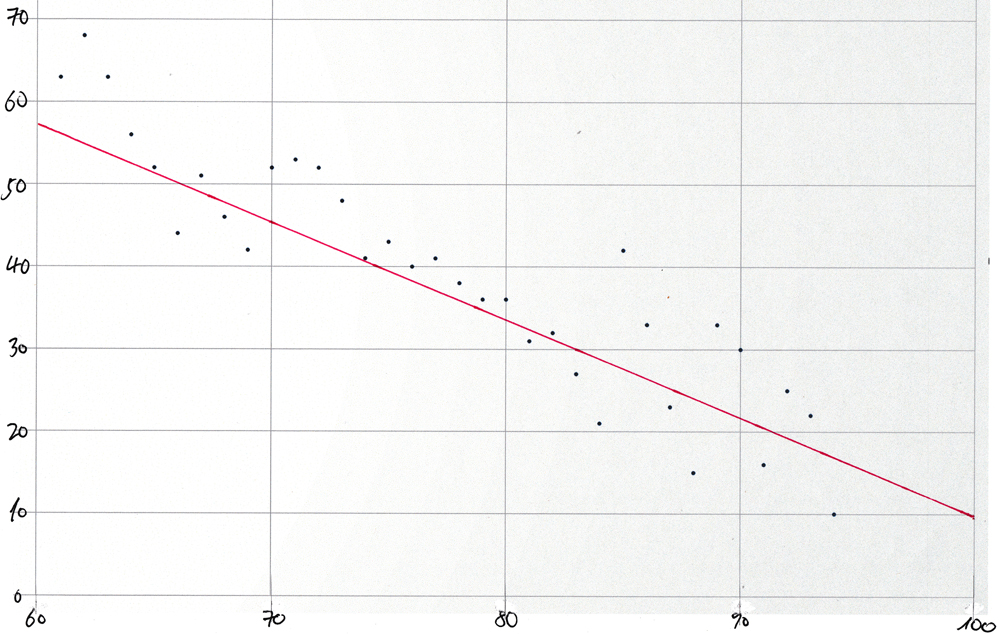 :
:
Note: The normal_rand() function produces a different set of pseudorandomly distributed values each time that synthetic-data.sql is run. But the overall shape of the scatter-plot will remain the same.