Configure authentication for YugabyteDB Anywhere
You can configure YugabyteDB Anywhere to use LDAP to manage access to your YugabyteDB Anywhere instance. YugabyteDB Anywhere integration with LDAP enables you to use your LDAP server for authentication purposes instead of having to create user accounts on YugabyteDB Anywhere.
(For information on using LDAP to manage user access to universes, refer to LDAP authentication for universes.)
LDAP provides means for querying directory services. A directory typically stores credentials and permissions assigned to a user, therefore allowing to maintain a single repository of user information for all applications across the organization. In addition, having a hierarchical structure, LDAP allows creation of user groups requiring the same credentials.
LDAP authentication is similar to a direct password authentication, except that it employs the LDAP protocol to verify the password. This means that only users who already exist in the database and have appropriate permissions can be authenticated via LDAP.
Because YugabyteDB Anywhere and the LDAP server are synchronized during sign in, YugabyteDB Anywhere always uses the up-to-date credentials and roles information (such as role and password changes), as well as removal of users deleted in the LDAP server.
If configured by the LDAP server, YugabyteDB Anywhere can prevent the user from being able to change their password.
Enable LDAP authentication
Use the YugabyteDB Anywhere UI
You can use the YugabyteDB Anywhere UI to enable LDAP authentication for YugabyteDB Anywhere, as follows:
-
Navigate to Admin > Access Management > User Authentication > LDAP Configuration.
-
Select LDAP Enabled and complete the fields in the LDAP Configuration page shown in the following illustration:
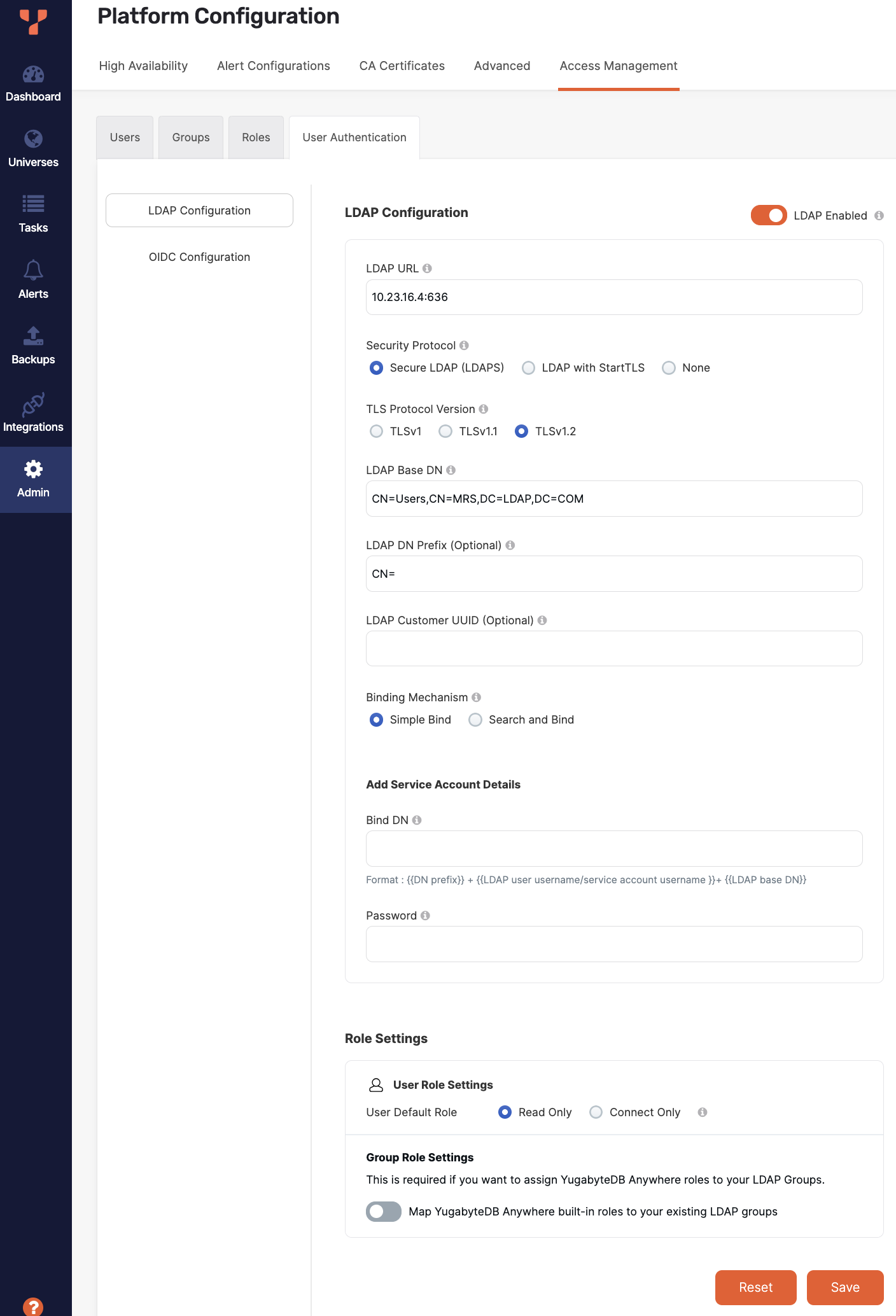
With the exception of the following fields, the descriptions of the preceding settings are provided in Use the YugabyteDB Anywhere API.
-
The LDAP URL field value represents a combination of the
ldap_urlandldap_portvalues separated by a colon, as in0.0.0.0:9000. -
The Binding Mechanism field allows you to select one of the following:
- Simple Bind, in which case you can proceed with the typical configuration.
- Search and Bind, in which case you are presented with a dialog to enter the Search Attribute value used for searching and binding. Note that this requires you to complete the Service Account Details fields.
-
The Bind DN field value represents the distinguished name (DN) used for searching and binding.
-
You can map LDAP groups to YugabyteDB Anywhere roles by enabling group mapping. See Role management.
-
Optionally, enter your LDAP service account credentials. If you are using group mapping, these credentials are required.
-
-
Click Save.
Use the YugabyteDB Anywhere API
To enable LDAP authentication for YugabyteDB Anywhere, you can perform a number of runtime configurations to specify the following:
-
LDAP usage
yb.security.ldap.use_ldap, set totrue, as follows:curl --location --request PUT 'https://10.9.140.199/api/v1/customers/f3a63f07-e3d6-4475-96e4-57a6453072e1/runtime_config/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/key/yb.security.ldap.use_ldap' \ --header 'X-AUTH-YW-API-TOKEN: 5182724b-1891-4cde-bcd1-b8f7a3b7331e' \ --header 'Content-Type: text/plain' \ --header 'Cookie: csrfCookie=d5cdb2b36b00fcad1f4fdb24605aee412f8dfaa0-1641544510767-641be933bf684abcade3c592' \ --data-raw 'true' -
Your LDAP server endpoint
yb.security.ldap.ldap_url, set using the 0.0.0.0 format, as follows:curl --location --request PUT 'https://10.9.140.199/api/v1/customers/f3a63f07-e3d6-4475-96e4-57a6453072e1/runtime_config/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/key/yb.security.ldap.ldap_url' \ --header 'X-AUTH-YW-API-TOKEN: 5182724b-1891-4cde-bcd1-b8f7a3b7331e' \ --header 'Content-Type: text/plain' \ --data-raw '10.9.140.199' -
The LDAP port
yb.security.ldap.ldap_port, set using the 000 format, as follows:curl --location --request PUT 'https://10.9.140.199/api/v1/customers/f3a63f07-e3d6-4475-96e4-57a6453072e1/runtime_config/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/key/yb.security.ldap.ldap_port' \ --header 'X-AUTH-YW-API-TOKEN: 5182724b-1891-4cde-bcd1-b8f7a3b7331e' \ --header 'Content-Type: text/plain' \ --header 'Cookie: csrfCookie=d5cdb2b36b00fcad1f4fdb24605aee412f8dfaa0-1641544510767-641be933bf684abcade3c592' \ --data-raw '389' -
The base DN
yb.security.ldap.ldap_basednto enable restriction of users and user groups, as follows:curl --location --request PUT 'https://10.9.140.199/api/v1/customers/f3a63f07-e3d6-4475-96e4-57a6453072e1/runtime_config/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/key/yb.security.ldap.ldap_basedn' \ --header 'X-AUTH-YW-API-TOKEN: 5182724b-1891-4cde-bcd1-b8f7a3b7331e' \ --header 'Content-Type: text/plain' \ --header 'Cookie: csrfCookie=d5cdb2b36b00fcad1f4fdb24605aee412f8dfaa0-1641544510767-641be933bf684abcade3c592' \ --data-raw '[LDAP DN]'Replace
[LDAP DN]with the actual value, as per the following example:DC=yugabyte,DC=com -
Prefix to the common name (CN) of the user
yb.security.ldap.ldap_dn_prefix, as follows:curl --location --request PUT 'https://10.9.140.199/api/v1/customers/f3a63f07-e3d6-4475-96e4-57a6453072e1/runtime_config/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/key/yb.security.ldap.ldap_dn_prefix' \ --header 'X-AUTH-YW-API-TOKEN: 5182724b-1891-4cde-bcd1-b8f7a3b7331e' \ --header 'Content-Type: text/plain' \ --header 'Cookie: csrfCookie=d5cdb2b36b00fcad1f4fdb24605aee412f8dfaa0-1641544510767-641be933bf684abcade3c592' \ --data-raw '[LDAP DN PREFIX]'Replace
[LDAP DN PREFIX]with the actual value, as per the following example:CN=Note that YugabyteDB Anywhere combines
ldap_basednandldap_dn_prefixwith the username provided during sign in to query the LDAP server.ldap_basednandldap_dn_prefixshould be set accordingly. -
The universally unique identifier (UUID)
yb.security.ldap.ldap_customeruuid, if you have a multi-tenant setup, as follows:curl --location --request PUT 'https://10.9.140.199/api/v1/customers/f3a63f07-e3d6-4475-96e4-57a6453072e1/runtime_config/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/key/yb.security.ldap.ldap_customeruuid' \ --header 'X-AUTH-YW-API-TOKEN: 5182724b-1891-4cde-bcd1-b8f7a3b7331e' \ --header 'Content-Type: text/plain' \ --header 'Cookie: csrfCookie=d5cdb2b36b00fcad1f4fdb24605aee412f8dfaa0-1641544510767-641be933bf684abcade3c592' \ --data-raw '[UUID]'Replace
[UUID]with the actual value.If the UUID is not specified, then single-tenant is assumed by YugabyteDB Anywhere.
-
SSL usage with LDAP
yb.security.ldap.enable_ldaps, set totrueorfalse(default), as follows:curl --location --request PUT 'https://10.9.140.199/api/v1/customers/f3a63f07-e3d6-4475-96e4-57a6453072e1/runtime_config/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/key/yb.security.ldap.enable_ldaps' \ --header 'X-AUTH-YW-API-TOKEN: 5182724b-1891-4cde-bcd1-b8f7a3b7331e' \ --header 'Content-Type: text/plain' \ --header 'Cookie: csrfCookie=d5cdb2b36b00fcad1f4fdb24605aee412f8dfaa0-1641544510767-641be933bf684abcade3c592' \ --data-raw 'true'If the port is configured for an SSL connection, then you can enable SSL when you configure the LDAP server on YugabyteDB Anywhere.
-
TLS usage with LDAP
yb.security.ldap.enable_ldap_start_tls, set totrueorfalse(default), as follows:curl --location --request PUT 'https://10.9.140.199/api/v1/customers/f3a63f07-e3d6-4475-96e4-57a6453072e1/runtime_config/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/key/yb.security.enable_ldap_start_tls' \ --header 'X-AUTH-YW-API-TOKEN: 5182724b-1891-4cde-bcd1-b8f7a3b7331e' \ --header 'Content-Type: text/plain' \ --header 'Cookie: csrfCookie=d5cdb2b36b00fcad1f4fdb24605aee412f8dfaa0-1641544510767-641be933bf684abcade3c592' \ --data-raw 'true'If the port is configured for a TLS connection, then you can enable StartTLS when you configure the LDAP server on YugabyteDB Anywhere.
By default, if neither
ldap.enable_ldapsorldap.enable_ldap_start_tlsis enabled, the connection will be unsecured.
When configured, YugabyteDB Anywhere users are able to sign in by specifying the common name of the user and the password to bind to the LDAP server.
For more information, see Update a configuration key.
In addition to the preceding parameters, you may choose to specify parameters for the service account credentials. This would be helpful in certain scenarios. For example, the Windows Active Directory (AD) server does not typically provide regular users with query permissions for the LDAP server. Setting service account credentials would enable these users to query the LDAP server (the yugabytePlatformRole attribute would be read and set accordingly). The service account should have enough permissions to query the LDAP server, find users, and read the user attributes.
The following is the runtime configuration to specify:
-
A service account password
yb.security.ldap.ldap_service_account_password, as follows:curl --location --request PUT 'https://10.9.140.199/api/v1/customers/f3a63f07-e3d6-4475-96e4-57a6453072e1/runtime_config/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/key/yb.security.ldap.ldap_service_account_password' \ --header 'X-AUTH-YW-API-TOKEN: 5182724b-1891-4cde-bcd1-b8f7a3b7331e' \ --header 'Content-Type: text/plain' \ --header 'Cookie: csrfCookie=d5cdb2b36b00fcad1f4fdb24605aee412f8dfaa0-1641544510767-641be933bf684abcade3c592' \ --data-raw '[SERVICE ACCOUNT PASSWORD]'Replace
[SERVICE ACCOUNT PASSWORD]with the actual value.
Role management
You can manage LDAP roles in YugabyteDB Anywhere using a combination of the following:
- Define group mappings
- Set the
yugabytePlatformRoleannotation on the LDAP server
Group mapping
You can map LDAP groups to YugabyteDB Anywhere roles. After signing in, the user's role is assigned based on whatever role their LDAP group has been mapped to in YugabyteDB Anywhere. If a user is in multiple mapped LDAP groups, YugabyteDB Anywhere performs a union of all the roles that are chosen as a result of group mapping and assigns the union to the user.
EA
You can map groups to fine-grained YugabyteDB Anywhere roles. To enable the feature in YugabyteDB Anywhere, set the Enable RBAC for Groups Global Runtime Configuration option (config key yb.security.group_mapping_rbac_support) to true. Refer to Manage runtime configuration settings. Note that only a Super Admin user can modify Global configuration settings.
To map LDAP groups to YugabyteDB Anywhere roles, do the following:
-
Navigate to Admin > Access Management > User Authentication and select LDAP Configuration.
-
Under Role Settings, enable the Map YugabyteDB Anywhere built-in roles to your existing LDAP groups option.
-
Choose how to look up LDAP group membership:
- Select User Attribute and set the name of the LDAP user attribute to use to find the groups that users belong to.
- Select Group Search Filter and enter an LDAP search filter to search for membership in group member listings. To specify a YugabyteDB Anywhere user in the filter, use the string
{username}. For all occurrences of this string in the query filter, YugabyteDB Anywhere will replace those with the actual username used to sign in to YugabyteDB Anywhere. Enter a group search base DN to use for the group search. Use the scope option to set the scope of the search; there are three levels - SUBTREE, ONELEVEL, and OBJECT.
-
Click Save when you are done.
Map groups to roles
To map groups to roles, on the Groups tab, do the following:
-
Click Add Group and select LDAP.
-
Enter the Group DN name.
-
Select the YugabyteDB Anywhere role (built-in or custom) that you want to map the group to.
-
To assign a built-in role, on the Built-in Role tab, select a role. You can't assign the SuperAdmin role to a group.
-
To assign a custom role (only available if you have enabled RBAC for groups), on the Custom Role tab, select a role and scope.
-
-
Click Save.
Define the YugabyteDB Anywhere role
In addition to group mapping, you can also define a YugabyteDB Anywhere-specific role for each user on your LDAP server by setting the yugabytePlatformRole annotation on the LDAP server. The value set for this annotation is read when signing in to YugabyteDB Anywhere. Note that if the value is modified on the LDAP server, the change is propagated to YugabyteDB Anywhere and automatically updated when signing in. Password updates are also automatically handled.
If the role is not specified, users are created with ReadOnly privileges by default, which can be modified by the local super admin.
When LDAP is set up on a Windows Active Directory (AD) server, the user is expected to have permissions to query the user's properties from that server. If the permissions have not been granted, YugabyteDB Anywhere defaults its role to ReadOnly, which can later be modified by the local super admin.
Role assignment
When a LDAP user logs in to YugabyteDB Anywhere, the system handles role assignment as follows:
-
If group mapping is enabled:
- If YugabyteDB Anywhere can obtain a valid role from the LDAP server (from either
yugabytePlatformRoleor group mappings), it assigns the role to the user. If both are defined, the union of roles is assigned. You can't subsequently change the role for this user in the Access Management tab. - If YugabyteDB Anywhere is unable to obtain a valid role from the LDAP server, the user is assigned the ReadOnly role. You can subsequently change the role for the user in the Access Management tab.
- If YugabyteDB Anywhere can obtain a valid role from the LDAP server (from either
-
If group mapping is disabled:
-
If YugabyteDB Anywhere can obtain a valid role from
yugabytePlatformRole, it assigns the role to the user. You can't subsequently change the role for this user in the Access Management tab. -
If YugabyteDB Anywhere is unable to obtain a valid role from
yugabytePlatformRole, it assigns roles depending on whether the user is new or returning.New users are assigned the ReadOnly role.
For a returning a user, YugabyteDB Anywhere assumes that the user's role was previously set by the administrator (regardless of whether the user's role was actually settable by the administrator), and retains that role. For this reason, if you use LDAP and plan to upgrade to a version of YugabyteDB Anywhere that supports group mapping (v2.18.1 or later), you should enable group mapping.
In either case, you can subsequently change the role for the user in the Access Management tab.
-