Restore universe data
To access backups from a specific universe, navigate to the universe and choose Backups.
To access all universe backups, navigate to Backups.
Restoring a backup using YBC
Backups from a stable track universe can only be restored to a higher version stable track YugabyteDB universe, and the same applies for preview track. Optionally, you can set a runtime flagyb.skip_version_checks, to skip all YugabyteDB and YugabyteDB Anywhere version checks during restores. For more information, contact Yugabyte Support.
Prerequisites
-
The target universe must have enough nodes to accommodate the restore.
-
If the source universe is encrypted, the KMS configuration that was used to encrypt the universe. See Back up and restore data from an encrypted at rest universe.
-
If the source backup has tablespaces, to restore the tablespaces the target universe must have a matching topology; that is, the zones and regions in the target must be the same as the zones and regions in the source.
If the topology of the target universe does not match, none of the tablespaces are preserved and all their data is written to the primary region. After the restore, you will have to re-add all the tablespaces. For more information on specifying data placement for tables and indexes, refer to Tablespaces.
Restore an entire or incremental backup
You can restore YugabyteDB universe data from a backup as follows:
-
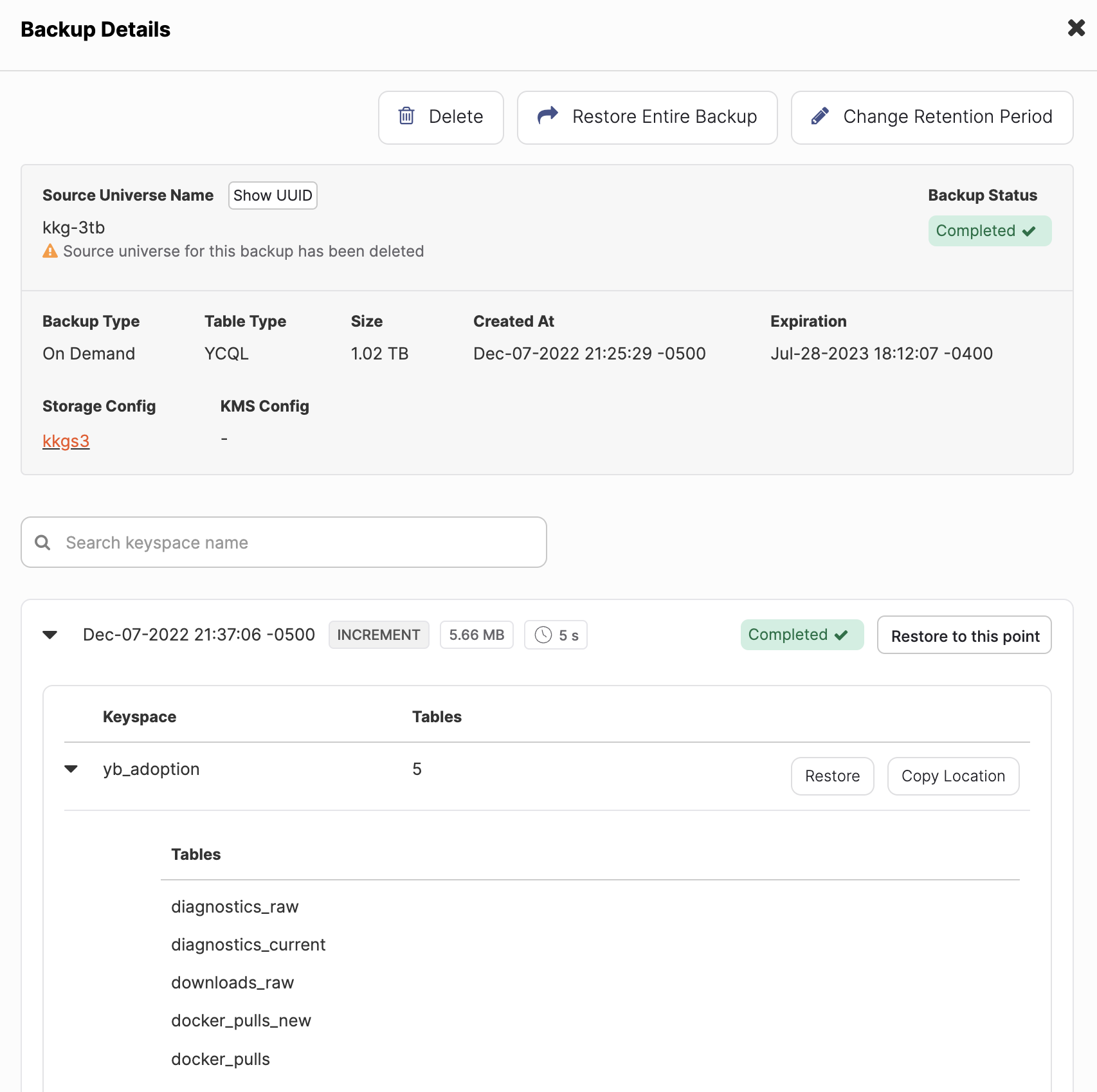
In the Backups list, select the backup to restore to display the Backup Details.
-
Click Restore Entire Backup. Alternatively, if your backup includes incremental backups, you can restore a part of an incremental backup chain by selecting an increment from the list in the Backup Details view and clicking its Restore to this point.
-
In the Restore Backup dialog, select the universe (target) to which you want to restore the backup.
-
If you are restoring data from a universe that has, or previously had, encryption at rest enabled, then you must select the KMS configuration to use so that the master keys referenced in the metadata file can be retrieved.
If the universe was previously encrypted at rest, but is not currently, then the retrieved keys assure that any existing files can be decrypted. The retrieved keys are used to build and augment the universe key registry on the restored universe with the required master keys. The universe data files are restored normally afterwards.
-
To rename databases (YSQL) or keyspaces (YCQL), select the Rename option.
If you are restoring a backup to a universe with an existing databases of the same name, you must rename the database.
-
If you are restoring data from a universe that has tablespaces, select the Restore tablespaces and data to their respective regions option.
To restore tablespaces, the target universe must have a topology that matches the source.
You can restore without tablespaces, in which case none of the tablespaces are preserved and all their data is written to the primary region.
-
If you chose to rename databases or keyspaces, click Next, then enter new names for the databases or keyspaces that you want to rename.
-
Click Restore.
The restore begins immediately. When finished, a completed Restore Backup task appears under Tasks > Task History.
To confirm that the restore succeeded, select the Tables tab to compare the original table with the table to which you restored.
To view the details of a restored database, navigate to Universes > your universe > Backups > Restore History, or Backups > Restore History.
Restore selected databases or keyspaces and tables
You can restore only a specific database (YSQL) or keyspace (YCQL).
In addition, if you are restoring a YCQL keyspace, you can choose the tables in the keyspace you want to restore.
For instructions on restoring a single table in YSQL, refer to Restore a single table in YSQL.
To restore, do the following:
-
In the Backups list, select the backup to restore to display the Backup Details.
-
In the list of databases (YSQL) or keyspaces (YCQL), click Restore for the database or keyspace you want to restore. If your backup includes incremental backups, to display the databases or keyspaces, click the down arrow for the increment at which you want to restore.
-
In the Restore Backup dialog, select the universe (target) to which you want to restore the backup.
Note that the Creation time shown in the dialog indicates the backup job start time, not the time that the particular database was actually snapshotted and backed up. When multiple databases are included in a backup job, each databases is snapshotted and backed up in serial order; thus, each individual database's actual snapshot and backup time is not the same as the backup job start time. To restore a database to a specific point in time, use Point-in-time recovery.
-
If you are restoring data from a universe that has, or previously had, encryption at rest enabled, then you must select the KMS configuration to use so that the master keys referenced in the metadata file can be retrieved.
If the universe was previously encrypted at rest, but is not currently, then the retrieved keys assure that any existing files can be decrypted. The retrieved keys are used to build and augment the universe key registry on the restored universe with the required master keys. The universe data files are restored normally afterwards.
-
To rename databases (YSQL) or keyspaces (YCQL), select the Rename option.
If you are restoring a YSQL backup to a universe with an existing database with the same name, you must rename the database.
-
If you selected a YCQL backup, you can choose to select specific tables to restore, by selecting the Select a subset of tables option.
Note that this option is only available if the following conditions are met:
- The backup was made on a universe running YugabyteDB v2.16.0 or later.
- The selected target universe is running YugabyteDB v2.18.0 or later.
-
If you chose to rename databases/keyspaces or select tables, click Next to rename keyspaces and, if applicable, select tables.
-
Click Restore.
The restore begins immediately. When finished, a completed Restore Backup task appears under Tasks > Task History.
To confirm that the restore succeeded, select the Tables tab to compare the original table with the table to which you restored.
To view the details of a restored database, navigate to Universes > Restore History, or Backups > Restore History.
Restore a PITR-enabled backup
EA
You can restore entire backups with or without PITR. To enable the feature in YugabyteDB Anywhere, set the Option for Off-Cluster PITR based Backup Schedule Global Runtime Configuration option (config key yb.ui.feature_flags.off_cluster_pitr_enabled) to true. Refer to Manage runtime configuration settings. Note that only a Super Admin user can modify Global configuration settings.
If you created backups using a scheduled backup policy with PITR, you can restore YugabyteDB universe data from a backup as follows:
-
In the Backups list, select the backup to restore to display the Backup Details.
-
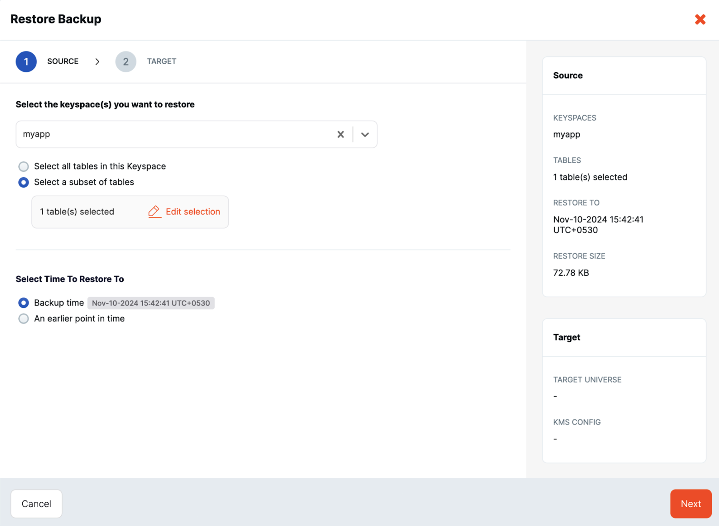
Select Restore Entire Backup to open the Restore Backup dialog.
-
Select the Keyspaces/Databases you want to restore. You can choose to backup either All Databases/Keyspaces, or a single database/keyspace.
-
You can select time to restore to based on the backup time or to an earlier point in time. Select the An earlier point in time option to show the available restore window (start and end times) for the restoration.
For YCQL backups, you can select a subset of tables to restore. If a table is not available in the specified restore window, an error message is displayed.
Note that you cannot restore to a point in time earlier than the most recent DDL change.
-
When finished, click Next.
-
Select the Target Universe where you want to restore the backup. You also have the option to rename the keyspaces/databases.
-
If the backup is encrypted, choose the appropriate KMS configuration.
-
If you are renaming keyspaces/databases, click Next and enter the new names.
-
Click Restore when you are done.
The restore begins immediately. When finished, a completed Restore Backup task appears under Tasks > Task History.
To confirm that the restore succeeded, select the Tables tab to compare the original table with the table to which you restored.
To view the details of a restored database, navigate to Universes > Restore History, or Backups > Restore History.
Advanced restore procedure
In addition to the basic restore, an advanced restore option is available for the following circumstances:
- you have more than one YugabyteDB Anywhere installation and want to restore a database or keyspace from a different YugabyteDB Anywhere installation to the current universe.
- you want to restore a backup that was moved to a different location (for example, for long-term storage) and is no longer being managed by YugabyteDB Anywhere; that is, is no longer listed in the Backups list.
For information regarding components of a backup, refer to Access backups in storage.
Prerequisites
To perform an advanced restore, you need the following:
-
If the backup had encryption at rest enabled, a matching KMS configuration in the target YugabyteDB Anywhere installation so that the backup can be decrypted.
-
A matching storage configuration in the target YugabyteDB Anywhere installation with credentials to access the storage where the backup is located.
If you are restoring from a backup that was moved to another location, copy the backup to a location with a corresponding storage configuration in YugabyteDB Anywhere.
-
The storage address of the database or keyspace backup you want to restore.
If the backup is on a different YugabyteDB Anywhere installation, you can obtain the location address as follows:
-
In the Backups list, click the backup (row) to display the Backup Details.
-
In the list of databases (YSQL) or keyspaces (YCQL), click Copy Location for the database or keyspace you want to restore. If your backup includes incremental backups, to display the databases or keyspaces, click the down arrow for the increment at which you want to restore.
-
Note the Storage Config used by the backup, along with the database or keyspace name.
To determine the address from the backup folder structure, refer to Access backups in storage.
-
Perform an advanced restore
To perform an advanced restore, on the YugabyteDB Anywhere installation where you want to perform the advanced restore, do the following:
-
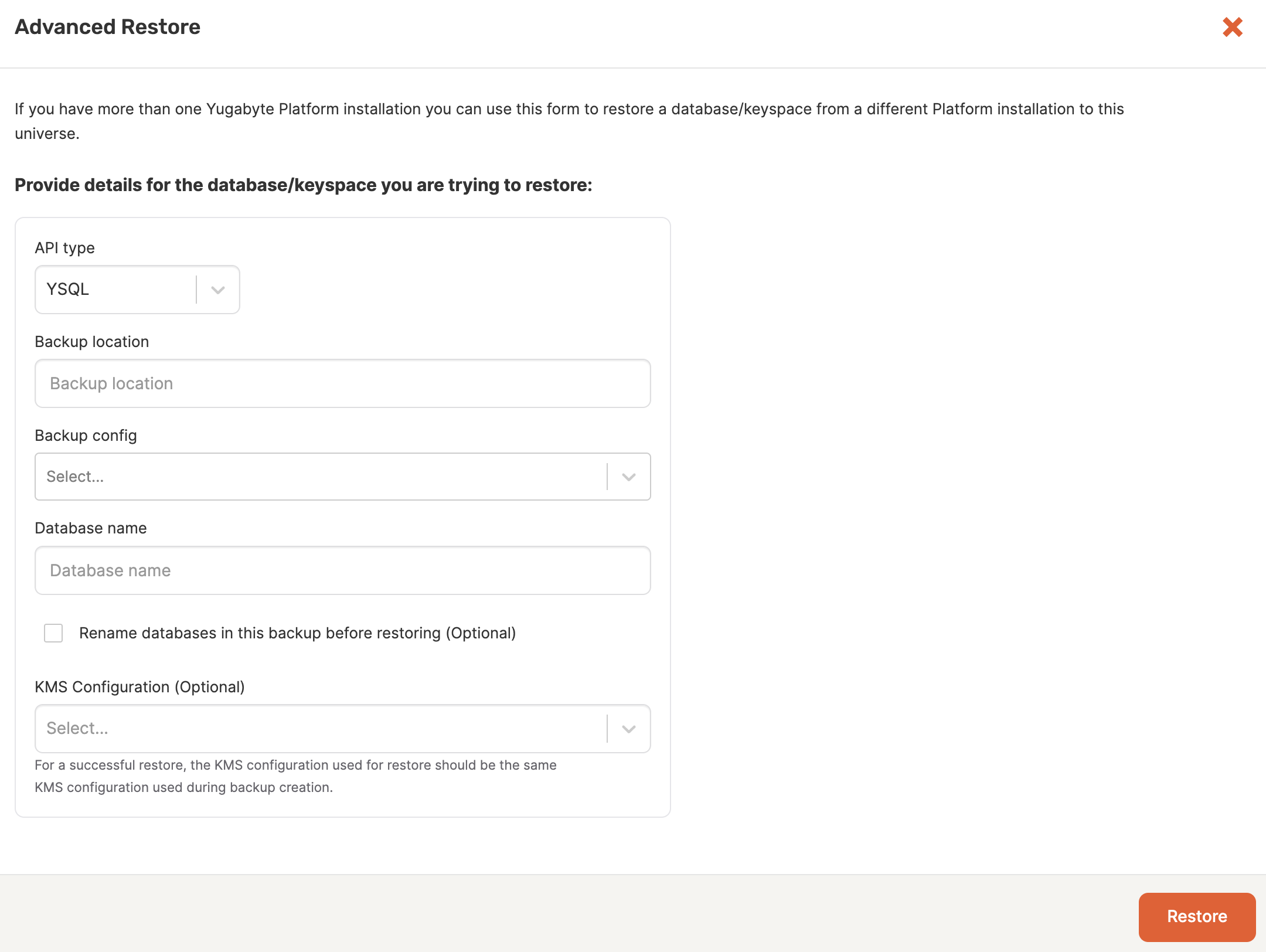
On the Backups tab of the universe to which you want to restore, click Advanced and choose Advanced Restore to display the Advanced Restore dialog.
-
Choose the type of API.
-
In the Backup location field, paste the location of the backup you are restoring. For example:
s3://user_bucket/some/sub/folders/univ-a85b5b01-6e0b-4a24-b088-478dafff94e4/ybc_backup-92317948b8e444ba150616bf182a061/incremental/20204-01-04T12: 11: 03/multi-table-postgres_40522fc46c69404893392b7d92039b9e -
Select the Backup config that corresponds to the storage configuration that was used for the backup. The storage could be on Google Cloud, Amazon S3, Azure, or Network File System.
Note that the storage configuration bucket takes precedence over the bucket specified in the backup location.
For example, if the storage configuration you select is for the following S3 Bucket:
s3://test_bucket/testAnd the address provided in the Backup location has the following:
s3://user_bucket/test/univ-xyz...YugabyteDB Anywhere looks for the backup in
test_bucket/test, notuser_bucket/test. -
Specify the name of the database or keyspace from which you are performing a restore.
-
To rename databases (YSQL) or keyspaces (YCQL) in the backup before restoring, select the rename option.
-
If the backup involved universes that had encryption at rest enabled, then select the KMS configuration to use.
-
If you chose to rename databases/keyspaces, click Next, then enter new names for the databases/keyspaces that you want to rename.
-
Click Restore.