Geo-placement with Tablespaces
YugabyteDB extends the concept of PostgreSQL tablespaces for a distributed database. In PostgreSQL, tablespaces allow administrators to specify where on a disk specific tables and indexes should reside based on how users want to store and access the data. This control over data placement enables fine-grained performance tuning. You can, for example, place heavily accessed smaller tables and indexes in SSDs.
YSQL tablespaces re-purpose this concept for a geo-distributed deployment by allowing you to specify the number of replicas for a table or index, and how they can be distributed across a set of clouds, regions, and zones. Replicating and pinning tables in specific regions can lower read latency, improve resilience, and achieve compliance with data residency laws. For example, you can create duplicate indexes on the same column of a table and place these indexes close to users in different regions for fast access. Similarly, you can partition a master table and associate the partitions with different tablespaces to pin the data geographically.
The ability to control the placement of tables in a fine-grained manner provides the following advantages:
- Tables with critical information can have higher replication factor and increased fault tolerance compared to the rest of the data.
- Based on the access pattern, a table can be constrained to the region or zone where it's accessed most frequently.
- A table can have an index with an entirely different placement policy, thereby boosting the read performance without affecting the placement policy of the table itself.
- Coupled with table partitioning, tablespaces can be used to implement row-level geo-partitioning. This allows pinning the rows of a table in different geo-locations based on the values of certain columns in that row.
Data placement and latency
In a distributed cloud-native database such as YugabyteDB, the location of tables and indexes plays an important role in achieving optimal performance for any workload. The following diagram illustrates the ping latencies amongst nodes in a geo-distributed cluster. Nodes closer to each other communicate with visibly lesser latency than nodes physically far away from each other.
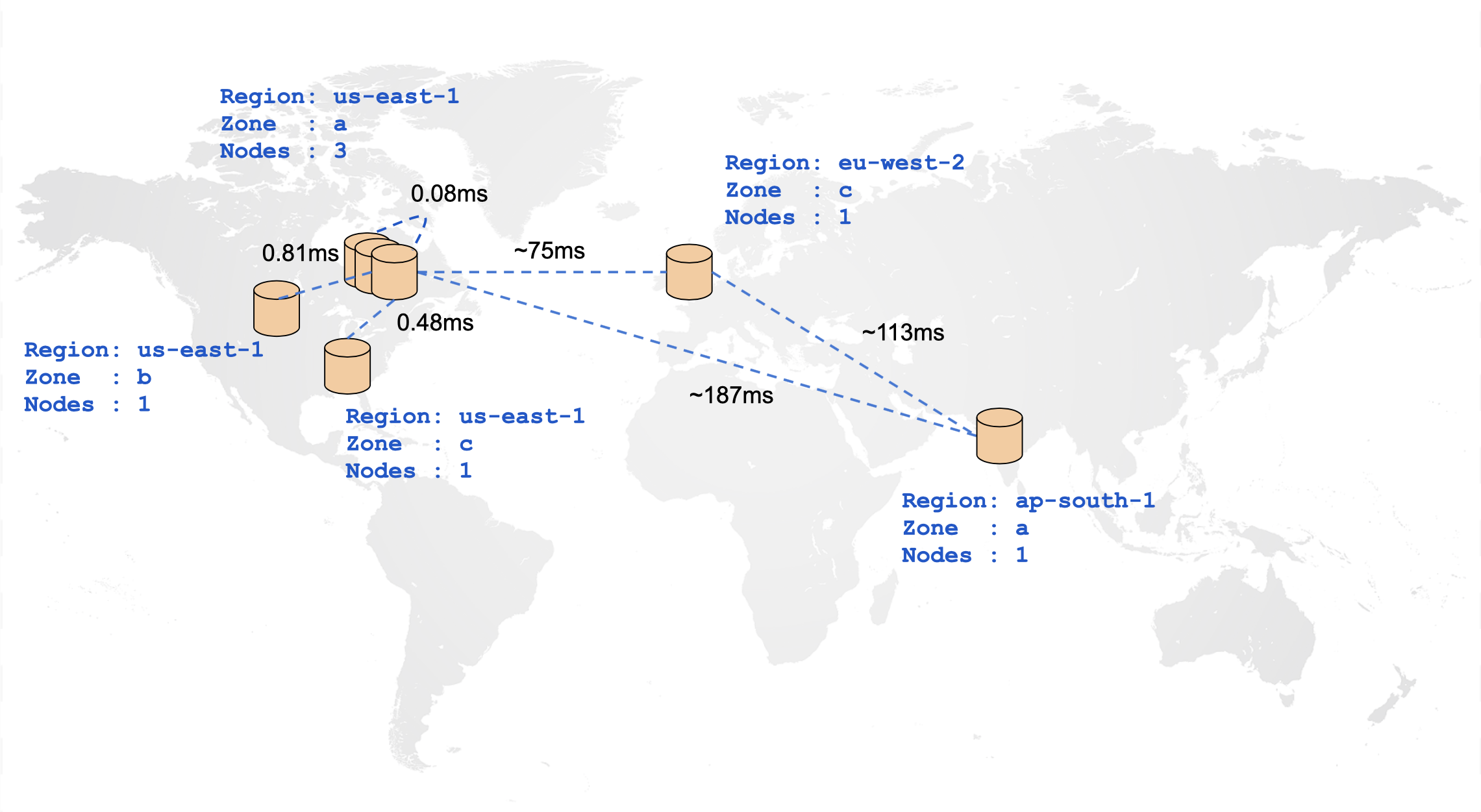
Given the impact of distance on node-to-node communication, it's beneficial to be able to specify at a table level, how its data should be spread across the cluster. This way, you can move tables closer to their clients and decide which tables actually need to be geo-distributed. Using tablespaces you can specify the number of replicas for a set of tables or indexes, and how each of these replicas should be distributed across a set of cloud, regions, and zones.
Cluster setup
The example describes how to create the following:
- A cluster that is spread across multiple regions across the world.
- Tablespaces that specify single-zone, multi-zone, and multi-region placement policies.
- Tables associated with the created tablespaces.
In addition, the example demonstrates the effect of geo-distribution on basic YSQL commands by measuring the effect of various geo-distribution policies on the latencies observed while running INSERT and SELECT statements. The results can be seen in the following table:
| Geo-Distribution | INSERT Latency (ms) | SELECT Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|
| Single Zone | 4.676 | 1.880 |
| Multi Zone | 11.825 | 4.145 |
| Multi Region | 836.616 | 337.154 |
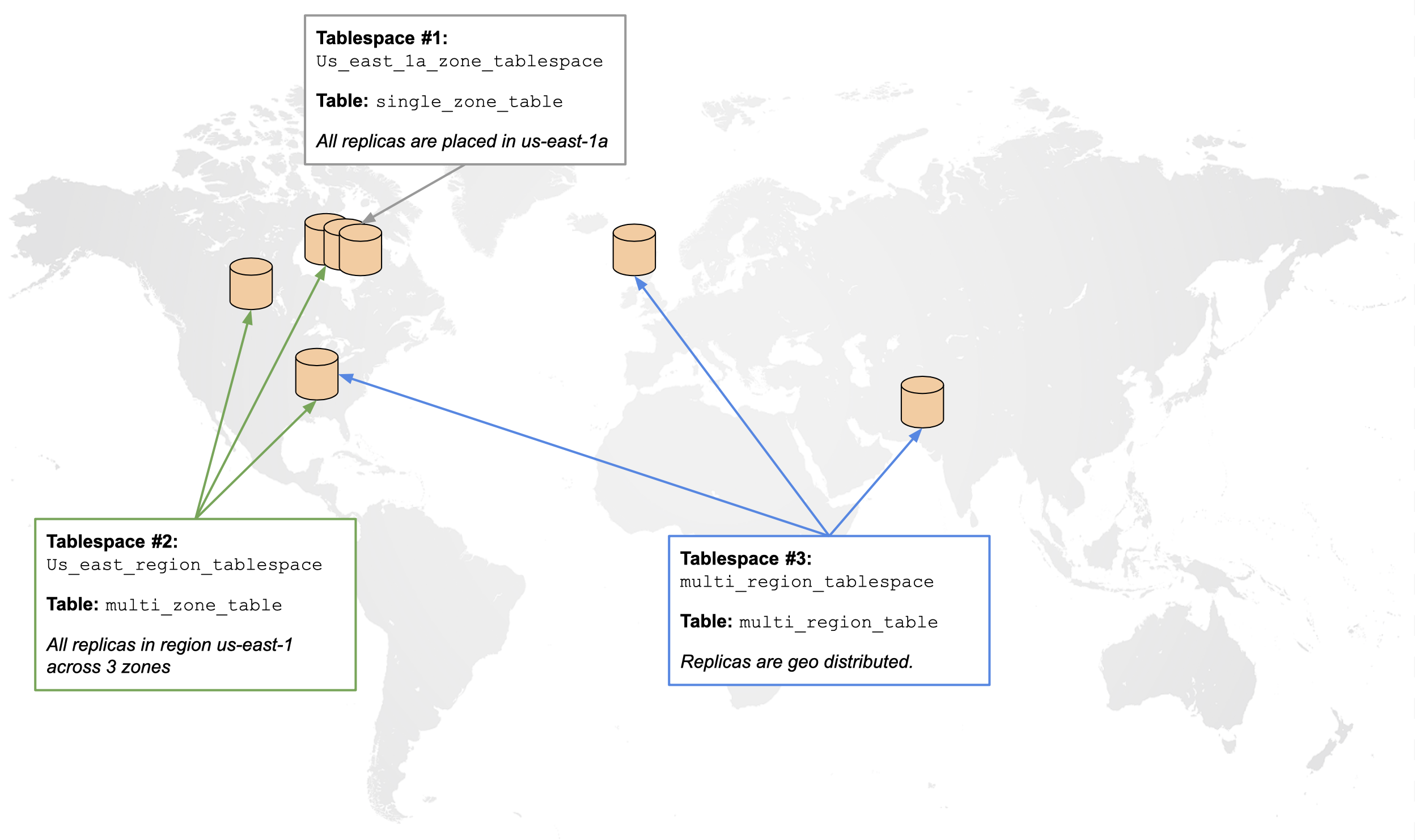
The differences between a single-zone, multi-zone, and multi-region configuration becomes apparent when a cluster with the following topology is deployed. This topology is chosen for illustrative purposes as it can allow creation of node, zone, region fault-tolerant placement policies in the same cluster with minimum nodes.
| Region | Zone | Number of nodes |
|---|---|---|
| us-east-1 (N.Virginia) | us-east-1a | 3 |
| us-east-1 (N.Virginia) | us-east-1b | 1 |
| us-east-1 (N.Virginia) | us-east-1c | 1 |
| ap-south-1 (Mumbai) | ap-south-1a | 1 |
| eu-west-2 (London) | eu-west-2c | 1 |
The topology is shown in the following illustration:
Create the cluster
To create a local cluster with the preceding configuration, use the following yugabyted commands:
./bin/yugabyted start \
--base_dir=/home/yugabyte/<IP1>/yugabyte-data \
--advertise_address=<IP1> \
--cloud_location=aws.us-east-1.us-east-1a \
./bin/yugabyted start \
--base_dir=/home/yugabyte/<IP2>/yugabyte-data \
--advertise_address=<IP2> \
--join=<IP1> \
--cloud_location=aws.us-east-1.us-east-1b \
./bin/yugabyted start \
--base_dir=/home/yugabyte/<IP3>/yugabyte-data \
--advertise_address=<IP3> \
--join=<IP1> \
--cloud_location=aws.us-east-1.us-east-1c \
./bin/yugabyted start \
--base_dir=/home/yugabyte/<IP4>/yugabyte-data \
--advertise_address=<IP4> \
--join=<IP1> \
--cloud_location=aws.ap-south-1.ap-south-1a \
./bin/yugabyted start \
--base_dir=/home/yugabyte/<IP5>/yugabyte-data \
--advertise_address=<IP5> \
--join=<IP1> \
--cloud_location=aws.eu-west-2.eu-west-2c \
./bin/yugabyted start \
--base_dir=/home/yugabyte/<IP6>/yugabyte-data \
--advertise_address=<IP6> \
--join=<IP1> \
--cloud_location=aws.us-east-1.us-east-1a \
./bin/yugabyted start \
--base_dir=/home/yugabyte/<IP7>/yugabyte-data \
--advertise_address=<IP7> \
--join=<IP1> \
--cloud_location=aws.us-east-1.us-east-1a \
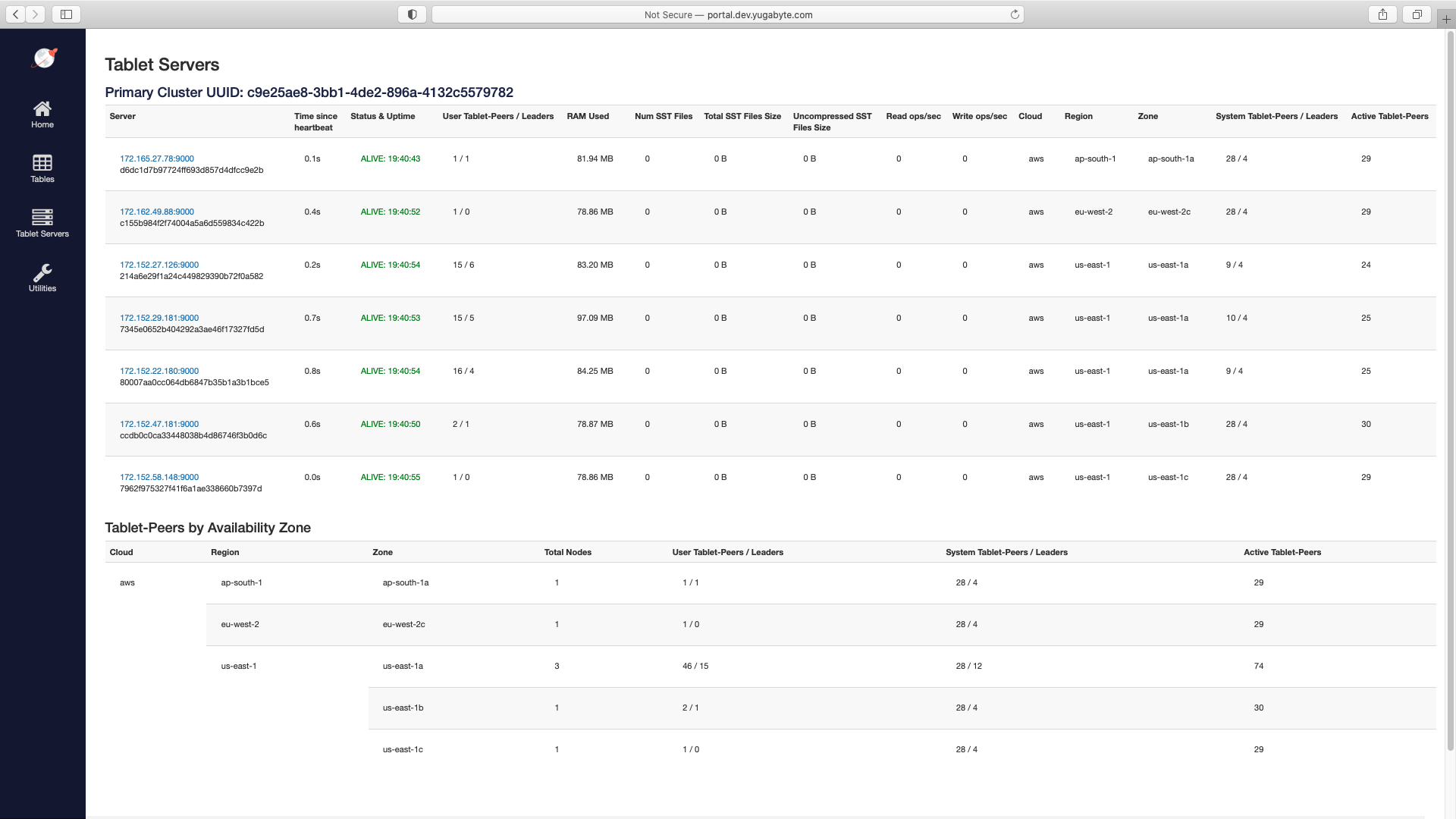
After cluster creation, verify that the nodes have been created with the given configuration by navigating to the Tablet Servers page in the YB-Master UI.
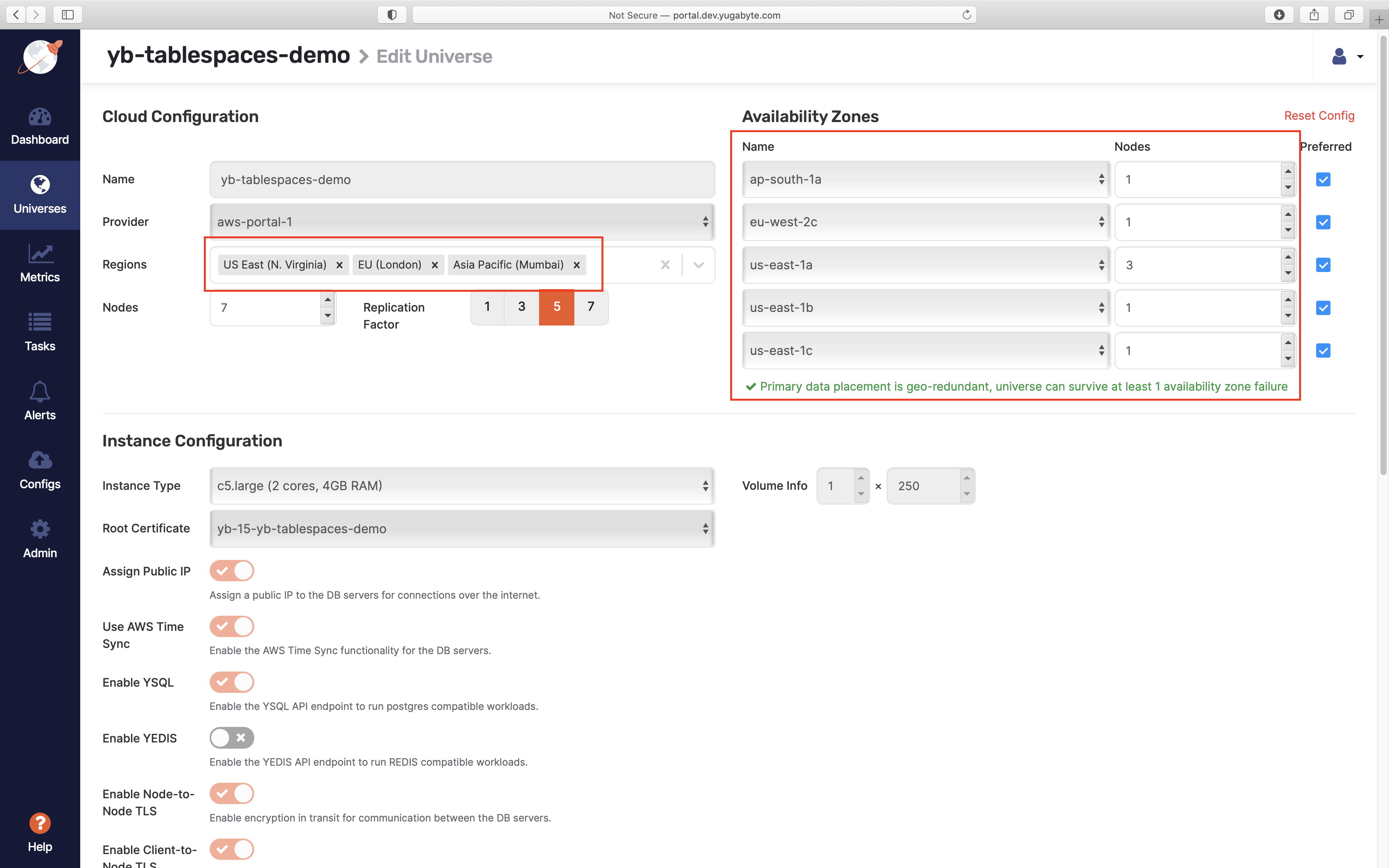
To create a universe with the preceding configuration in YugabyteDB Anywhere, set the following options on the Edit Universe page:
After universe creation, verify that the nodes have been created with the given configuration by navigating to the Nodes tab on the Universes page.
Create a single-zone table
By default, creating any tables in the preceding cluster spreads all of its data across all regions. Using tablespaces, you can constrain table data in a single zone. The placement policy is illustrated using the following diagram:
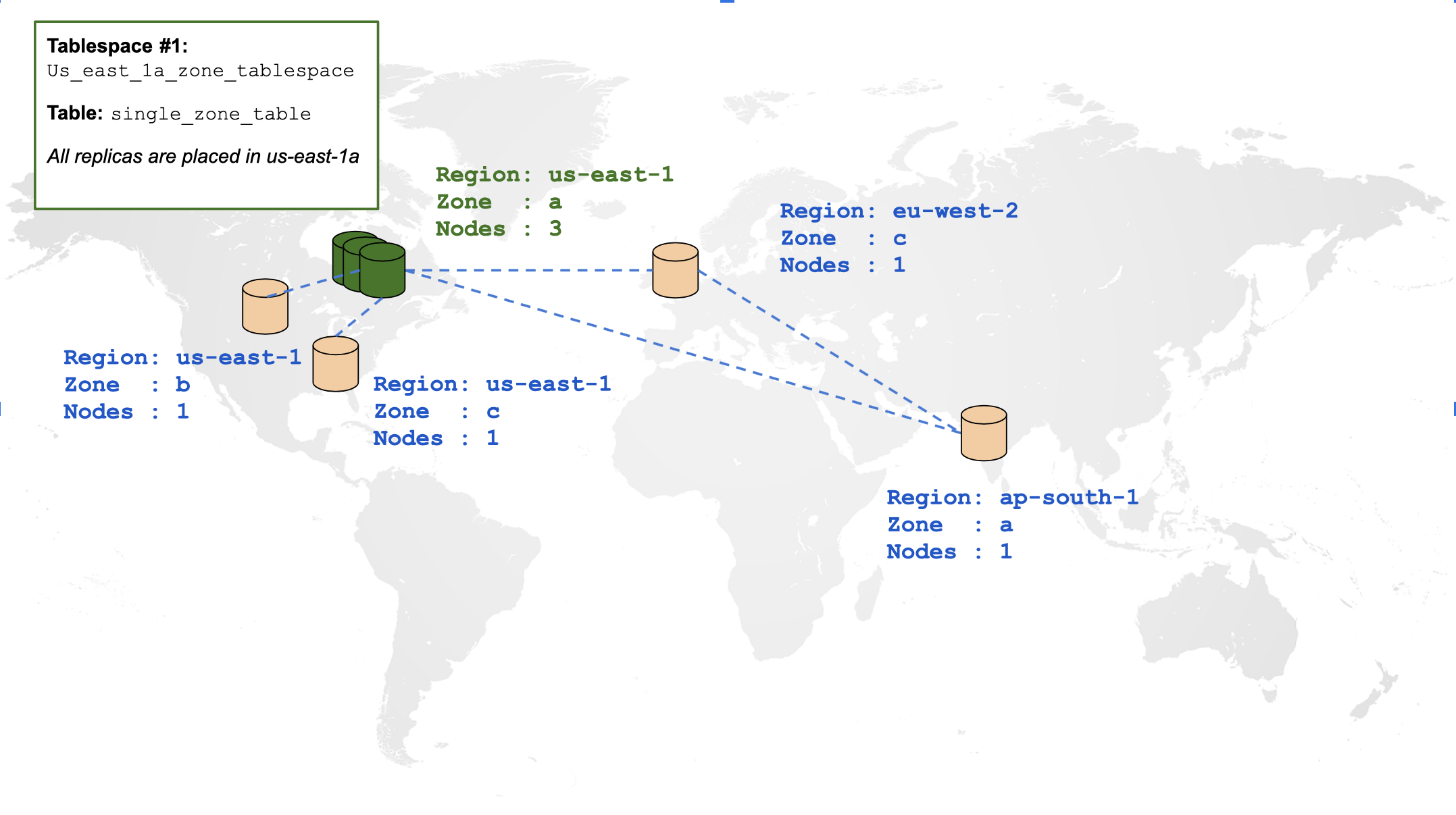
Create a tablespace outlining the preceding placement policy and a table associated with that tablespace:
CREATE TABLESPACE us_east_1a_zone_tablespace
WITH (replica_placement='{"num_replicas": 3, "placement_blocks": [
{"cloud":"aws","region":"us-east-1","zone":"us-east-1a","min_num_replicas":3}]}');
CREATE TABLE single_zone_table (id INTEGER, field text)
TABLESPACE us_east_1a_zone_tablespace SPLIT INTO 1 TABLETS;
To view your tablespaces, you can enter the following command:
SELECT * FROM pg_tablespace;
Note from the preceding cluster configuration that the nodes in us-east-1a were 172.152.29.181, 172.152.27.126, and 172.152.22.180. By navigating to the table view in the YB-Master UI, you can verify that the tablet created for this table was indeed placed in us_east_1a_zone:
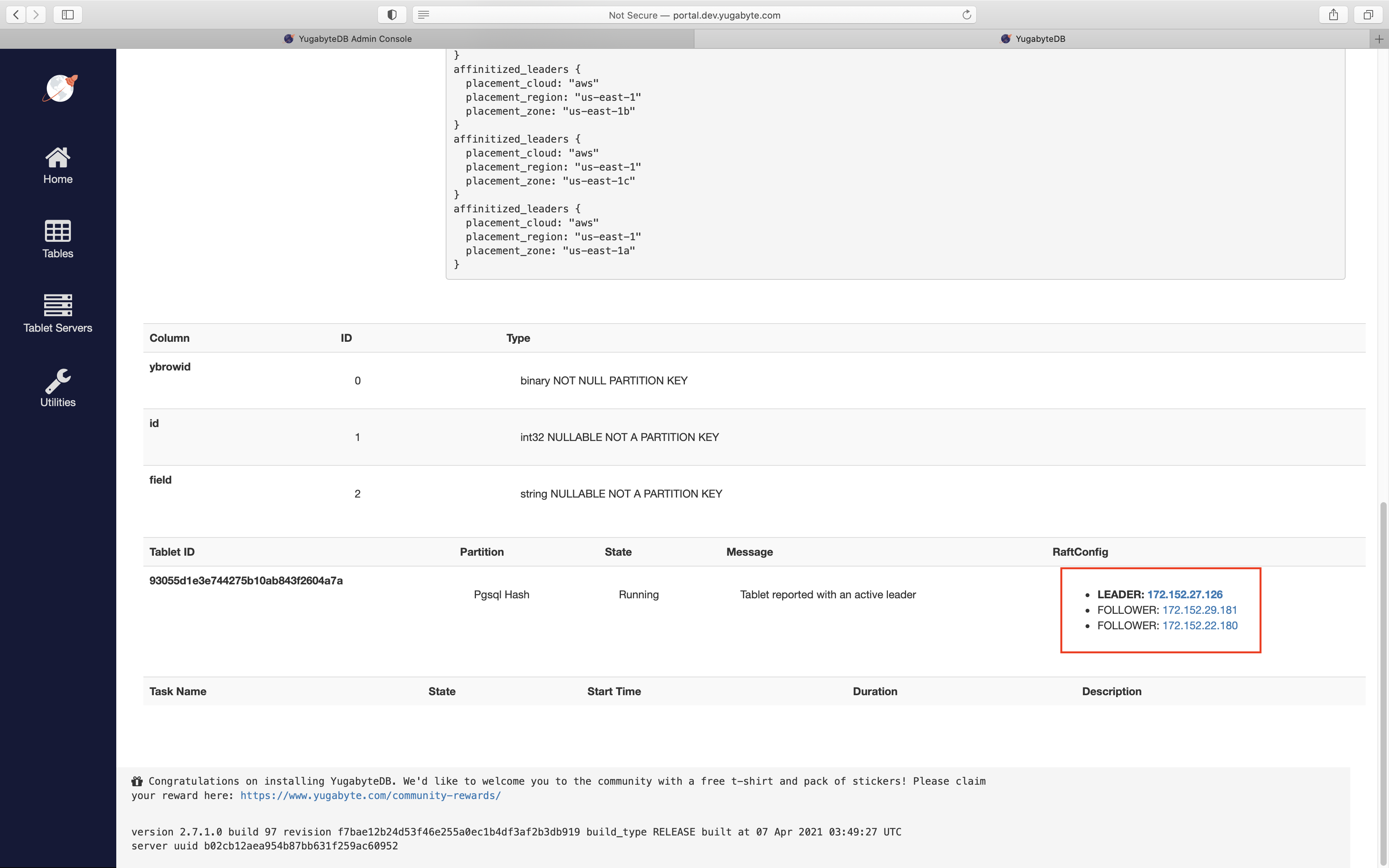
To measure the latencies incurred for INSERTs and SELECTs on this table, where the client is in us-east-1a zone, enter the following command:
yugabyte=# INSERT INTO single_zone_table VALUES (1, 'field1'), (2, 'field2'), (3, 'field3');
Time: 4.676 ms
yugabyte=# SELECT * FROM single_zone_table;
id | field
----+--------
2 | field2
1 | field1
3 | field3
(3 rows)
Time: 1.880 ms
Create a multi-zone table
The following diagram is a graphical representation of a table that is spread across multiple zones in the same region:
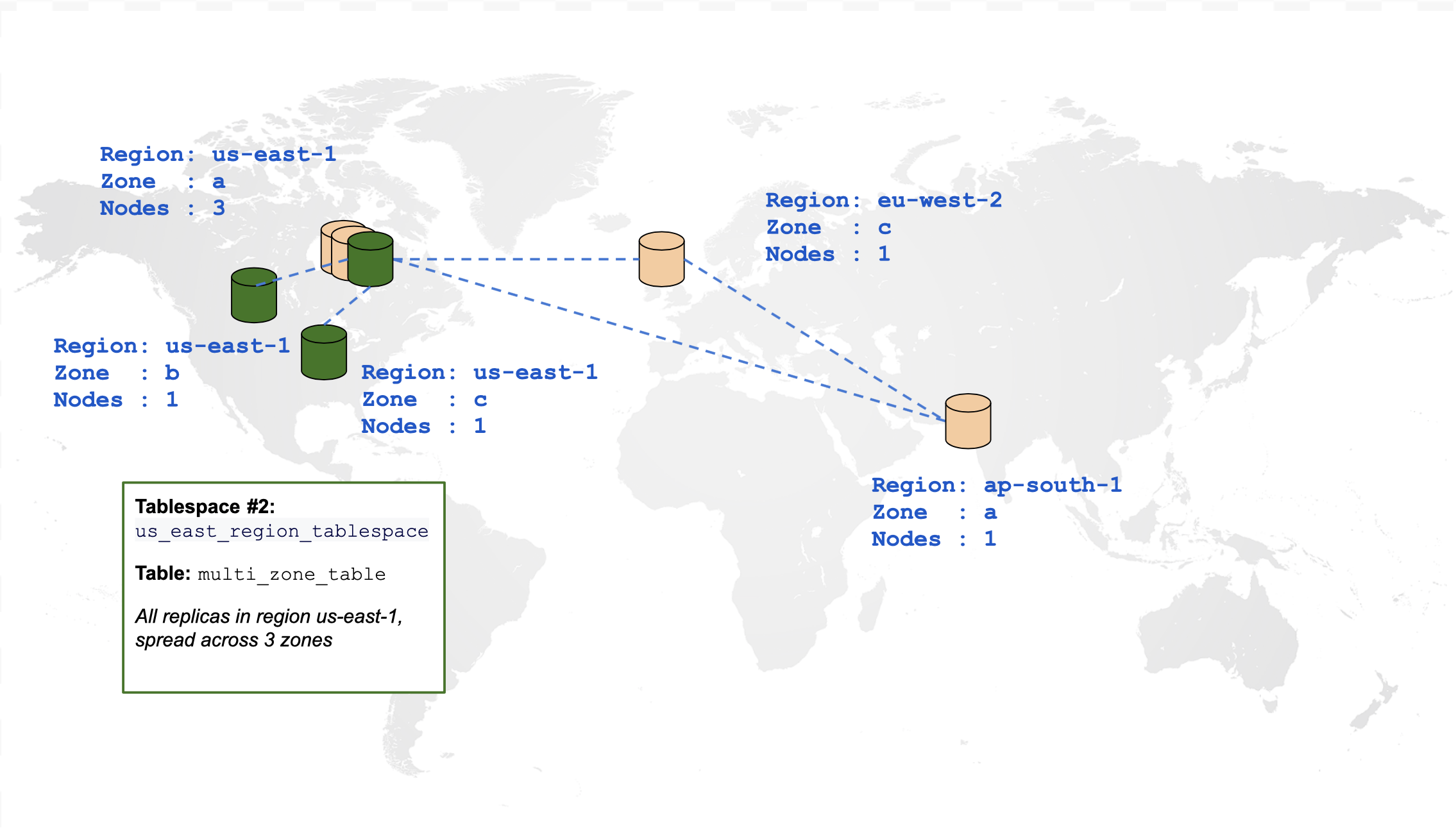
CREATE TABLESPACE us_east_region_tablespace
WITH (replica_placement='{"num_replicas": 3, "placement_blocks": [
{"cloud":"aws","region":"us-east-1","zone":"us-east-1a","min_num_replicas":1},
{"cloud":"aws","region":"us-east-1","zone":"us-east-1b","min_num_replicas":1},
{"cloud":"aws","region":"us-east-1","zone":"us-east-1c","min_num_replicas":1}]}');
CREATE TABLE multi_zone_table (id INTEGER, field text)
TABLESPACE us_east_region_tablespace SPLIT INTO 1 TABLETS;
The following demonstrates how to measure the latencies incurred for INSERTs and SELECTs on this table, where the client is in us-east-1a zone:
yugabyte=# INSERT INTO multi_zone_table VALUES (1, 'field1'), (2, 'field2'), (3, 'field3');
Time: 11.825 ms
yugabyte=# SELECT * FROM multi_zone_table;
id | field
----+--------
1 | field1
3 | field3
2 | field2
(3 rows)
Time: 4.145 ms
Create a multi-region table
The following diagram is a graphical representation of a table spread across multiple regions:
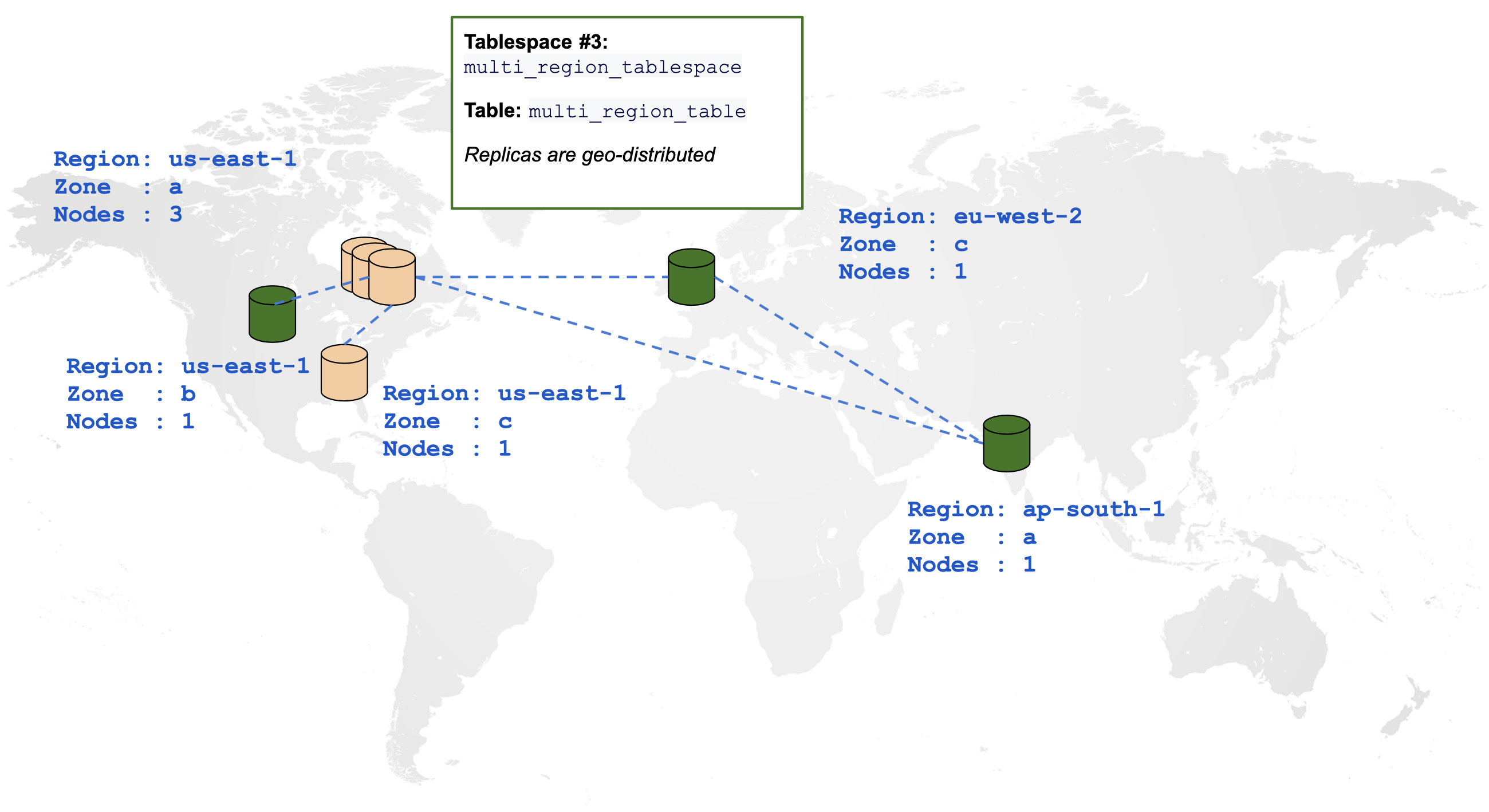
CREATE TABLESPACE multi_region_tablespace
WITH (replica_placement='{"num_replicas": 3, "placement_blocks": [
{"cloud":"aws","region":"us-east-1","zone":"us-east-1b","min_num_replicas":1},
{"cloud":"aws","region":"ap-south-1","zone":"ap-south-1a","min_num_replicas":1},
{"cloud":"aws","region":"eu-west-2","zone":"eu-west-2c","min_num_replicas":1}]}');
CREATE TABLE multi_region_table (id INTEGER, field text)
TABLESPACE multi_region_tablespace SPLIT INTO 1 TABLETS;
The following demonstrates how to measure the latencies incurred for INSERTs and SELECTs on this table, where the client is in us-east-1a zone:
yugabyte=# INSERT INTO multi_region_table VALUES (1, 'field1'), (2, 'field2'), (3, 'field3');
Time: 863.616 ms
yugabyte=# SELECT * FROM multi_region_table;
id | field
----+--------
3 | field3
2 | field2
1 | field1
(3 rows)
Time: 337.154 ms
Leader preference
The example below expects the following servers to be added to the cluster:
./bin/yugabyted start \
--base_dir=/home/yugabyte/<IP8>/yugabyte-data \
--advertise_address=<IP8> \
--join=<IP1> \
--cloud_location=aws.us-east-1.us-east-1b \
./bin/yugabyted start \
--base_dir=/home/yugabyte/<IP9>/yugabyte-data \
--advertise_address=<IP9> \
--join=<IP1> \
--cloud_location=aws.us-east-2.us-east-2a \
./bin/yugabyted start \
--base_dir=/home/yugabyte/<IP10>/yugabyte-data \
--advertise_address=<IP10> \
--join=<IP1> \
--cloud_location=aws.us-west-1.us-west-1a \
Leader preference helps optimize workloads that require distribution of data over multiple zones for zone-level fault tolerance, but which have clients only in a subset of those zones. It overrides the default behavior of spreading the tablet leaders across all placement zones of the tablespace, and instead places them closer to the clients.
The leaders handle all reads and writes, which reduces the number of network hops, which in turn reduces latency for increased performance. Leader preference allows you to specify the zones in which to place the leaders when the system is stable, and fallback zones when an outage or maintenance occurs in the preferred zones.
In the following example, the tablespace is set up to have replicas in us-east-1, us-east-2, and us-west-1. This enables it to survive the loss of an entire region. The clients are located in us-east-1. By default, a third of the leaders would reside in us-west-1, which has a latency of 62ms from the clients.
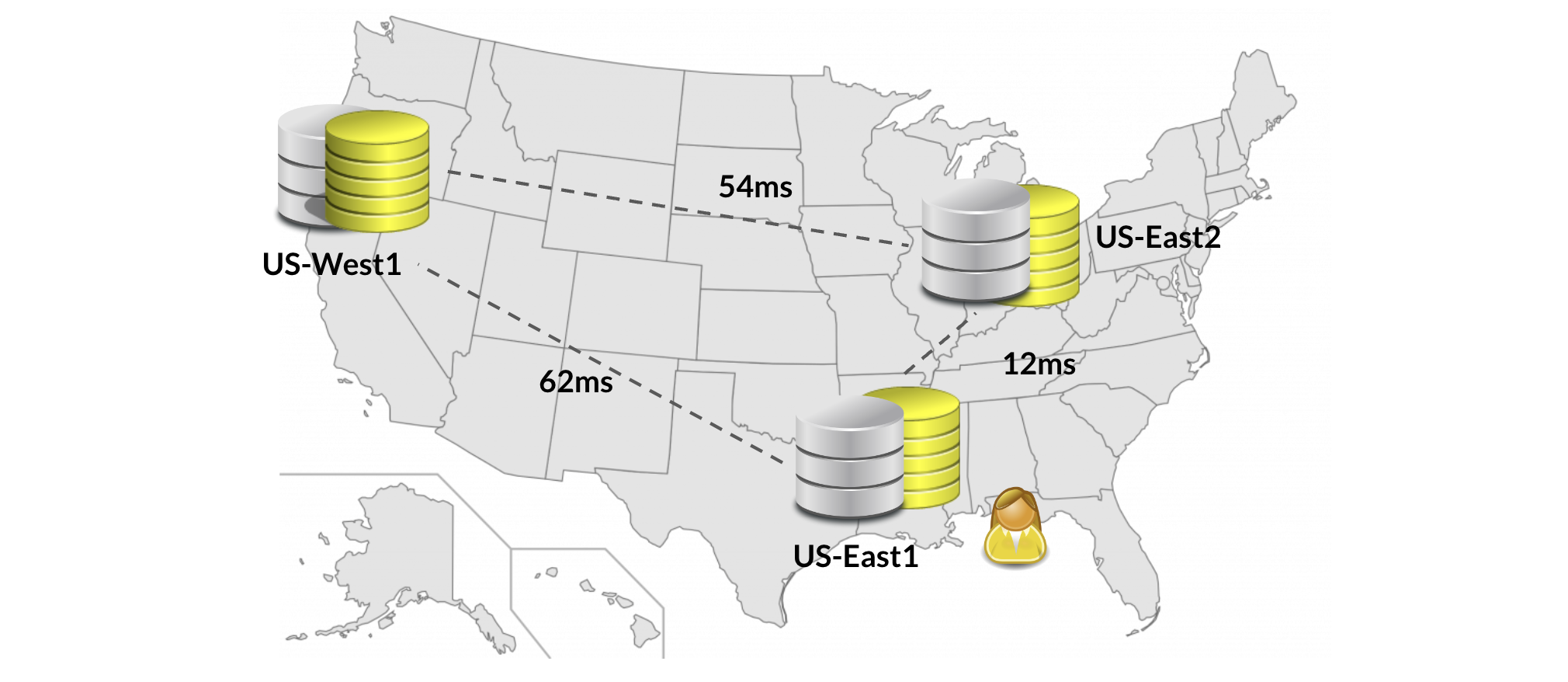
However, setting leader_preference of us-east-1b to 1 (most preferred) informs the YugabyteDB load balancer to place all associated tablet leaders in this zone, dropping the latency to less than 1ms. If all the nodes in us-east-1a are unavailable, they fall back to the next preferred zone us-east-2a, which has a 12ms latency. The following example creates the tablespace with leader preferences specified:
CREATE TABLESPACE us_east1_region_tablespace
WITH (replica_placement='{"num_replicas": 3, "placement_blocks": [
{"cloud":"aws","region":"us-east-1","zone":"us-east-1b","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":1},
{"cloud":"aws","region":"us-east-2","zone":"us-east-2a","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":2},
{"cloud":"aws","region":"us-west-1","zone":"us-west-1a","min_num_replicas":1}]}');
CREATE TABLE preferred_leader_table (id INTEGER, field text)
TABLESPACE us_east1_region_tablespace;
yugabyte=# INSERT INTO preferred_leader_table VALUES (1, 'field1'), (2, 'field2'), (3, 'field3');
Time: 43.712 ms
yugabyte=# SELECT * FROM preferred_leader_table;
id | field
----+--------
3 | field3
2 | field2
1 | field1
(3 rows)
Time: 1.052 ms
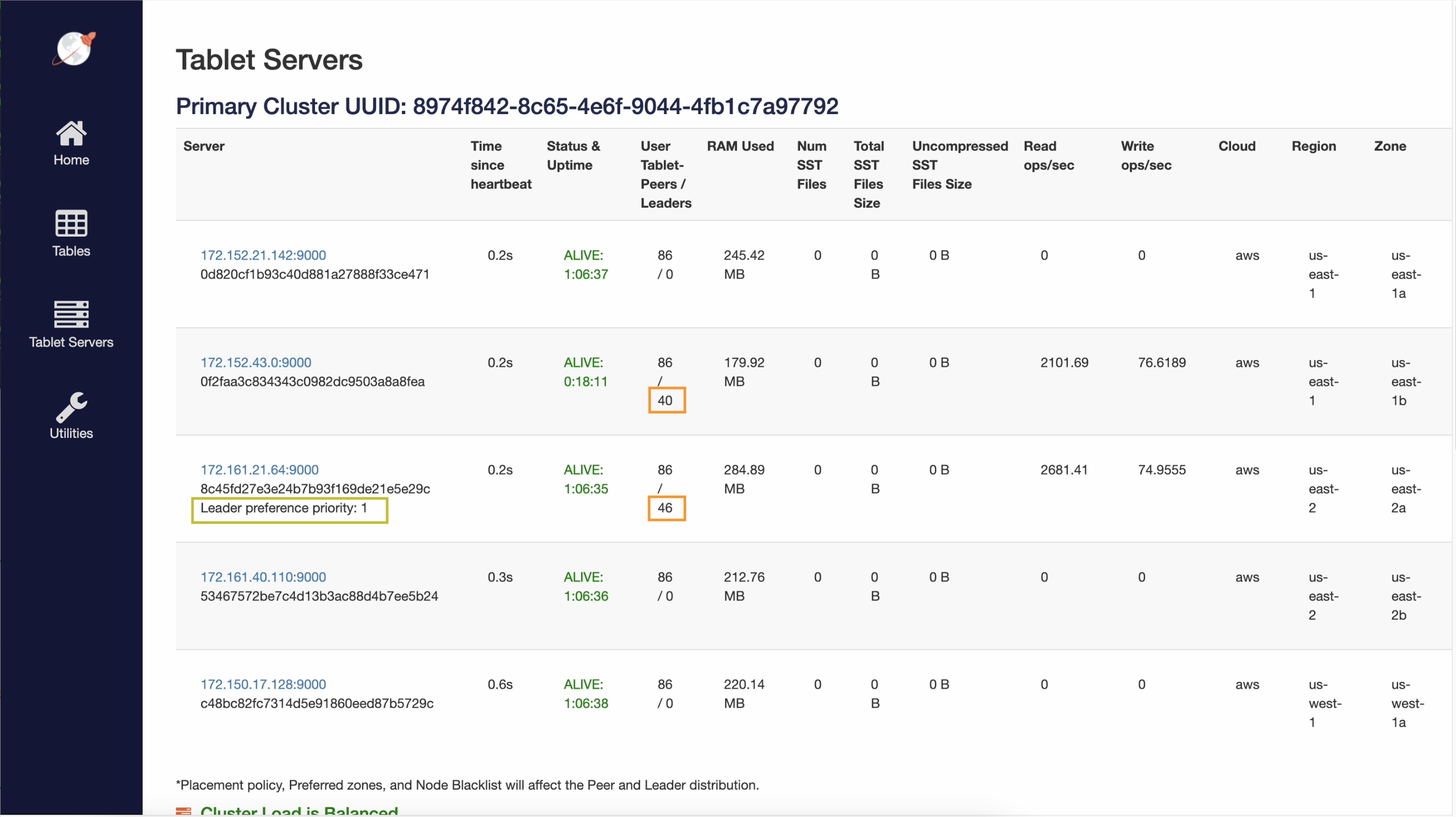
You can specify non-zero contiguous integer values for each zone. When multiple zones have the same preference, the leaders are evenly spread across them. Zones without any values are least preferred.
You can check the overall leader distribution and cluster level leader preference on the tablet-servers page.
Indexes
Like tables, indexes can be associated with a tablespace. If a table has more than one index, YugabyteDB picks the closest index to serve the query. The following example creates three indexes for each region occupied by the multi_region_table from above:
CREATE TABLESPACE us_east_tablespace
WITH (replica_placement='{"num_replicas": 1, "placement_blocks": [
{"cloud":"aws","region":"us-east-1","zone":"us-east-1b","min_num_replicas":1}]}');
CREATE TABLESPACE ap_south_tablespace
WITH (replica_placement='{"num_replicas": 1, "placement_blocks": [
{"cloud":"aws","region":"ap-south-1","zone":"ap-south-1a","min_num_replicas":1}]}');
CREATE TABLESPACE eu_west_tablespace
WITH (replica_placement='{"num_replicas": 1, "placement_blocks": [
{"cloud":"aws","region":"eu-west-2","zone":"eu-west-2c","min_num_replicas":1}]}');
CREATE INDEX us_east_idx ON multi_region_table(id) INCLUDE (field) TABLESPACE us_east_tablespace;
CREATE INDEX ap_south_idx ON multi_region_table(id) INCLUDE (field) TABLESPACE ap_south_tablespace;
CREATE INDEX eu_west_idx ON multi_region_table(id) INCLUDE (field) TABLESPACE eu_west_tablespace;
Run the following EXPLAIN command by connecting to each region:
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM multi_region_table WHERE id=3;
EXPLAIN output for querying the table from us-east-1:
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Index Only Scan using us_east_idx on multi_region_table (cost=0.00..5.06 rows=10 width=36)
Index Cond: (id = 3)
(2 rows)
EXPLAIN output for querying the table from ap-south-1:
QUERY PLAN
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Index Only Scan using ap_south_idx on multi_region_table (cost=0.00..5.06 rows=10 width=36)
Index Cond: (id = 3)
(2 rows)
EXPLAIN output for querying the table from eu-west-2:
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Index Only Scan using eu_west_idx on multi_region_table (cost=0.00..5.06 rows=10 width=36)
Index Cond: (id = 3)
(2 rows)
Change to a different tablespace
The tablespace of a table, index, or materialized view can be altered after the object has been created. Let’s say we have a single-zone table in us-east-1a:
yugabyte=# CREATE TABLE critical_table (id INTEGER, field text)
yugabyte-# TABLESPACE us_east_1a_zone_tablespace SPLIT INTO 1 TABLETS;
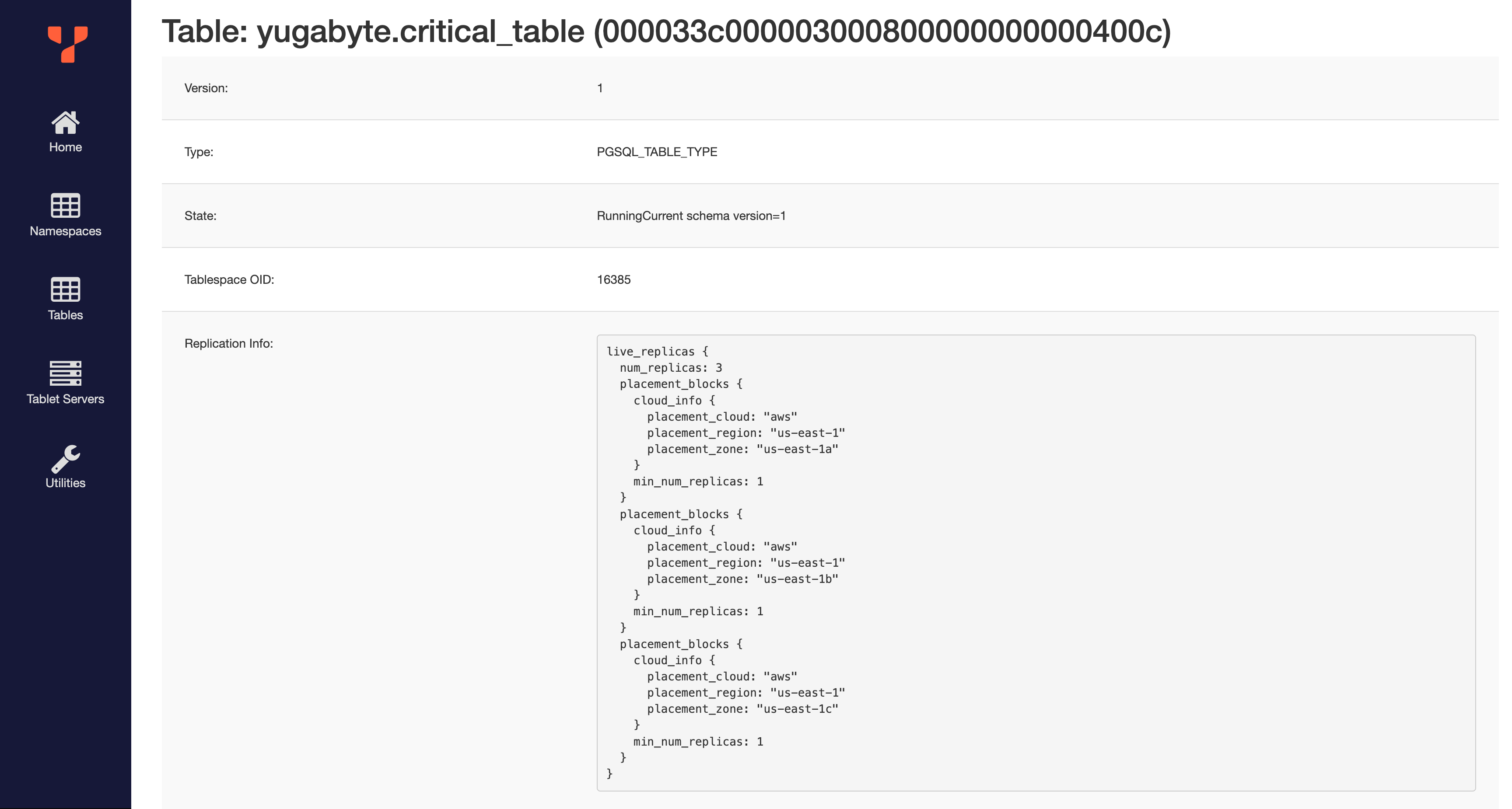
To check the placement of the tablets for this table, first navigate to the YB-Master UI, then click on "Tables" on the left:
Then, click on critical_table:
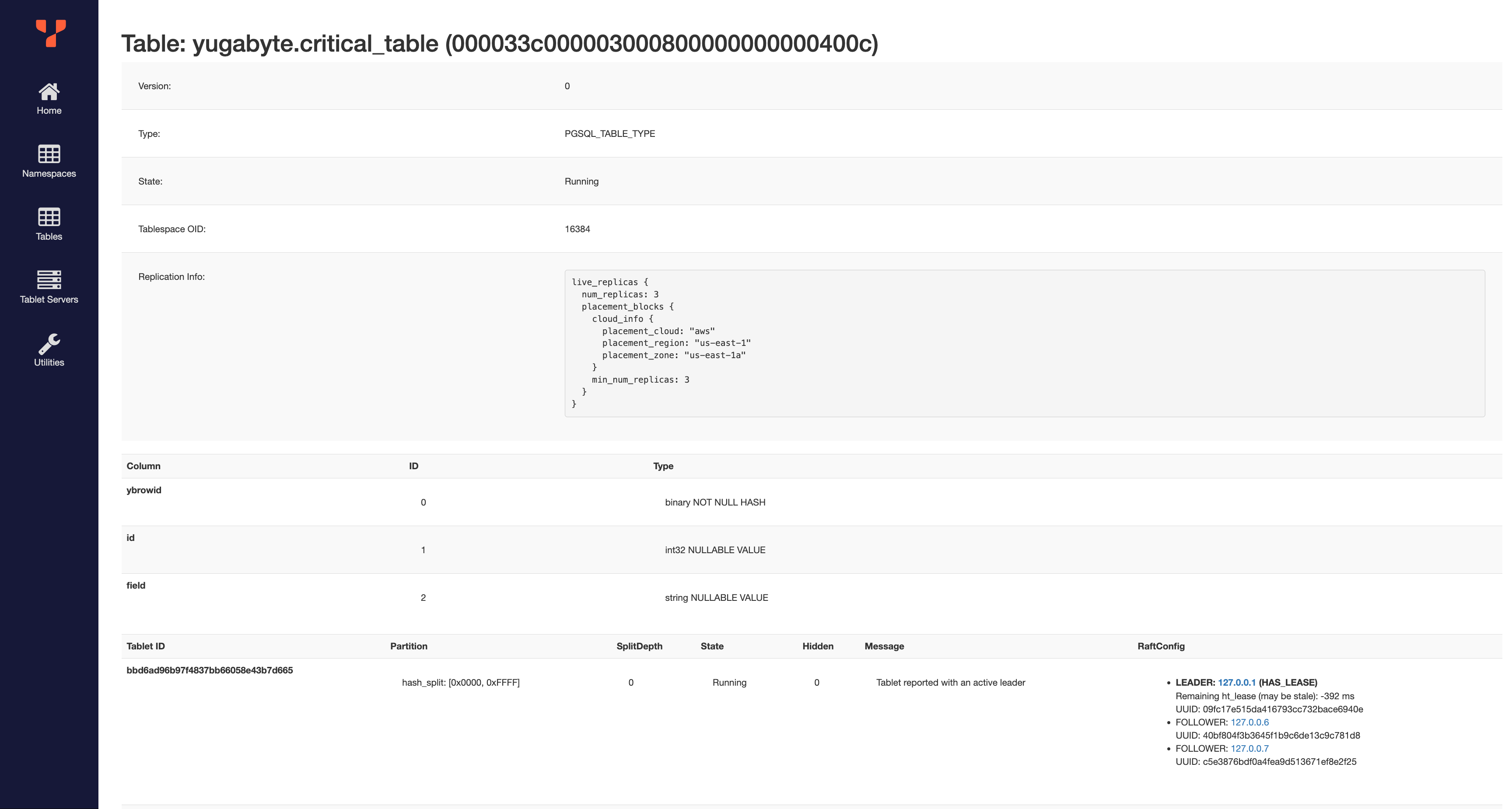
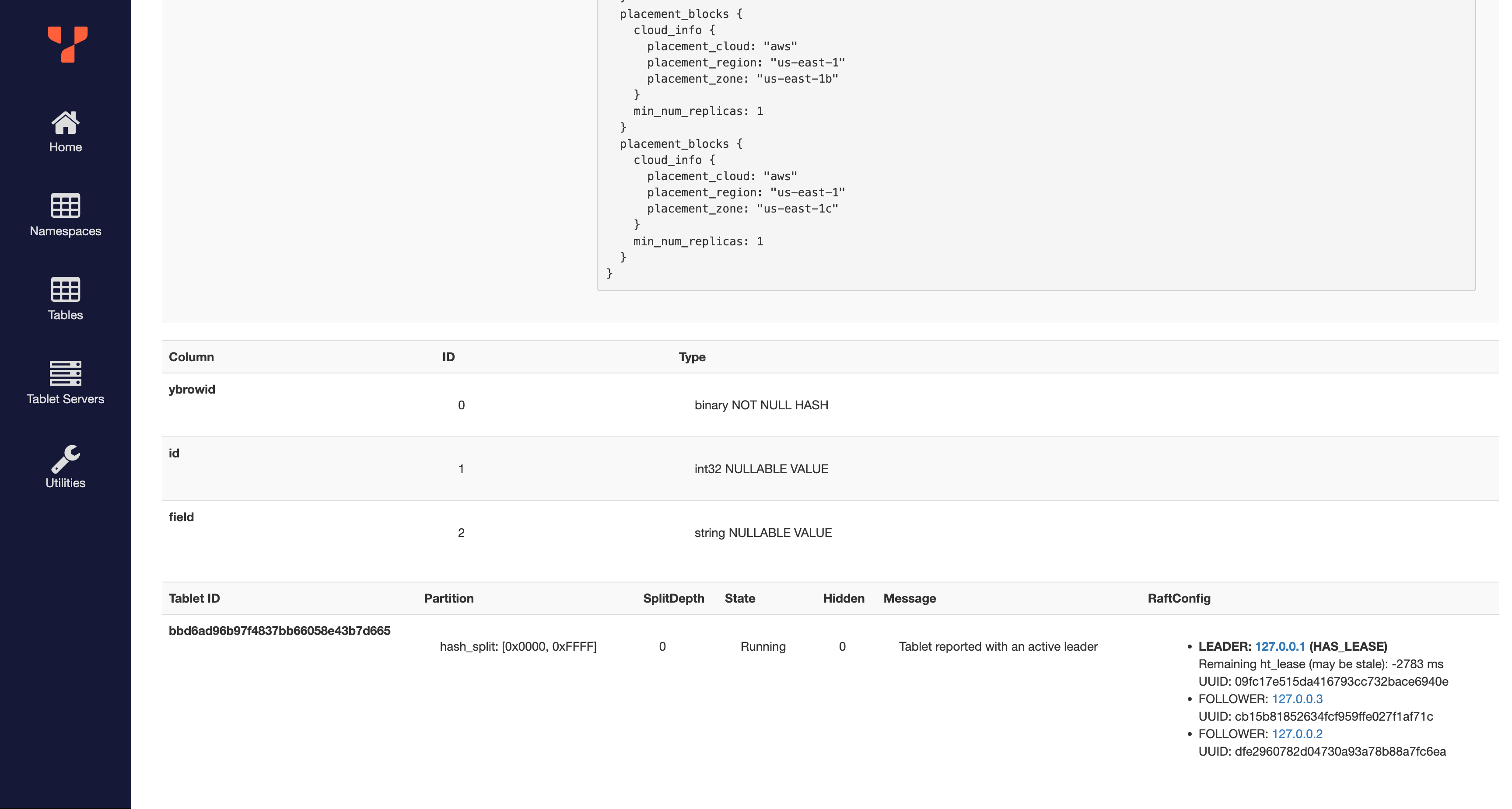
You can see the assigned placement policy under "Replication info". Under "RaftConfig", see that the replicas were placed on 127.0.0.1, 127.0.0.6, and 127.0.0.7. Clicking on "Tablet Servers" in the sidebar, you can see that these are the three nodes in us-east-1a, as expected.
Suppose you want to make this table resilient to single-zone failures. You can accomplish this by altering its tablespace to the multi-zone us_east_region_tablespace, where it will have replicas in the us-east-1a, us-east-1b, and us-east-1c regions:
yugabyte=# ALTER TABLE critical_table SET TABLESPACE us_east_region_tablespace;
NOTICE: Data movement for table single_zone_table is successfully initiated.
DETAIL: Data movement is a long running asynchronous process and can be monitored by checking the tablet placement in http://<YB-Master-host>:7000/tables
You can see the replication info for our table has changed:
The RaftConfig has also changed to match the new tablespace:
What's next?
The following features will be supported in upcoming releases:
- Support for
ALTER TABLESPACE. - Setting read replica placements using tablespaces.