Duplicate indexes
If you have applications running in multiple regions, they still have to go the tablet leaders in the other regions for reads and writes. Although writes must always go to the tablet leaders, the speed of reads can be improved by using follower reads or read replicas. But in both of these setups, the replicas may not be up-to-date with the latest data, resulting in stale reads. This may not be acceptable for some applications.
This is where Duplicate Indexes come in handy. Duplicate indexes guarantee immediately consistent reads in multiple regions. This section describes how applications can benefit from this pattern, and the associated costs.
Overview
Suppose you have an RF 3 Global Database spread across us-east, us-central, and us-west, your application is running in us-east, and so you have set the leader preference to us-east.
Setup
To set up a local universe, refer to Set up a local YugabyteDB universe.Setup
To set up a cluster, refer to Set up a YugabyteDB Aeon cluster.Setup
To create a universe, refer to Create a multi-zone universe.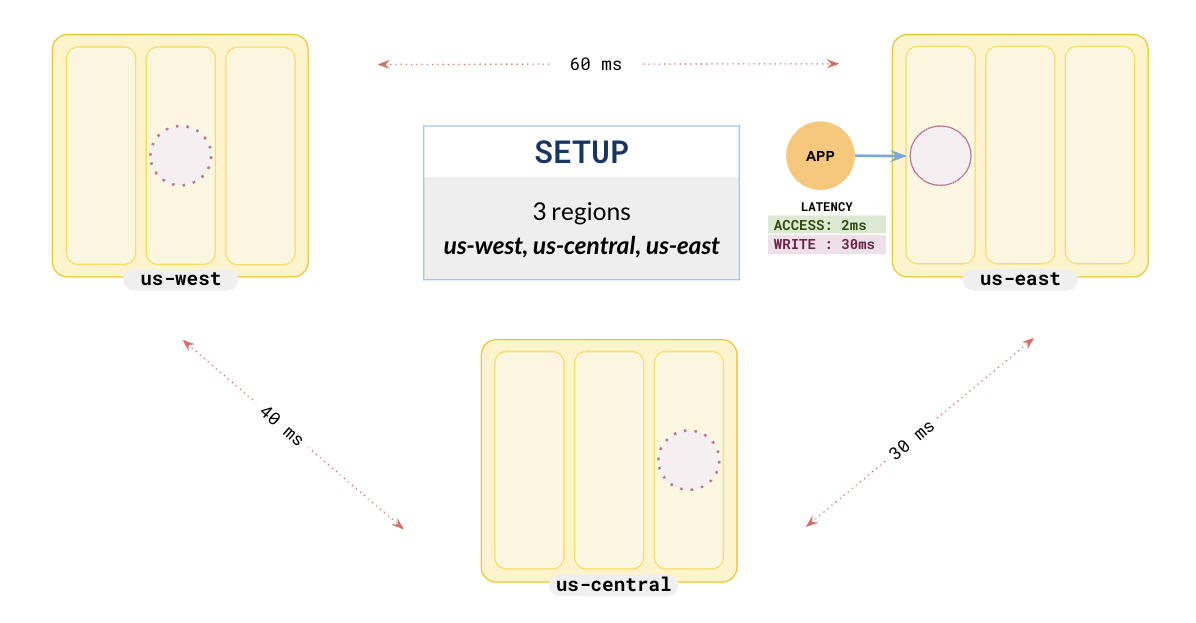
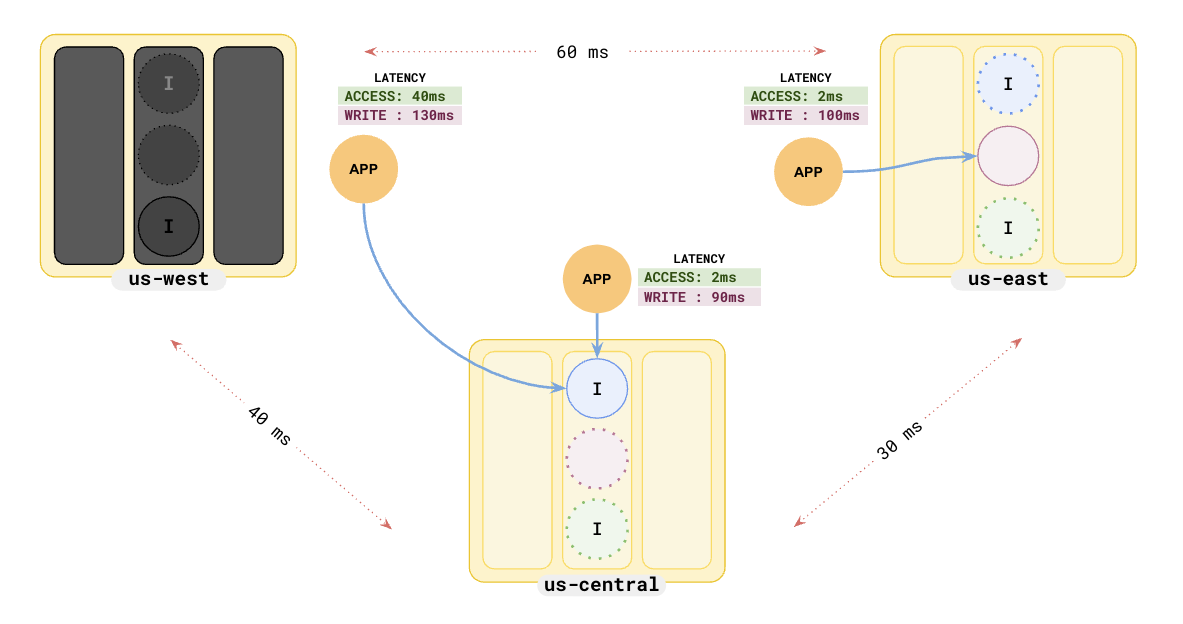
Adding an application in us-central gives the following setup.
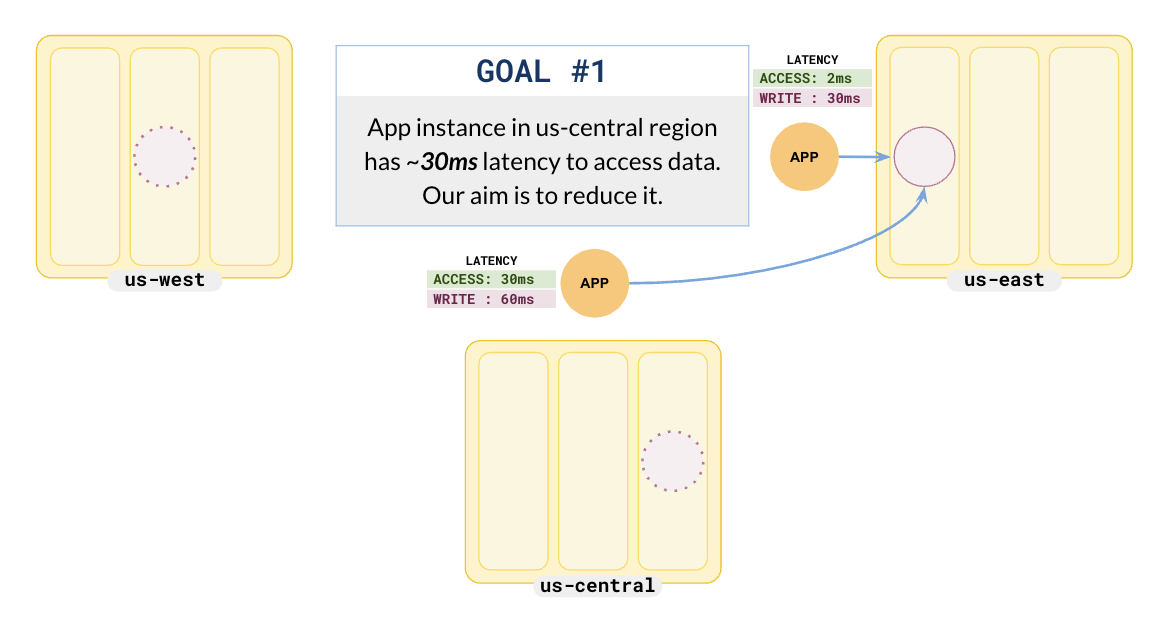
In this scenario, the application in us-central has a read latency of 30 ms, whereas the application in us-east has a read latency of only 2 ms.
us-central.This becomes worse when you add an application in us-west.
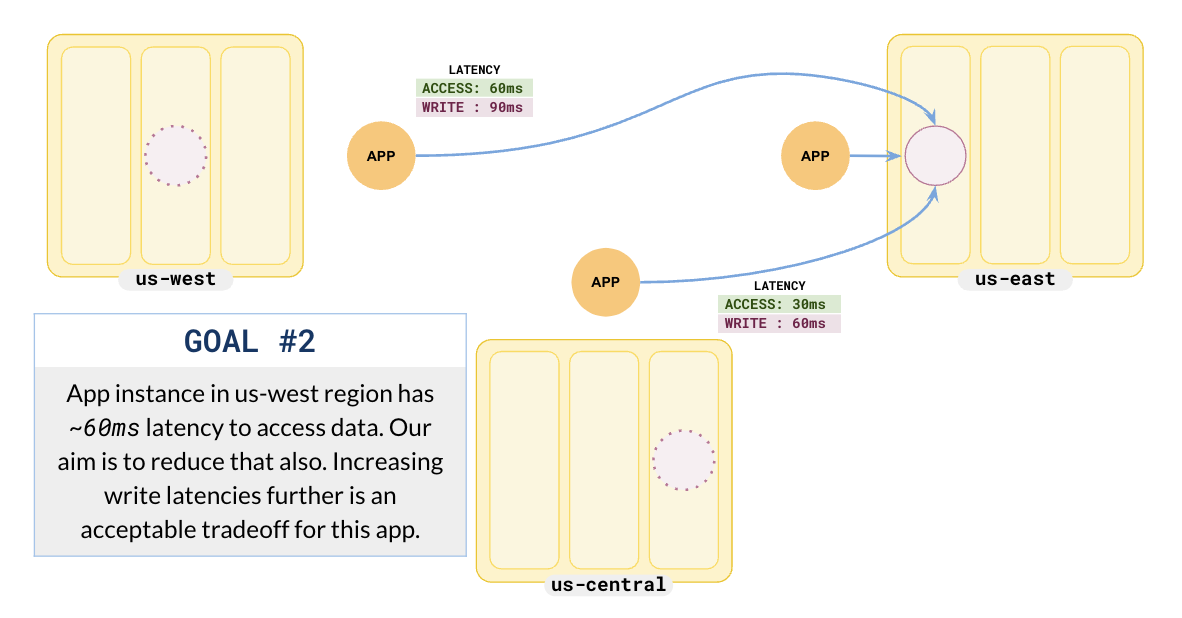
The application in us-west has a high read latency of 60 ms.
us-westDuplicate indexes
By default, all reads go to the leader, so even though the replicas are available in other regions, applications incur cross-region latency if the leaders are in a different region than the application.
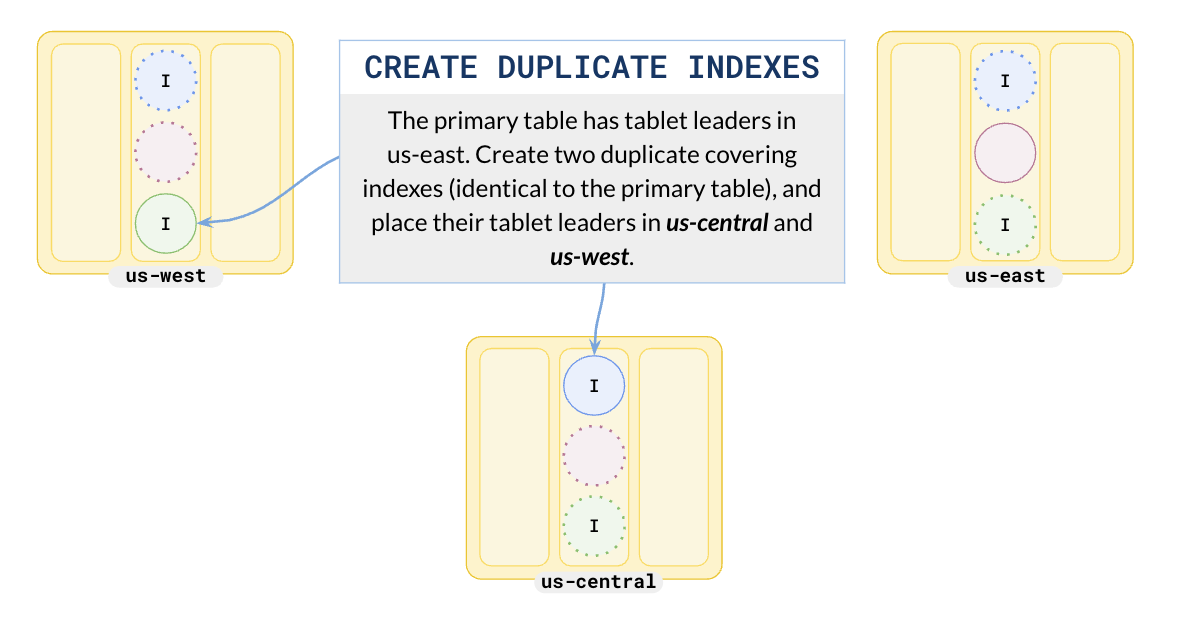
To address this, you can create multiple covering indexes with the same schema as the table, and attach them to different tablespaces, with leader preference set to each region.
To set this up, do the following:
-
Create a basic table of users, which has the
id,name, andcityfor each user.CREATE TABLE users ( id INTEGER NOT NULL, name VARCHAR, city VARCHAR ); -
Create multiple tablespaces (one for every region you want your index leader to be located in) and set leader preference to that region:
Note
Even though the leader preference is set to a region, you should place the replicas in other regions for outage scenarios, depending on your application setup.-- tablespace for west data CREATE TABLESPACE west WITH ( replica_placement= '{ "num_replicas" : 3, "placement_blocks" : [ {"cloud":"aws","region":"us-west","zone":"us-west-1a","leader_preference": 1,"min_num_replicas":1}, {"cloud":"aws","region":"us-east","zone":"us-east-1a","min_num_replicas":1}, {"cloud":"aws","region":"us-central","zone":"us-central-1a","min_num_replicas":1} ]}'); -- tablespace for central data CREATE TABLESPACE central WITH ( replica_placement= '{ "num_replicas" : 3, "placement_blocks" : [ {"cloud":"aws","region":"us-west","zone":"us-west-1a","min_num_replicas":1}, {"cloud":"aws","region":"us-east","zone":"us-east-1a","min_num_replicas":1}, {"cloud":"aws","region":"us-central","zone":"us-central-1a","leader_preference": 1,"min_num_replicas":1} ]}'); -- tablespace for east data CREATE TABLESPACE east WITH ( replica_placement= '{ "num_replicas" : 3, "placement_blocks" : [ {"cloud":"aws","region":"us-west","zone":"us-west-1a","min_num_replicas":1}, {"cloud":"aws","region":"us-east","zone":"us-east-1a","leader_preference": 1,"min_num_replicas":1}, {"cloud":"aws","region":"us-central","zone":"us-central-1a","min_num_replicas":1} ]}'); -
Create multiple duplicate indexes and attach them to region-level tablespaces.
CREATE INDEX idx_west ON users (name) INCLUDE (id, city) TABLESPACE west; CREATE INDEX idx_east ON users (name) INCLUDE (id, city) TABLESPACE east; CREATE INDEX idx_central ON users (name) INCLUDE (id, city) TABLESPACE central;
This creates three clones of the covering index, with leaders in different regions, and at the same time replicated in the other regions. The following illustration shows the result.
Reduced read latency
Consider the query plan to fetch the id and city for a user John Wick for the application running in us-west:
explain analyze select id, city from users where name = 'John Wick' ;
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Index Only Scan using idx_west on users (actual time=2.274..2.274 rows=1 loops=1)
Index Cond: (name = 'John Wick'::text)
Heap Fetches: 0
Planning Time: 0.225 ms
Execution Time: 2.386 ms
Peak Memory Usage: 8 kB
Because you have added all of the columns needed for your queries as part of the covering index, the query executor doesn't have to go to the tablet leader (in a different region) to fetch the data. The geo-aware query planner will prefer to use the index (idx_west), whose leaders are local to the region, when querying. Note that the read latency is just ~2.2 ms instead of the original ~60 ms.
Note
The query planner optimizations related to picking the right index by taking into consideration the leader preference of the tablespace in which the index lives are available in v2.17.3 and later.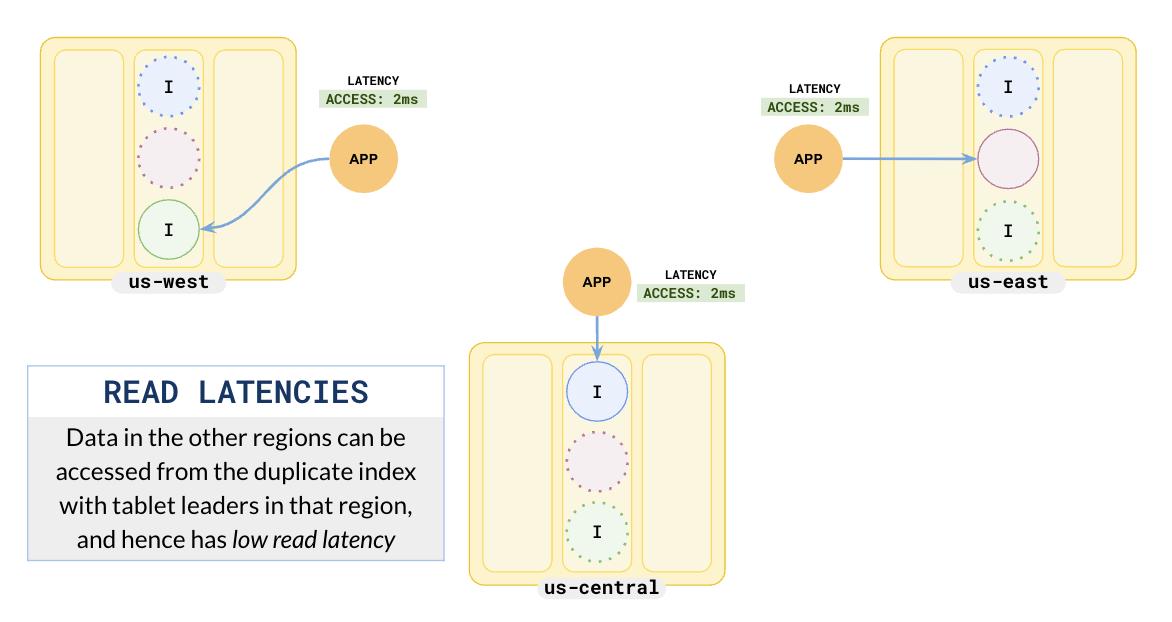
All the applications now read locally with a reduced read latency of 2 ms. When you set up your cluster using duplicate indexes, it has the effect of having consistent leaders for the table in each region.
Increased write latency
The following illustration shows the write latencies.
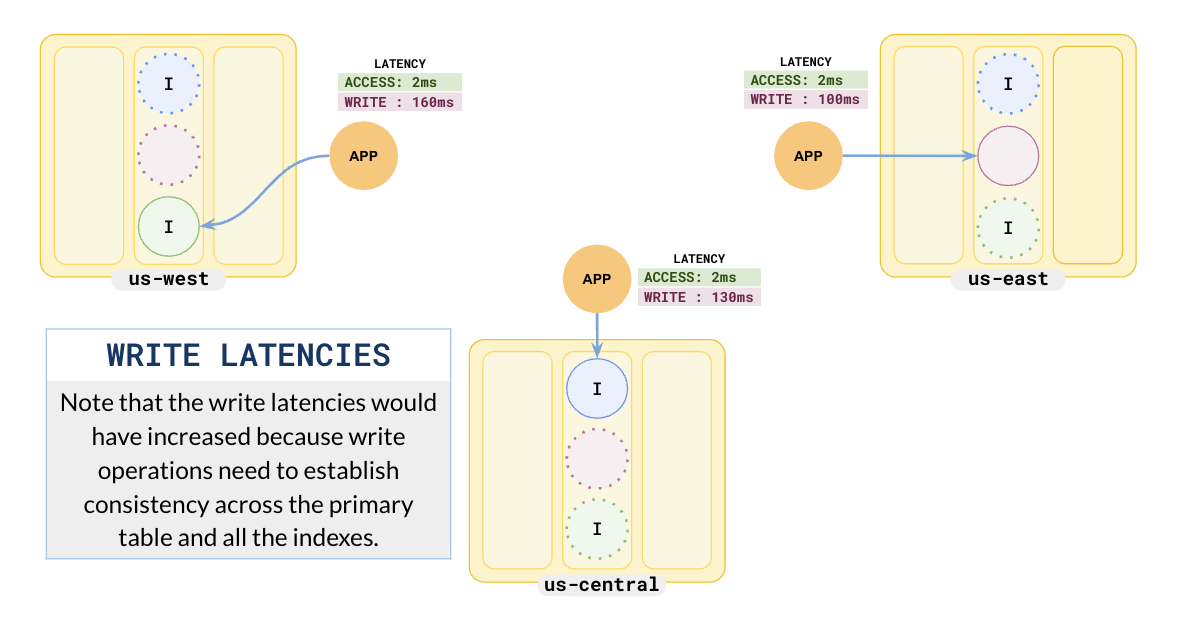
The write latencies have increased because each write has to update the tablet leader, its replicas, and three index leaders and their replicas. Effectively you are sacrificing write latency to achieve highly reduced read latency.
Failover
In the case of zone or region failures, followers in other regions are elected leaders and the applications connect to the closest region automatically as shown in the following illustration.