Data distribution
Horizontal scaling is a first-class feature in YugabyteDB, which is designed to scale horizontally seamlessly when adding nodes. YugabyteDB stores table data in tablets (also known as shards). Sharding is the process of distributing table data into tablets.
Horizontal scalability requires transparent sharding of data. Let's go over how data is distributed seamlessly across nodes without any service interruption with a basic illustration.
Cluster setup
For the purpose of illustration, suppose you have a 3-node cluster with a replication factor (RF) of 3, and you are going to store a basic table with an integer as a primary key. The data is stored in a single tablet (T1). The table starts with a single tablet with a tablet leader (node-2) and two followers (replicas on node-1 and node-3) for high availability.
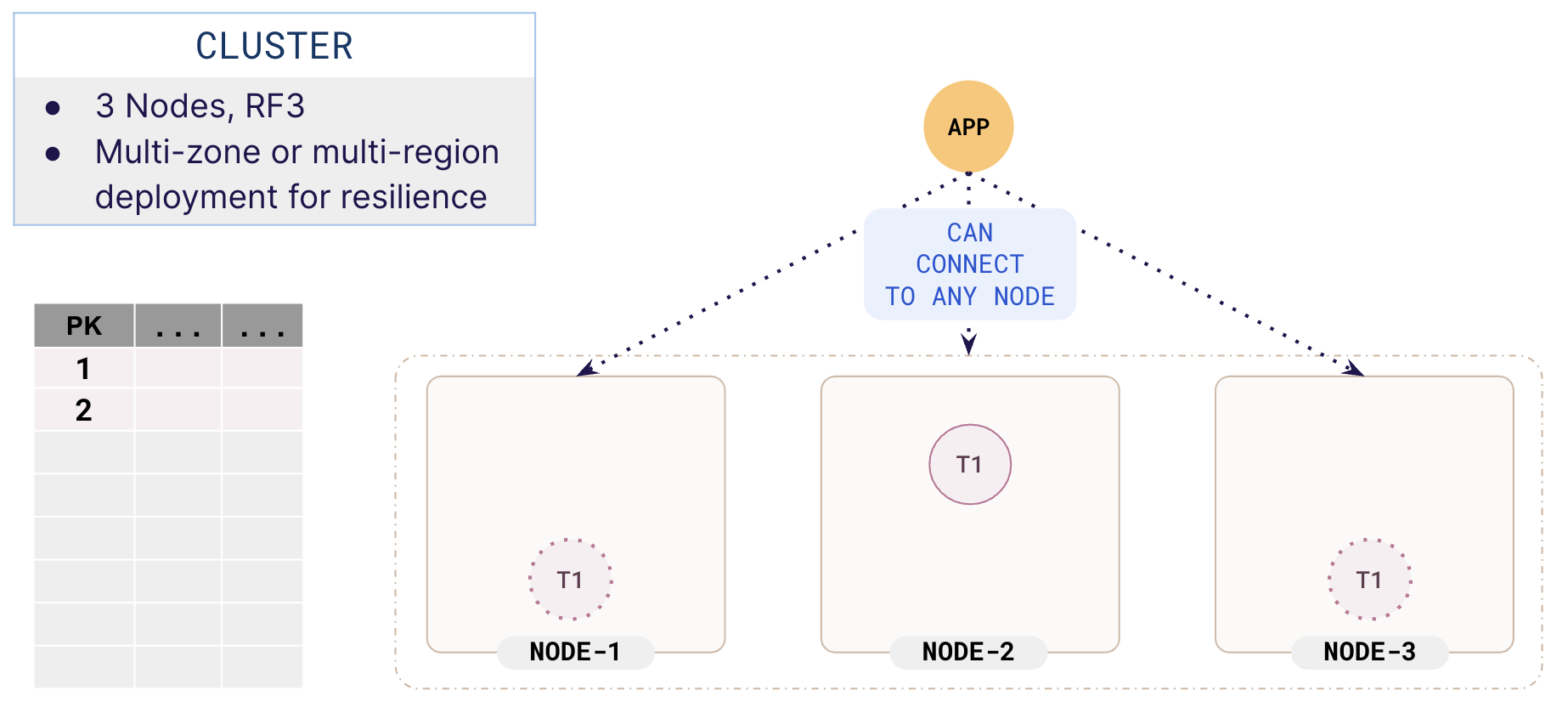
Sharding
Each row of a table is mapped to a single tablet based on a sharding strategy. The mapping of a row to a tablet is deterministic so when data has to be fetched from a row or a row has to be updated, the database knows exactly which tablet to go to.
In our illustration, both rows are mapped to the same tablet T1. As you add more data to the table, the rows are mapped to the same tablet and both leaders and followers of tablet T1 start to grow.
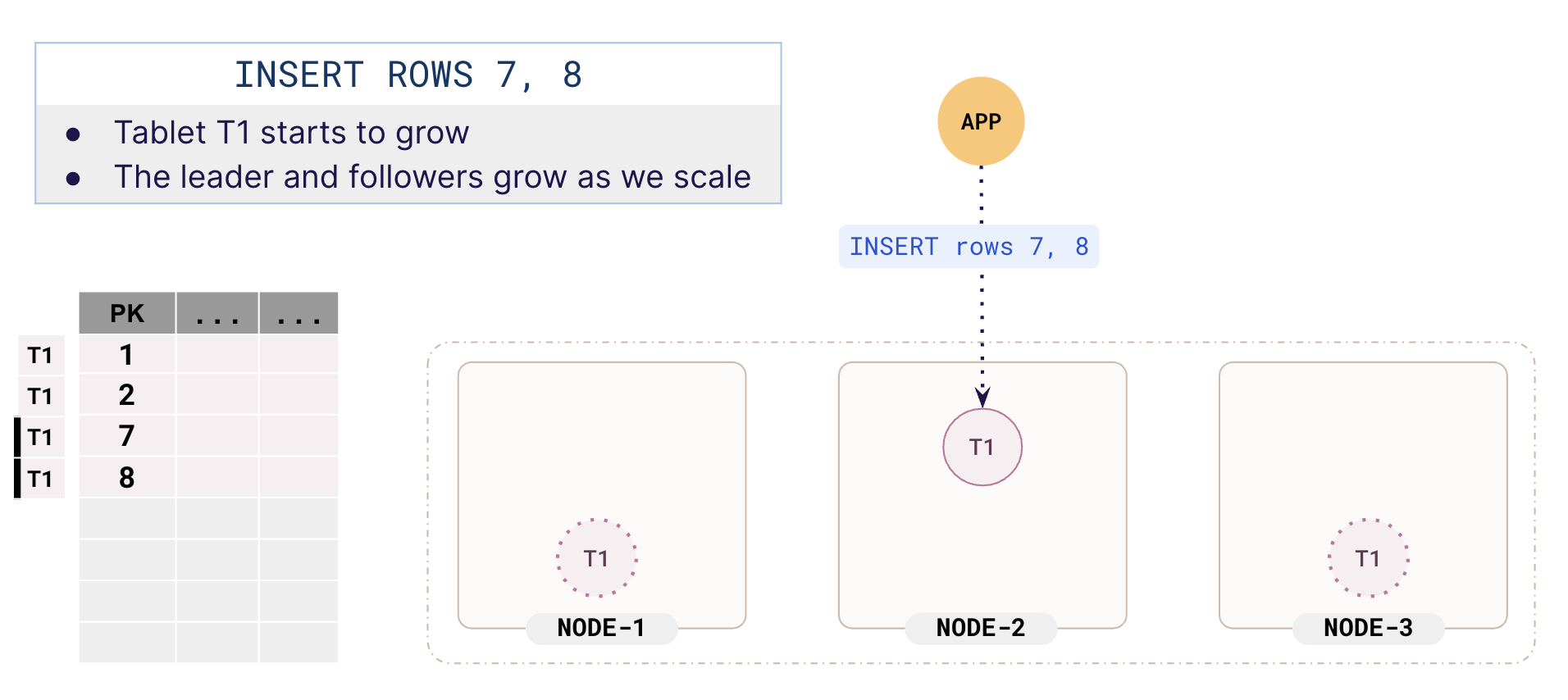
Tablet splitting
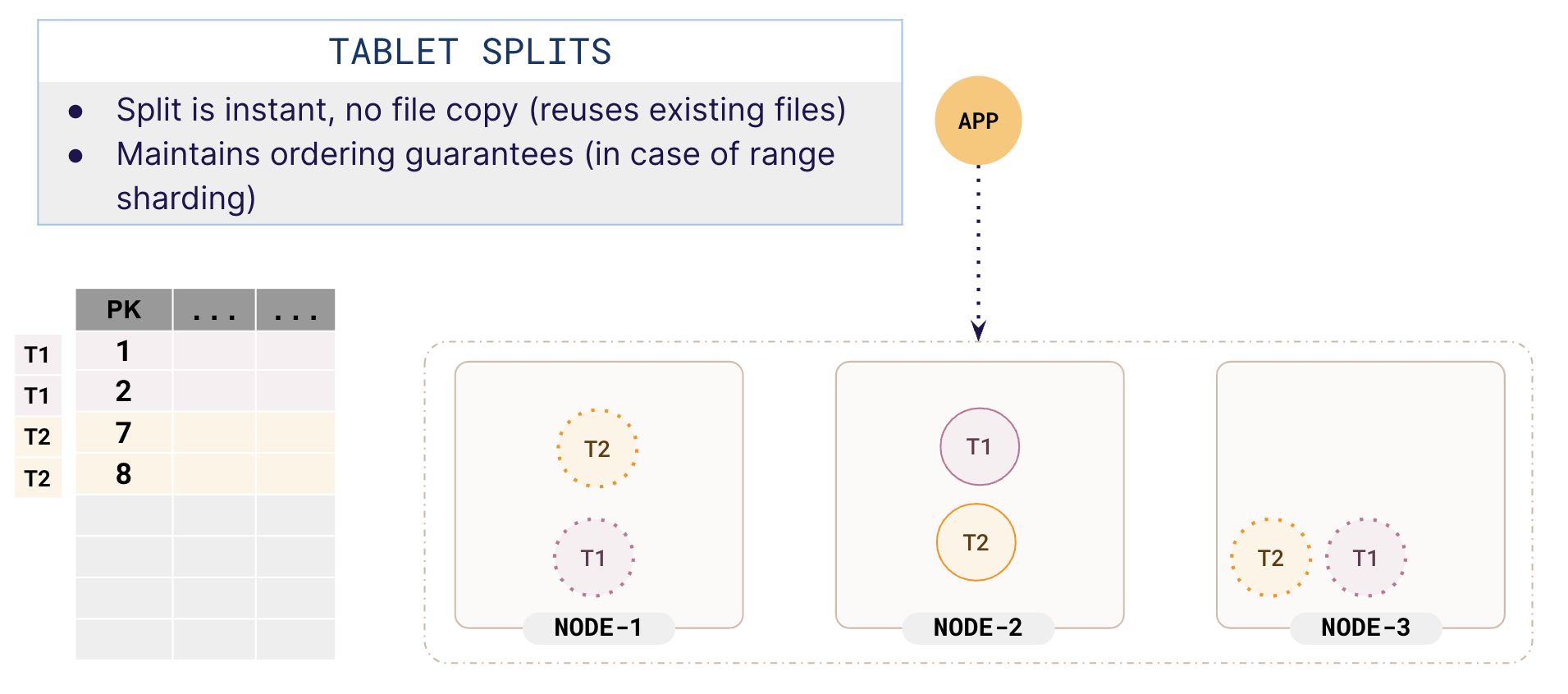
When a tablet reaches a threshold size, the tablet splits into two. Many different scenarios can trigger a tablet to split, but for simplicity, we will stick to a threshold size of 4 rows.
Now, the tablet T1 splits into two by creating a new tablet, T2. Tablet splitting is almost instantaneous and is transparent to the application. The newly created tablet will have leaders and followers.
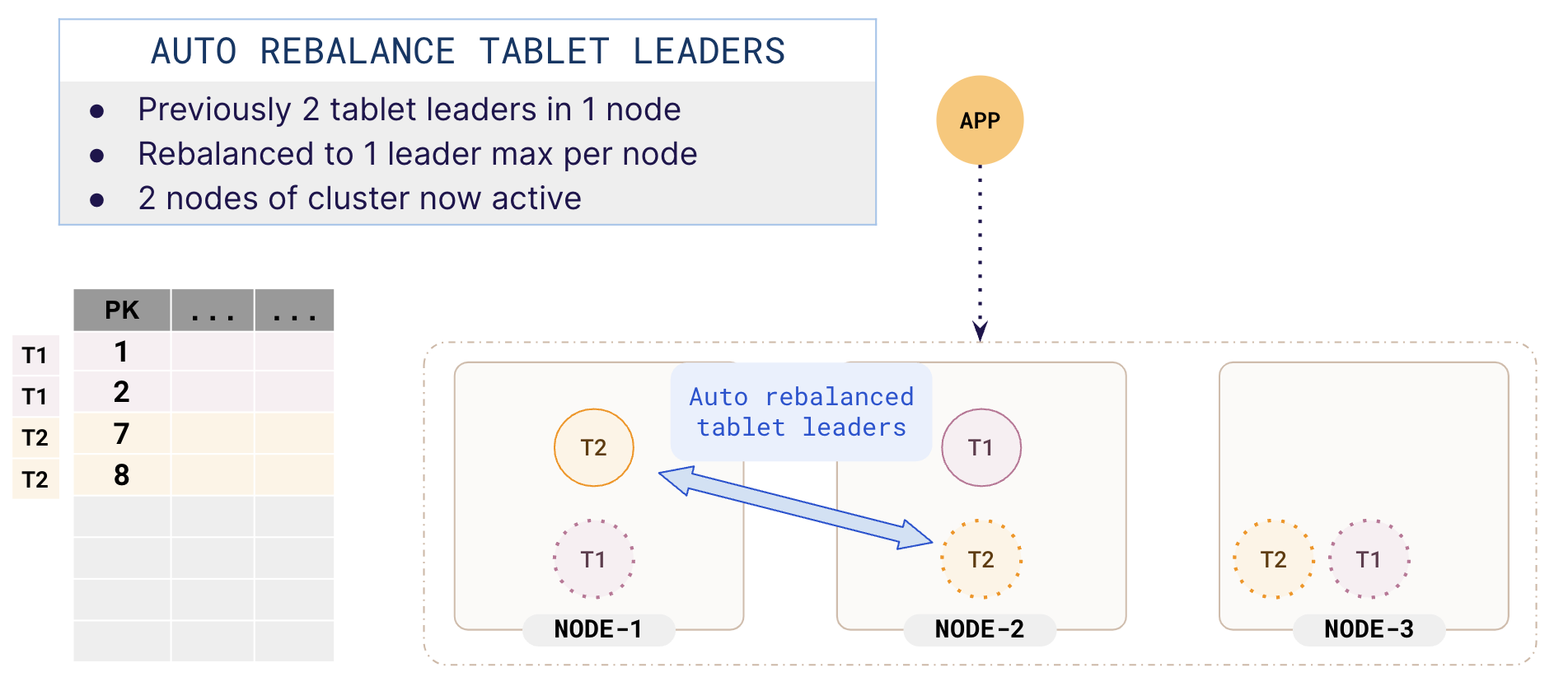
Rebalancing
Depending on how many tablets are split, the tablet distribution across the nodes may not be even. YugabyteDB tries to keep the number of tablets on each node the same so as to keep the load across the nodes distributed in an even fashion.
In the previous illustration, T1 and T2 are in the same node (node-2). YugabyteDB realizes that the leaders are not balanced and automatically distributes the leaders across different nodes. This ensures that the cluster is used optimally.
Scaling out
As more data is added to the table, the tablets split further and are rebalanced as needed. With more data added, you would get a distribution similar to the following illustration:
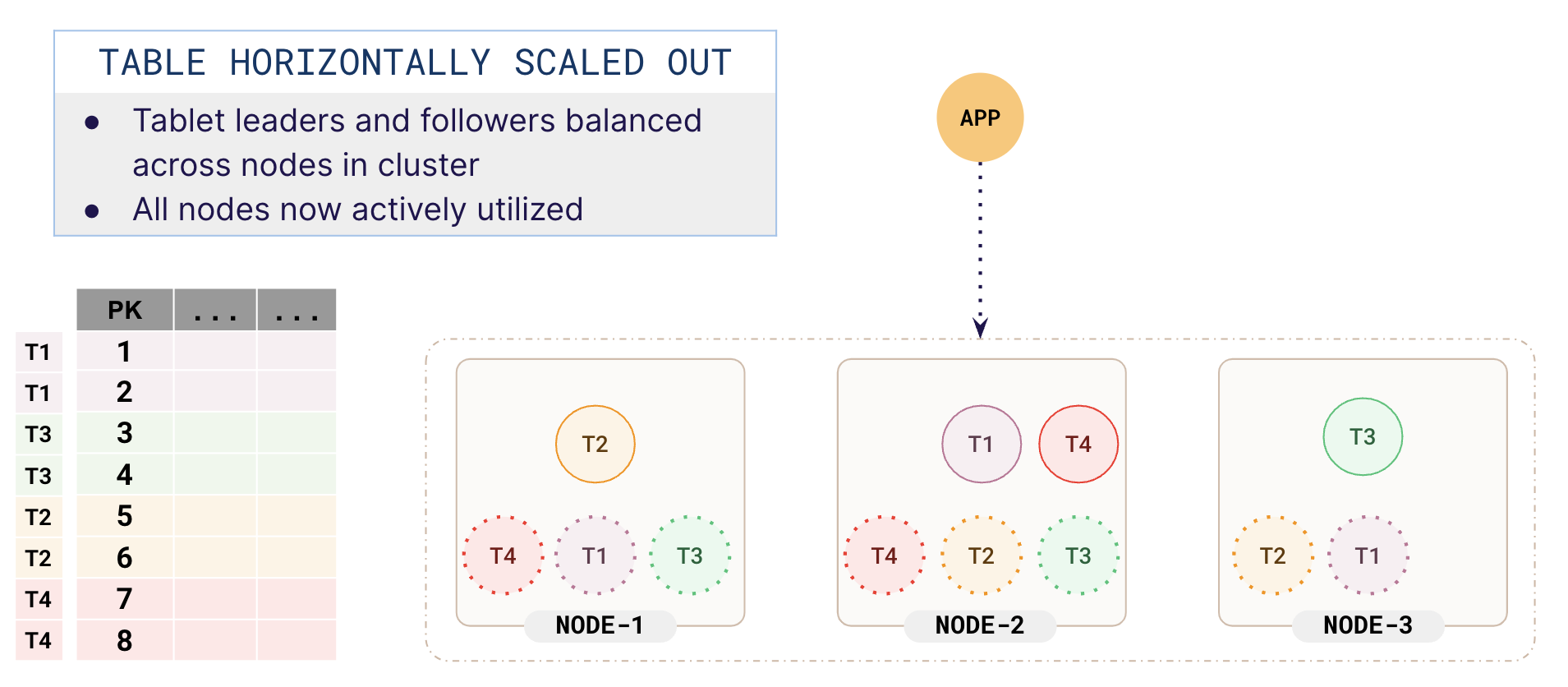
This process of sharding, replication, and rebalancing is fully automatic, taking place in the background as you scale horizontally, and is completely transparent to applications. While this example shows a single table with a few tablets, real-world YugabyteDB clusters can have many more tables and tablets (100+).
Sharding is fully configurable, and you can also pre-split tables when you create them.