Built-in connection pooling EARLY ACCESS
YugabyteDB inherits the architecture of creating one backend process for every connection to the database from PostgreSQL. These backend processes consume memory and CPU, limiting the number of connections YugabyteDB can support. To solve this problem, you can use a connection pooler, which allows multiplexing multiple client connections to a smaller number of actual server connections, thereby supporting a larger number of connections from applications. PgBouncer and Odyssey are some of the popular PostgreSQL-based server-side connection pooling mechanisms that are fully compatible with YugabyteDB.
However, connection poolers have some limitations:
- Added complexity. Deploying and maintaining a connection pooler adds complexity to your application stack.
- They don't support all PostgreSQL features. For example, neither PgBouncer nor Odyssey supports SET statements in the transaction pooling mode.
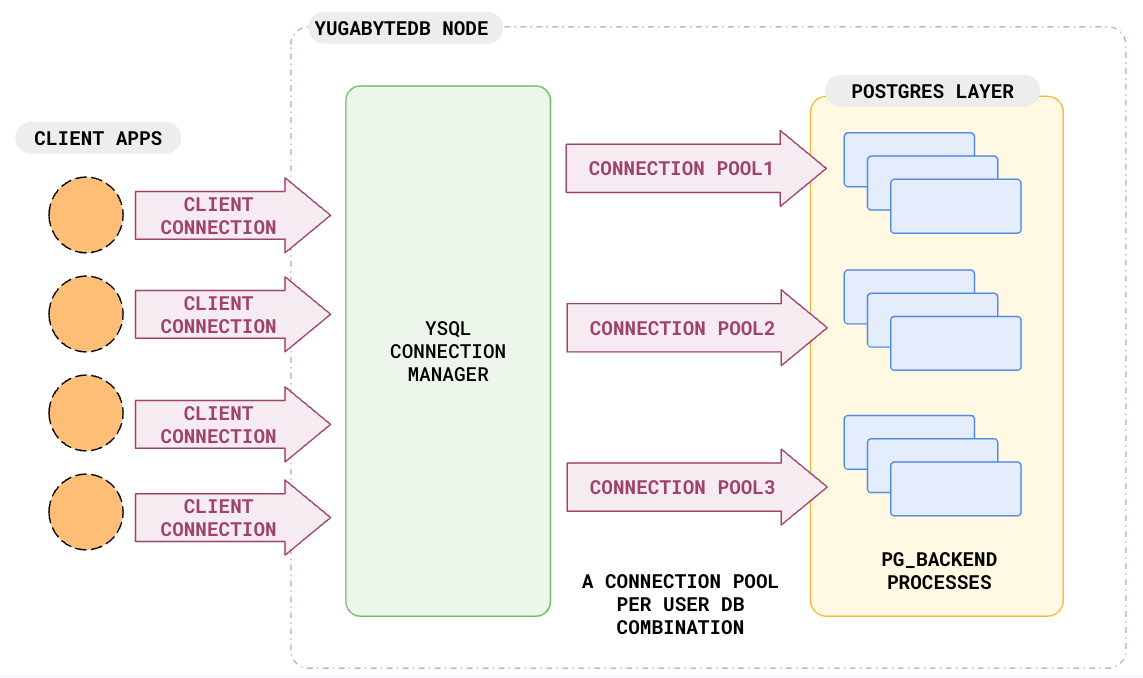
To provide the advantages of connection pooling, but without the limitations, YugabyteDB includes a built-in connection pooler, YSQL Connection Manager. Because the manager is bundled with the product, it is convenient to manage, monitor, and configure the server connections without additional third-party tools. When combined with smart drivers, YugabyteDB simplifies application architecture and enhances developer productivity.
Key features
YSQL Connection Manager is a modified version of the open-source connection pooler Odyssey. YSQL Connection Manager uses Odyssey in the transaction pooling mode and has been modified at the wire protocol level for tighter integration with YugabyteDB to overcome some SQL limitations.
YSQL Connection Manager has the following key features:
-
No SQL limitations. Unlike other pooling solutions running in transaction mode, YSQL Connection Manager supports SQL features such as TEMP TABLE, WITH HOLD CURSORS, and more.
-
Per user and database pool, with quota sharing. Like PgBouncer and Odyssey, YSQL Connection Manager creates a pool for each unique combination of user and database. However, it also allows connection quotas to be shared across multiple such pools, enabling more efficient use of resources and improved scalability.
-
Support for session parameters. YSQL Connection Manager supports SET statements, which are not supported by other connection poolers.
-
Support for prepared statements. Odyssey supports protocol-level prepared statements and YSQL Connection Manager inherits this feature.
Start YSQL Connection Manager
To start a YugabyteDB cluster with YSQL Connection Manager, set the yb-tserver flag enable_ysql_conn_mgr to true.
For example, to create a single-node cluster with YSQL Connection Manager using yugabyted, use the following command:
./bin/yugabyted start --tserver_flags "enable_ysql_conn_mgr=true" --ui false
When enable_ysql_conn_mgr is set, each YB-TServer starts the YSQL Connection Manager process along with the PostgreSQL process. You should see one YSQL Connection Manager process per YB-TServer.
To create a large number of client connections, ensure that "SHMMNI" (the maximum number of concurrent shared memory segments an OS allows) as well as ulimit is set correctly as follows:
- Open the file
/etc/sysctl.conf. - Add
kernel.shmmni = 32768(support for 30000 clients) at the end of the file. - To refresh the settings, use
sudo sysctl -p.
EA
While in Early Access, YSQL Connection Manager is not available in YugabyteDB Anywhere by default. To make connection pooling available, set the Allow users to enable or disable connection pooling Global Runtime Configuration option (config key yb.universe.allow_connection_pooling) to true. Refer to Manage runtime configuration settings. You must be a Super Admin to set global runtime configuration flags.
To enable built-in connection pooling for universes deployed using YugabyteDB Anywhere:
- Turn on the Connection pooling option when creating a universe. Refer to Create a multi-zone universe.
- Edit connection pooling on an existing universe. Refer to Edit connection pooling.
Note that when managing universes using YugabyteDB Anywhere, do not set connection pooling flags, enable_ysql_conn_mgr, ysql_conn_mgr_port, and pgsql_proxy_bind_address.
Connect
To connect to the YSQL Connection Manager, use the ysqlsh command with the -h <IP> flag, instead of specifying the Unix-domain socket directory.
Using the socket directory along with -p (custom PostgreSQL port or default 6433) will connect you to the PostgreSQL process, not the YSQL connection manager process.
EA You can enable built-in connection pooling on YugabyteDB Aeon clusters in the following ways:
- When creating a cluster, turn on the Connection Pooling option. (Connection Pooling is enabled by default for Sandbox clusters.)
- For clusters that are already created, navigate to the cluster Settings>Connection Pooling tab.
Enabling connection pooling on an Aeon cluster gives 10 client connections for every server connection by default.