Architecture
YugabyteDB is a distributed database that seamlessly combines the principles of distributed systems, where multiple machines collaborate, with the familiar concepts of traditional databases, where data is organized in tables with standard interfaces for reading and writing data.
Unlike traditional centralized databases, YugabyteDB is designed to manage and process data across multiple nodes or servers, ensuring resiliency, consistency, high availability, scalability, fault tolerance, and other design goals.
Layered architecture
In general, operations in YugabyteDB are split logically into 2 layers, the query layer and the storage layer. The query layer is responsible for handling user requests and sending the requests to the right data. The storage layer is responsible for optimally storing the data on disk and managing replication and consistency.
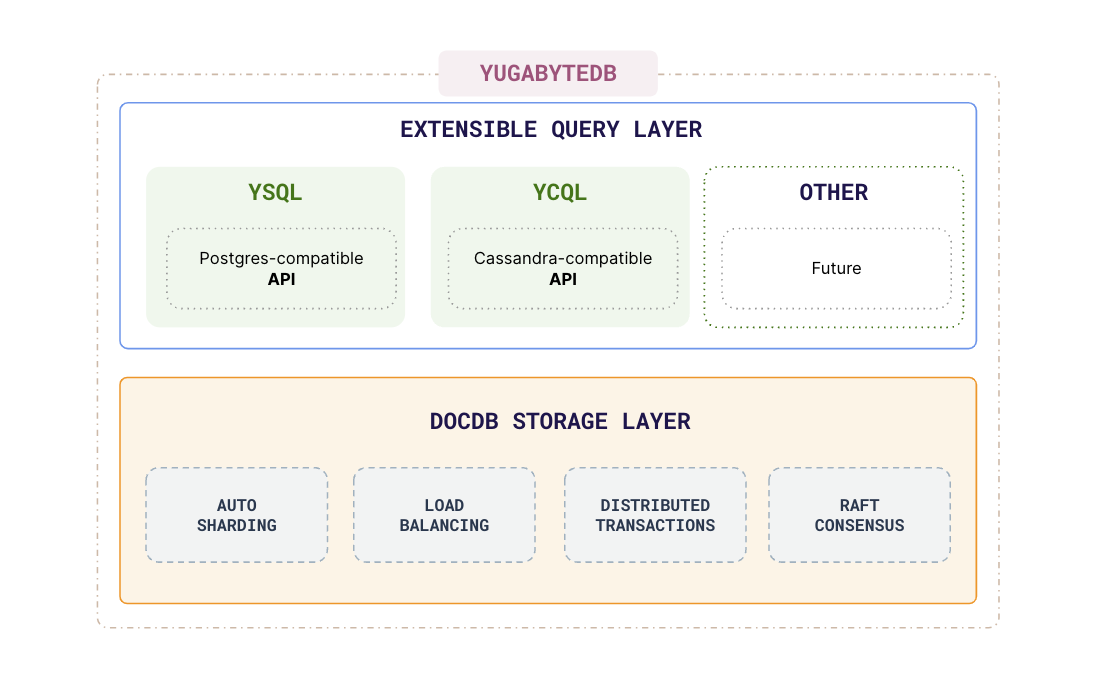
Query layer
For operating (CRUD) on the data that is split and stored across multiple machines, YugabyteDB provides two APIs, YSQL and YCQL. The query layer takes the user query submitted via the API and sends or fetches data to and from the right set of tablets.
Storage layer
The tablet data is optimally stored and managed by DocDB, a document store that has been built on top of RocksDB for higher performance and persistence.
Sharding
YugabyteDB splits table data into smaller pieces called tablets so that the data can be stored in parts across multiple machines. The mapping of a row to a tablet is deterministic and this process is known as sharding.
Replication
Tablets are replicated for resiliency, high availability, and fault tolerance. Each tablet has a leader that is responsible for consistent reads and writes to the data of the tablet and a few followers. The replication is done using the Raft protocol to ensure consistency of data across the leader and followers.
Transactions
Transactions are a set of operations (CRUD) that are executed atomically with the option to roll back all actions if any operation fails.
Master server
The master service acts a catalog manager and cluster orchestrator, and manages many background tasks.
TServer
YugabyteDB splits table data into tablets. These tablets are maintained and managed on each node by the TServer.