Cluster balancing
Overview
Cluster balancing is the process by which YugabyteDB automatically distributes data and queries across the nodes in a cluster to maintain fault tolerance and maximize performance. This page describes the various scenarios in which YugabyteDB performs cluster balancing and how to monitor its progress.
Cluster balancing is performed by a component of the YB-Master called the cluster balancer. The cluster balancer continuously monitors the cluster configuration and moves tablet data and leaders to evenly distribute data and query load, thus distributing CPU, disk, and network load across the cluster.
Terminology
Many of the flags and metrics on this page refer to the cluster balancer as the "load balancer". This document uses the more precise term "cluster balancer" to avoid confusion with network load balancers or client-side load balancers.Placement policy
A placement policy is a specification of how data and queries should be distributed across the cluster. For example, a typical replication factor of 3 (RF-3) placement might specify that there should be one replica of each tablet in three separate regions (for example, us-west-1a, us-east-2a, and us-central-1a), with leader preference towards us-west-1a.
The default placement policy is automatically inferred when a cluster is created, but you can change it at the cluster-level using yb-admin, or override it on a per-table basis using tablespaces (for YSQL clusters).
Remote bootstrap
The cluster balancer creates new tablet replicas by a process called remote bootstrap. This involves copying data from a YB-TServer hosting an up-to-date tablet peer (typically, the geographically closest peer) to the destination YB-TServer.
Blacklisting
A YB-TServer can be blacklisted or leader blacklisted to prevent it from hosting data or leaders, respectively. Blacklists are used to facilitate graceful shutdowns (for example, when performing staged restarts or OS patching on a node).
Cluster balancing scenarios
Cluster balancing happens automatically when you scale a cluster in or out, when there are node outages (for example, a failed node, or a network partition), and after creating or deleting tables and tablets.
Cluster balancing when scaling
Scaling out
When scaling out (adding nodes), the cluster balancer will gracefully move tablet data and leaders to the new nodes, without any application impact. Because tablet leaders handle queries, moving leaders also moves the location of where queries execute.
Scaling in
When scaling in, removed nodes are marked as "blacklisted". This signals to the cluster balancer that it should do the following:
- Gracefully transfer leadership off of the node being removed.
- Re-replicate the data that was on the node to other nodes in the same region.
After all data and queries have moved off of the node, the node can be removed safely.
Blacklisting is performed automatically by YugabyteDB Anywhere and YugabyteDB Aeon. For yugabyted clusters, you should use yb-admin to blacklist the node being removed.
Cluster balancing after node outages
On an unplanned node outage, cluster balancing occurs twice: first when the node goes down, and again if the node recovers.
When a node goes down, the cluster balancer automatically transfers tablet leadership to healthy nodes. This happens in 3 seconds or less.
If the node stays down for a predetermined length of time (15 minutes by default, as set using the follower_unavailable_considered_failed_sec flag) the cluster balancer starts creating new replicas of the data that was on the failed node on other nodes in the same region (if any exist).
Queries will succeed as soon as tablet leaders move off of the failed node. The data balancing phase does not impact the availability of the database.
If or when the failed node recovers, the cluster balancer rebalances tablet leaders onto the recovered node, as well as tablet data (if data had moved off of the node).
Table and tablet creation and deletion
Operations that create or delete tablets may also trigger cluster balancing. These can include the following:
- Creating a table
- Dropping a table
- Tablet splitting
Monitoring cluster balancer progress
While leader rebalancing is fast, data rebalancing can take anywhere from seconds to hours. The major factors influencing how long data rebalancing takes are:
- The size of data on the failed node.
- The configured network and disk throughput.
- Cluster balancer configuration flags (see Flags for details).
With yugabyted, you can access the YB-Master UI at http://localhost:7000 to access two views to monitor the cluster balancer progress.
Tablet Servers view
The Tablet Servers view provides information about how many peers and leaders are hosted on each tablet server, as well as whether each tablet server is currently data or leader blacklisted.
To access the view, click Tablet Servers on your YB-Master UI.
Cluster Balancer view
This view is available in YugabyteDB v2024.2.6 and later, and v2025.1.1 and later.
The Cluster Balancer view displays the following information:
- Ongoing cluster balancing tasks (for example, moving tablet leaders, and tablets being added or removed).
- Any warnings during cluster balancing. For example, if a placement policy cannot be satisfied because there are no TServers in the requested zone.
- Ongoing remote bootstraps from one tablet server to another, including the speed of data transfer.
To access the view, click Utilities > Load Balancer on your YB-Master UI.
The YugabyteDB Anywhere Metrics page includes the following charts for monitoring cluster balancing progress.
You access metrics by navigating to Universes > Universe-Name > Metrics.
Data Disk Usage
Data Disk Usage displays the amount of disk space used by the selected tablet server. The disk usage should be similar on all tablet servers after data is balanced.
To view the chart, select the Resources tab on your universe Metrics page.
Cluster load balancer statistics
This chart is available in v2024.2.6 and later, and v2025.1.1 and later.
Cluster load balancer statistics displays an estimate of the number of tablets that still have to be moved before the cluster is considered balanced.
To view the chart, select the Master Server tab on your universe Metrics page as per the following illustration:
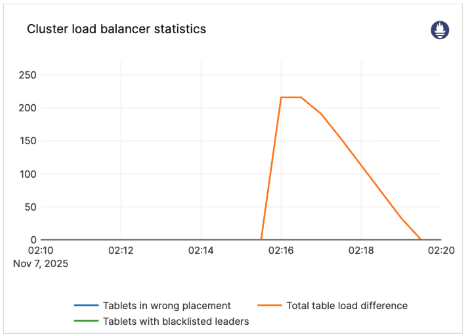
The chart shows the following metrics, which can be used to track the number of tablet moves that are required before the cluster is considered balanced:
total_table_load_differenceblacklisted_leaderstablets_in_wrong_placement
Cluster balancing is complete when all metrics reach 0.
The metric estimated_data_to_balance_bytes tracks how much data (in bytes) must be transferred before a cluster is balanced. This is the most accurate indicator of how long cluster balancing will take for clusters that are limited by data transfer speed.
Configuration and tuning
Starting in v2025.1.1 and later, you configure cluster balancing using the remote_bootstrap_rate_limit_bytes_per_sec flag. This flag controls how much data each node sends or receives each second. Set the flag according to your network and disk provisioning limits, and also based on the requirements of your workload.
For example, if you provisioned your network and disk to 1 GiB/s, and your workload typically uses 500 MiB/s of network and disk, you might want to set remote_bootstrap_rate_limit_bytes_per_sec to 300 MiB/s to leave some headroom (200 MiB/s) for workload spikes. Alternatively, you could set it to 500 MiB/s to minimize the time taken for node recovery and cluster scaling operations (at the cost of some workload impact).
Versions prior to v2025.1.1 have many more flags available for tuning cluster balancing performance (see Legacy flags). In cases where the cluster has a significant amount of data, the defaults should be sufficient. Increasing the defaults may be required if a cluster has many thousands of tablets with very little data.
Upgrades
If you upgrade YugabyteDB to a version later than v2025.1.1, you must unset the legacy flags for YugabyteDB to use the simpler cluster balancing defaults.Flags
Current flags
The following flags are recommended for use in v2025.1.1 and later.
remote_bootstrap_rate_limit_bytes_per_sec
The maximum transmission rate during a remote bootstrap. This is the total limit across all remote bootstrap sessions for which this process is acting as a sender or receiver. The total limit is therefore 2 × remote_bootstrap_rate_limit_bytes_per_sec because a YB-TServer or YB-Master can act as both a sender and receiver at the same time.
enable_load_balancing
Enables cluster balancing. Default is true.
Warning
It's strongly recommended not to disable the cluster balancer. If the balancer is disabled, the cluster cannot automatically re-replicate data after a node failure.Legacy flags
The following flags are available in releases prior to v2025.1.1 for fine-tuning cluster balancing performance. These flags are deprecated in favor of the automatic defaults in v2025.1.1 and later.
load_balancer_max_concurrent_tablet_remote_bootstraps
The maximum number of tablets being remote bootstrapped across the cluster. If set to -1, there is no global limit on the number of concurrent remote bootstraps; per-table or per YB-TServer limits still apply.
load_balancer_max_concurrent_tablet_remote_bootstraps_per_table
The maximum number of tablets being remote bootstrapped for any table. The maximum number of remote bootstraps across the cluster is still limited by the flag load_balancer_max_concurrent_tablet_remote_bootstraps. This flag prevents a single table from using all the available remote bootstrap sessions and starving other tables.
load_balancer_max_inbound_remote_bootstraps_per_tserver
Maximum number of tablets simultaneously remote bootstrapping on a YB-TServer.
load_balancer_min_inbound_remote_bootstraps_per_tserver
Minimum number of tablets simultaneously remote bootstrapping on a YB-TServer (if any are required).
load_balancer_max_over_replicated_tablets
Maximum number of running tablet replicas per table that are allowed to be over the configured replication factor. This controls the amount of space amplification in the cluster when tablet removal is slow. A value less than 0 means no limit.
load_balancer_max_concurrent_adds
Maximum number of tablet peer replicas to add in any one run of the cluster balancer.
load_balancer_max_concurrent_removals
Maximum number of over-replicated tablet peer removals to do in any one run of the cluster balancer. A value less than 0 means no limit.
load_balancer_max_concurrent_moves
Maximum number of tablet leaders on tablet servers (across the cluster) to move in any one run of the cluster balancer.
load_balancer_max_concurrent_moves_per_table
Maximum number of tablet leaders per table to move in any one run of the cluster balancer. The maximum number of tablet leader moves across the cluster is still limited by the flag load_balancer_max_concurrent_moves. This flag is meant to prevent a single table from using all of the leader moves quota and starving other tables. If set to -1, the number of leader moves per table is set to the global number of leader moves (load_balancer_max_concurrent_moves).
Metrics
Use the following metrics to monitor cluster balancing progress.
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
estimated_data_to_balance_bytes |
The estimated amount of data (in bytes) that needs to be moved for the cluster to be balanced. |
total_table_load_difference |
The estimated number of tablet moves required for the cluster to be balanced. |
blacklisted_leaders |
The number of leaders on leader blacklisted TServers. |
tablets_in_wrong_placement |
The number of tablet peers in invalid or blacklisted TServers. (An invalid TServer is one that is not part of the tablet's current placement policy.) |
load_balancer_duration |
How long the previous cluster balancer run took, in milliseconds. |